Diglyceride: Difference between revisions
m →Production: task, replaced: Journal of the American Oil Chemists Society → Journal of the American Oil Chemists' Society |
→See also: Improve link |
||
| (21 intermediate revisions by 14 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{short description|Type of fat derived from glycerol and two fatty acids}} |
|||
{{multiple image |
{{multiple image |
||
|direction=vertical |
|direction=vertical |
||
| Line 5: | Line 6: | ||
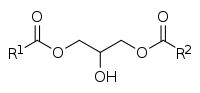
|caption2 = General chemical structures of 1,2-diacylglycerols (top) and 1,3-diacylglycerols (bottom), where R<sup>1</sup> and R<sup>2</sup> are fatty acid side chains |
|caption2 = General chemical structures of 1,2-diacylglycerols (top) and 1,3-diacylglycerols (bottom), where R<sup>1</sup> and R<sup>2</sup> are fatty acid side chains |
||
}} |
}} |
||
A '''diglyceride''', or '''diacylglycerol''' ('''DAG'''), is a [[glyceride]] consisting of two [[fatty acid]] chains [[covalent bond|covalently bonded]] to a [[glycerol]] molecule through [[ester]] linkages.<ref>{{GoldBookRef|title=glycerides|file=G02647}}</ref> Two possible forms exist, 1,2-diacylglycerols and 1,3-diacylglycerols. DAGs can act as [[surfactants]] and are commonly used as [[emulsifier]]s in processed foods. [[Diacylglycerol oil|DAG-enriched oil]] (particularly 1,3-DAG) has been investigated extensively as a [[fat substitute]] due to its ability to suppress the accumulation of body fat;<ref name="PhuahTang2015">{{cite journal|last1=Phuah|first1=Eng-Tong|last2=Tang|first2=Teck-Kim|last3=Lee|first3=Yee-Ying|last4=Choong|first4=Thomas Shean-Yaw|last5=Tan|first5=Chin-Ping|last6=Lai|first6=Oi-Ming|title=Review on the Current State of Diacylglycerol Production Using Enzymatic Approach|journal=Food and Bioprocess Technology|volume=8|issue=6|year=2015|pages=1169–1186|issn=1935-5130|doi=10.1007/s11947-015-1505-0}}</ref><ref name="LoTan2008">{{cite journal|last1=Lo|first1=Seong-Koon|last2=Tan|first2=Chin-Ping|last3=Long|first3=Kamariah|last4=Yusoff|first4=Mohd. Suria Affandi|last5=Lai|first5=Oi-Ming|title=Diacylglycerol Oil—Properties, Processes and Products: A Review|journal=Food and Bioprocess Technology|volume=1|issue=3|year=2008|pages=223–233|issn=1935-5130|doi=10.1007/s11947-007-0049-3}}</ref> with total annual sales of approximately USD 200 million in Japan since its introduction in the late 1990s till 2009.<ref name="PhuahTang2015"/> |
A '''diglyceride''', or '''diacylglycerol''' ('''DAG'''), is a [[glyceride]] consisting of two [[fatty acid]] chains [[covalent bond|covalently bonded]] to a [[glycerol]] molecule through [[ester]] linkages.<ref>{{GoldBookRef|title=glycerides|file=G02647}}</ref> Two possible forms exist, 1,2-diacylglycerols and 1,3-diacylglycerols. Diglycerides are natural components of food fats, though minor in comparison to [[triglyceride]]s.<ref>{{Cite web | url = https://www.inchem.org/documents/jecfa/jecmono/v05je44.htm | title = Toxicological evaluation of some food additives including anticaking agents, antimicrobials, antioxidants, emulsifiers and thickening agents | publisher = World Health Organization }}</ref> DAGs can act as [[surfactants]] and are commonly used as [[emulsifier]]s in processed foods. [[Diacylglycerol oil|DAG-enriched oil]] (particularly 1,3-DAG) has been investigated extensively as a [[fat substitute]] due to its ability to suppress the accumulation of body fat;<ref name="PhuahTang2015">{{cite journal|last1=Phuah|first1=Eng-Tong|last2=Tang|first2=Teck-Kim|last3=Lee|first3=Yee-Ying|last4=Choong|first4=Thomas Shean-Yaw|last5=Tan|first5=Chin-Ping|last6=Lai|first6=Oi-Ming|display-authors=3|title=Review on the Current State of Diacylglycerol Production Using Enzymatic Approach|journal=Food and Bioprocess Technology|volume=8|issue=6|year=2015|pages=1169–1186|issn=1935-5130|doi=10.1007/s11947-015-1505-0|s2cid=84353775|url=http://psasir.upm.edu.my/id/eprint/46178/1/Review%20on%20the%20current%20state%20of%20diacylglycerol%20production%20using%20enzymatic%20approach.pdf}}</ref><ref name="LoTan2008">{{cite journal|last1=Lo|first1=Seong-Koon|last2=Tan|first2=Chin-Ping|last3=Long|first3=Kamariah|last4=Yusoff|first4=Mohd. Suria Affandi|last5=Lai|first5=Oi-Ming|display-authors=3|title=Diacylglycerol Oil—Properties, Processes and Products: A Review|journal=Food and Bioprocess Technology|volume=1|issue=3|year=2008|pages=223–233|issn=1935-5130|doi=10.1007/s11947-007-0049-3|s2cid=86604260|url=http://psasir.upm.edu.my/id/eprint/14039/1/Diacylglycerol%20oil%20properties.pdf}}</ref> with total annual sales of approximately USD 200 million in Japan since its introduction in the late 1990s till 2009.<ref name="PhuahTang2015"/> |
||
==Production== |
==Production== |
||
Diglycerides are a minor component of many [[seed oil]]s and are normally present at ~1–6%; or in the case of [[cottonseed oil]] as much as 10%.<ref>{{cite journal|last1=Flickinger|first1=Brent D.|last2=Matsuo|first2=Noboru|title=Nutritional characteristics of DAG oil|journal=Lipids|date=February 2003|volume=38|issue=2|pages=129–132|doi=10.1007/s11745-003-1042-8}}</ref> Industrial production is primarily achieved by a [[glycerolysis]] reaction between [[triglycerides]] and glycerol. The raw materials for this may be either [[vegetable]] or [[animal]] |
Diglycerides are a minor component of many [[seed oil]]s and are normally present at ~1–6%; or in the case of [[cottonseed oil]] as much as 10%.<ref>{{cite journal|last1=Flickinger|first1=Brent D.|last2=Matsuo|first2=Noboru|title=Nutritional characteristics of DAG oil|journal=Lipids|date=February 2003|volume=38|issue=2|pages=129–132|doi=10.1007/s11745-003-1042-8|pmid=12733744|s2cid=4061326}}</ref> Industrial production is primarily achieved by a [[glycerolysis]] reaction between [[triglycerides]] and glycerol. The raw materials for this may be either [[vegetable oil]]s or [[animal fat]]s.<ref name="Sonntag1982">{{cite journal|last1=Sonntag|first1=Norman O. V.|title=Glycerolysis of fats and methyl esters — Status, review and critique|journal=Journal of the American Oil Chemists' Society|volume=59|issue=10|year=1982|pages=795A–802A|issn=0003-021X|doi=10.1007/BF02634442|s2cid=84808531}}</ref> |
||
== Food additive == |
== Food additive == |
||
Diglycerides, generally in a mix with |
Diglycerides, generally in a mix with [[monoglyceride]]s ([[E471]]), are common food additives largely used as [[Emulsion|emulsifiers]]. The values given in the nutritional labels for total fat, saturated fat, and ''trans'' fat do not include those present in mono- and diglycerides.{{Citation needed|date=July 2013}} They often are included in bakery products, beverages, [[ice cream]], [[peanut butter]], [[chewing gum]], [[shortening]], whipped toppings, [[margarine]], confections, and some snack products, such as [[Pringles]]. |
||
== Biological functions == |
== Biological functions == |
||
| Line 17: | Line 18: | ||
===Protein kinase C activation=== |
===Protein kinase C activation=== |
||
[[Image:PIP2 cleavage to IP3 and DAG.jpg|thumb|PIP2 cleavage to IP3 and DAG initiates intracellular calcium release and PKC activation. Note: PLC is not an intermediate like the image may confuse, it actually catalyzes the IP3/DAG separation]] |
[[Image:PIP2 cleavage to IP3 and DAG.jpg|thumb|PIP2 cleavage to IP3 and DAG initiates intracellular calcium release and PKC activation. Note: PLC is not an intermediate like the image may confuse, it actually catalyzes the IP3/DAG separation]] |
||
In biochemical signaling, diacylglycerol functions as a [[second messenger]] [[lipid signaling|signaling lipid]], and is a product of the [[hydrolysis]] of the phospholipid [[phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate]] ( |
In biochemical signaling, diacylglycerol functions as a [[second messenger]] [[lipid signaling|signaling lipid]], and is a product of the [[hydrolysis]] of the phospholipid [[phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate]] (PIP<sub>2</sub>) by the enzyme [[phospholipase C]] (PLC) (a [[cell membrane|membrane]]-bound enzyme) that, through the same reaction, produces [[inositol trisphosphate]] (IP<sub>3</sub>). Although inositol trisphosphate diffuses into the [[cytosol]], diacylglycerol remains within the [[plasma membrane]], due to its [[hydrophobe|hydrophobic]] properties. IP<sub>3</sub> stimulates the release of calcium ions from the smooth [[endoplasmic reticulum]], whereas DAG is a physiological activator of [[protein kinase C]] (PKC). The production of DAG in the membrane facilitates translocation of PKC from the cytosol to the [[plasma membrane]]. |
||
===Munc13 |
===Munc13 activation=== |
||
| ⚫ | Diacylglycerol has been shown to exert some of its excitatory actions on vesicle release through interactions with the presynaptic priming protein family [[Munc-13|Munc13]]. Binding of DAG to the C1 domain of Munc13 increases the fusion competence of synaptic vesicles resulting in potentiated release. |
||
| ⚫ | |||
Diacylglycerol can be mimicked by the tumor-promoting compounds [[phorbol esters]].<ref>{{cite journal |pmid=3275491 |year=1988 |last1=Blumberg |first1=Peter M. |title=Protein Kinase C as the Receptor for the Phorbol Ester Tumor Promoters: Sixth Rhoads Memorial Award Lecture |volume=48 |issue=1 |pages=1–8 |journal=Cancer Research |url=http://cancerres.aacrjournals.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=3275491}}</ref> |
Diacylglycerol can be mimicked by the tumor-promoting compounds [[phorbol esters]].<ref>{{cite journal |pmid=3275491 |year=1988 |last1=Blumberg |first1=Peter M. |title=Protein Kinase C as the Receptor for the Phorbol Ester Tumor Promoters: Sixth Rhoads Memorial Award Lecture |volume=48 |issue=1 |pages=1–8 |journal=Cancer Research |url=http://cancerres.aacrjournals.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=3275491}}</ref> |
||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
== Metabolism == |
== Metabolism == |
||
| ⚫ | |||
[[File:Glycerol-3-phosphate.png|thumb|[[glycerol-3-phosphate]]]] |
[[File:Glycerol-3-phosphate.png|thumb|[[glycerol-3-phosphate]]]] |
||
Synthesis of diacylglycerol begins with [[glycerol-3-phosphate]], which is derived primarily from [[dihydroxyacetone phosphate]], a product of [[glycolysis]] (usually in the cytoplasm of liver or adipose tissue cells). Glycerol-3-phosphate is first [[acylation|acylated]] with acyl-coenzyme A (acyl-CoA) to form [[lysophosphatidic acid]], which is then acylated with another molecule of acyl-CoA to yield [[phosphatidic acid]]. Phosphatidic acid is then de-phosphorylated to form diacylglycerol. |
Synthesis of diacylglycerol begins with [[glycerol-3-phosphate]], which is derived primarily from [[dihydroxyacetone phosphate]], a product of [[glycolysis]] (usually in the cytoplasm of liver or adipose tissue cells). Glycerol-3-phosphate is first [[acylation|acylated]] with acyl-coenzyme A (acyl-CoA) to form [[lysophosphatidic acid]], which is then acylated with another molecule of acyl-CoA to yield [[phosphatidic acid]]. Phosphatidic acid is then de-phosphorylated to form diacylglycerol. |
||
Dietary fat is mainly composed of [[triglyceride]]s. Because triglycerides cannot be absorbed by the digestive system, triglycerides must first be enzymatically digested into [[Monoglyceride|monoacylglycerol]], diacylglycerol, or free fatty acids. |
Dietary fat is mainly composed of [[triglyceride]]s. Because triglycerides cannot be absorbed by the digestive system, triglycerides must first be enzymatically digested into [[Monoglyceride|monoacylglycerol]], diacylglycerol, or free fatty acids. Diacylglycerol is a precursor to [[triacylglycerol]] (triglyceride), which is formed in the addition of a third fatty acid to the diacylglycerol under the catalysis of [[diglyceride acyltransferase]]. |
||
Since diacylglycerol is synthesized via phosphatidic acid, it will usually contain a saturated fatty acid at the C-1 position on the glycerol moiety and an unsaturated fatty acid at the C-2 position.<ref name=Stryer_2006>{{cite book |vauthors=Berg J, Tymoczko JL, Stryer L | title = Biochemistry | publisher = W. H. Freeman | edition = 6th | location = San Francisco | year = 2006 | isbn = 0-7167-8724-5 }}{{Page needed|date=May 2013}}</ref> |
Since diacylglycerol is synthesized via phosphatidic acid, it will usually contain a saturated fatty acid at the C-1 position on the glycerol moiety and an unsaturated fatty acid at the C-2 position.<ref name=Stryer_2006>{{cite book |vauthors=Berg J, Tymoczko JL, Stryer L | title = Biochemistry | publisher = W. H. Freeman | edition = 6th | location = San Francisco | year = 2006 | isbn = 0-7167-8724-5 }}{{Page needed|date=May 2013}}</ref> |
||
| Line 43: | Line 44: | ||
== Insulin resistance == |
== Insulin resistance == |
||
Activation of [[PRKCQ|PKC-θ]] by diacylglycerol may cause [[insulin resistance]] in muscle by decreasing [[IRS1]]-associated [[Phosphoinositide 3-kinase|PI3K]] activity.<ref name="pmid20376053">{{cite journal | vauthors=Erion DM, Shulman GI | title=Diacylglycerol-mediated insulin resistance | journal= [[Nature Medicine]] | volume=16 | issue=4 | pages=400–402| year=2010 | doi= 10.1038/nm0410-400 | pmc=3730126 | |
Activation of [[PRKCQ|PKC-θ]] by diacylglycerol may cause [[insulin resistance]] in muscle by decreasing [[IRS1]]-associated [[Phosphoinositide 3-kinase|PI3K]] activity.<ref name="pmid20376053">{{cite journal | vauthors=Erion DM, Shulman GI | title=Diacylglycerol-mediated insulin resistance | journal= [[Nature Medicine]] | volume=16 | issue=4 | pages=400–402| year=2010 | doi= 10.1038/nm0410-400 | pmc=3730126 | pmid = 20376053 }}</ref> Similarly, activation of [[PRKCE|PKCε]] by diacyglycerol may cause insulin resistance in the liver.<ref name="pmid20376053" /><ref name="pmid27760050">{{cite journal | vauthors=Petersen MC, Madiraju AK, Gassaway BM, Marcel M, Nasiri AR, Butrico G, Marcucci MJ, Zhang D, Abulizi A, Zhang XM, Philbrick W, Hubbard SR, Jurczak MJ, Samuel VT, Rinehart J, Shulman GI |display-authors=3| title=Insulin receptor Thr1160 phosphorylation mediates lipid-induced hepatic insulin resistance | journal= [[Journal of Clinical Investigation]] | volume=126 | issue=11 | pages=4361–4371 | year=2016 | doi= 10.1172/JCI86013 | pmc=5096902 | pmid = 27760050 }}</ref> |
||
==See also== |
==See also== |
||
| ⚫ | |||
* [[Lipid]] |
* [[Lipid]] |
||
* [[Monoglyceride]] |
* [[Monoglyceride]] |
||
* [[Triglyceride]] |
* [[Triglyceride]] |
||
* [[Ultra-processed food]] |
|||
==References== |
==References== |
||
{{Reflist}} |
{{Reflist|30em}} |
||
{{Glycerides}} |
{{Glycerides}} |
||
Latest revision as of 10:07, 15 October 2023
A diglyceride, or diacylglycerol (DAG), is a glyceride consisting of two fatty acid chains covalently bonded to a glycerol molecule through ester linkages.[1] Two possible forms exist, 1,2-diacylglycerols and 1,3-diacylglycerols. Diglycerides are natural components of food fats, though minor in comparison to triglycerides.[2] DAGs can act as surfactants and are commonly used as emulsifiers in processed foods. DAG-enriched oil (particularly 1,3-DAG) has been investigated extensively as a fat substitute due to its ability to suppress the accumulation of body fat;[3][4] with total annual sales of approximately USD 200 million in Japan since its introduction in the late 1990s till 2009.[3]
Production
[edit]Diglycerides are a minor component of many seed oils and are normally present at ~1–6%; or in the case of cottonseed oil as much as 10%.[5] Industrial production is primarily achieved by a glycerolysis reaction between triglycerides and glycerol. The raw materials for this may be either vegetable oils or animal fats.[6]
Food additive
[edit]Diglycerides, generally in a mix with monoglycerides (E471), are common food additives largely used as emulsifiers. The values given in the nutritional labels for total fat, saturated fat, and trans fat do not include those present in mono- and diglycerides.[citation needed] They often are included in bakery products, beverages, ice cream, peanut butter, chewing gum, shortening, whipped toppings, margarine, confections, and some snack products, such as Pringles.
Biological functions
[edit]Protein kinase C activation
[edit]
In biochemical signaling, diacylglycerol functions as a second messenger signaling lipid, and is a product of the hydrolysis of the phospholipid phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) by the enzyme phospholipase C (PLC) (a membrane-bound enzyme) that, through the same reaction, produces inositol trisphosphate (IP3). Although inositol trisphosphate diffuses into the cytosol, diacylglycerol remains within the plasma membrane, due to its hydrophobic properties. IP3 stimulates the release of calcium ions from the smooth endoplasmic reticulum, whereas DAG is a physiological activator of protein kinase C (PKC). The production of DAG in the membrane facilitates translocation of PKC from the cytosol to the plasma membrane.
Munc13 activation
[edit]Diacylglycerol has been shown to exert some of its excitatory actions on vesicle release through interactions with the presynaptic priming protein family Munc13. Binding of DAG to the C1 domain of Munc13 increases the fusion competence of synaptic vesicles resulting in potentiated release.
Diacylglycerol can be mimicked by the tumor-promoting compounds phorbol esters.[7]
Other
[edit]In addition to activating PKC, diacylglycerol has a number of other functions in the cell:
- a source for prostaglandins
- a precursor of the endocannabinoid 2-arachidonoylglycerol
- an activator of a subfamily of transient receptor potential canonical (TRPC) cation channels, TRPC3/6/7.
Metabolism
[edit]
Synthesis of diacylglycerol begins with glycerol-3-phosphate, which is derived primarily from dihydroxyacetone phosphate, a product of glycolysis (usually in the cytoplasm of liver or adipose tissue cells). Glycerol-3-phosphate is first acylated with acyl-coenzyme A (acyl-CoA) to form lysophosphatidic acid, which is then acylated with another molecule of acyl-CoA to yield phosphatidic acid. Phosphatidic acid is then de-phosphorylated to form diacylglycerol.
Dietary fat is mainly composed of triglycerides. Because triglycerides cannot be absorbed by the digestive system, triglycerides must first be enzymatically digested into monoacylglycerol, diacylglycerol, or free fatty acids. Diacylglycerol is a precursor to triacylglycerol (triglyceride), which is formed in the addition of a third fatty acid to the diacylglycerol under the catalysis of diglyceride acyltransferase.
Since diacylglycerol is synthesized via phosphatidic acid, it will usually contain a saturated fatty acid at the C-1 position on the glycerol moiety and an unsaturated fatty acid at the C-2 position.[8]
Diacylglycerol can be phosphorylated to phosphatidic acid by diacylglycerol kinase.
Insulin resistance
[edit]Activation of PKC-θ by diacylglycerol may cause insulin resistance in muscle by decreasing IRS1-associated PI3K activity.[9] Similarly, activation of PKCε by diacyglycerol may cause insulin resistance in the liver.[9][10]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book") (1997). Online corrected version: (2006–) "glycerides". doi:10.1351/goldbook.G02647
- ^ "Toxicological evaluation of some food additives including anticaking agents, antimicrobials, antioxidants, emulsifiers and thickening agents". World Health Organization.
- ^ a b Phuah, Eng-Tong; Tang, Teck-Kim; Lee, Yee-Ying; et al. (2015). "Review on the Current State of Diacylglycerol Production Using Enzymatic Approach" (PDF). Food and Bioprocess Technology. 8 (6): 1169–1186. doi:10.1007/s11947-015-1505-0. ISSN 1935-5130. S2CID 84353775.
- ^ Lo, Seong-Koon; Tan, Chin-Ping; Long, Kamariah; et al. (2008). "Diacylglycerol Oil—Properties, Processes and Products: A Review" (PDF). Food and Bioprocess Technology. 1 (3): 223–233. doi:10.1007/s11947-007-0049-3. ISSN 1935-5130. S2CID 86604260.
- ^ Flickinger, Brent D.; Matsuo, Noboru (February 2003). "Nutritional characteristics of DAG oil". Lipids. 38 (2): 129–132. doi:10.1007/s11745-003-1042-8. PMID 12733744. S2CID 4061326.
- ^ Sonntag, Norman O. V. (1982). "Glycerolysis of fats and methyl esters — Status, review and critique". Journal of the American Oil Chemists' Society. 59 (10): 795A–802A. doi:10.1007/BF02634442. ISSN 0003-021X. S2CID 84808531.
- ^ Blumberg, Peter M. (1988). "Protein Kinase C as the Receptor for the Phorbol Ester Tumor Promoters: Sixth Rhoads Memorial Award Lecture". Cancer Research. 48 (1): 1–8. PMID 3275491.
- ^ Berg J, Tymoczko JL, Stryer L (2006). Biochemistry (6th ed.). San Francisco: W. H. Freeman. ISBN 0-7167-8724-5.[page needed]
- ^ a b Erion DM, Shulman GI (2010). "Diacylglycerol-mediated insulin resistance". Nature Medicine. 16 (4): 400–402. doi:10.1038/nm0410-400. PMC 3730126. PMID 20376053.
- ^ Petersen MC, Madiraju AK, Gassaway BM, et al. (2016). "Insulin receptor Thr1160 phosphorylation mediates lipid-induced hepatic insulin resistance". Journal of Clinical Investigation. 126 (11): 4361–4371. doi:10.1172/JCI86013. PMC 5096902. PMID 27760050.