Icodextrin: Difference between revisions
Updating {{drugbox}} (changes to verified fields - updated 'UNII_Ref', 'ChemSpiderID_Ref', 'StdInChI_Ref', 'StdInChIKey_Ref', 'ChEMBL_Ref') per Chem/Drugbox validation (report [[Wikipedia talk:Wi |
→Chemistry: Daltons → daltons, see Dalton (unit)#Unit name |
||
| (28 intermediate revisions by 20 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{short description|Pharmaceutical drug}} |
|||
{{Drugbox |
{{Drugbox |
||
| Verifiedfields = changed |
| Verifiedfields = changed |
||
| Watchedfields = changed |
|||
| verifiedrevid = |
| verifiedrevid = 461936512 |
||
| IUPAC_name |
| IUPAC_name = |
||
| image = Icodextrin skeletal.svg |
|||
| image =Dextrin_skeletal.svg |
|||
| synonyms = |
|||
<!-- Clinical data --> |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| tradename = |
|||
| CAS_supplemental = |
|||
| Drugs.com = {{drugs.com|international|icodextrin}} |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| |
| pregnancy_AU = <!-- A / B1 / B2 / B3 / C / D / X --> |
||
| |
| pregnancy_US = C |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
<!-- Pharmacokinetic data --> |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| protein_bound = |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
<!-- Identifiers --> |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ATC_suffix = DA |
|||
| ATC_supplemental = |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| DrugBank_Ref = {{drugbankcite|correct|drugbank}} |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| UNII_Ref = {{fdacite|correct|FDA}} |
|||
| UNII = 2NX48Z0A9G |
|||
| KEGG_Ref = {{keggcite|changed|kegg}} |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ChEMBL_Ref = {{ebicite|changed|EBI}} |
| ChEMBL_Ref = {{ebicite|changed|EBI}} |
||
| ChEMBL = 1201472 |
| ChEMBL = 1201472 |
||
| ChemSpiderID_Ref = {{chemspidercite|changed|chemspider}} |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ChemSpiderID = none |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
<!-- Chemical data --> |
|||
| chemical_formula |
| chemical_formula = (C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>10</sub>O<sub>5</sub>)<sub>n</sub> |
||
| molecular_weight |
| molecular_weight = 13–19 kg/mol |
||
| smiles |
| smiles = |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| |
| synonyms = |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| pregnancy_AU = <!-- A / B1 / B2 / B3 / C / D / X --> |
|||
| pregnancy_US = C |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
}} |
}} |
||
'''Icodextrin''' ([[International Nonproprietary Name|INN]], [[United States Adopted Name|USAN]]) is a [[colloid]] [[osmotic]] agent used in form of an [[aqueous]] solution for [[peritoneal dialysis]] under the trade name '''Extraneal''',<ref name="RxList" /> and after gynecological [[laparoscopic]] surgery for the reduction of post-surgical [[adhesion (medicine)|adhesion]]s (fibrous bands that form between tissues and organs) under the trade name '''Adept'''.<ref name="FDA" /> |
'''Icodextrin''' ([[International Nonproprietary Name|INN]], [[United States Adopted Name|USAN]]) is a [[colloid]] [[osmotic]] agent, derived from [[maltodextrin]],<ref name="maltod">{{cite book |title=Clinical evidence, Issue 14 |pages=1046 |author=American College of Physicians--American Society of Internal Medicine |year=2005 |publisher=BMJ Pub. Group}}</ref> used in form of an [[aqueous]] solution for [[peritoneal dialysis]] under the trade name '''Extraneal''',<ref name="RxList" /> and after gynecological [[laparoscopic]] surgery for the reduction of post-surgical [[adhesion (medicine)|adhesion]]s (fibrous bands that form between tissues and organs) under the trade name '''Adept'''.<ref name="FDA" /> |
||
==Chemistry== |
|||
==Physical and chemical properties== |
|||
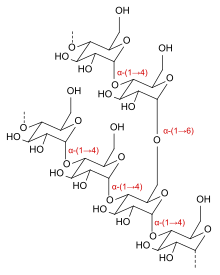
Icodextrin is a [[starch]]-derived, branched, water-soluble [[glucose]] [[polymer]] linked by α-(1→4) and less than 10% α-(1→6) [[glycosidic bond]]s, making it a type of [[dextrin]]. Its weight-average molecular weight is between 13,000 and 19,000 [[Dalton (unit)| |
Icodextrin is a [[starch]]-derived, branched, water-soluble [[glucose]] [[polymer]] linked by α-(1→4) and less than 10% α-(1→6) [[glycosidic bond]]s, making it a type of [[dextrin]]. Its weight-average molecular weight is between 13,000 and 19,000 [[Dalton (unit)|dalton]]s and its number-average molecular weight between 5,000 and 6,500 daltons. The substance is a white to off-white solid, and the solution is clear and colourless to pale yellow.<ref name="FDA" /> |
||
==Mechanism of action== |
==Mechanism of action== |
||
| Line 43: | Line 56: | ||
[[File:DP branchement.svg|thumb|left|upright|[[Peritoneal dialysis]]]] |
[[File:DP branchement.svg|thumb|left|upright|[[Peritoneal dialysis]]]] |
||
When used for peritoneal dialysis, the icodextrin solution absorbs waste products from the blood, and is removed from the peritoneum after a few hours together with the waste.<ref>{{ |
When used for peritoneal dialysis, the icodextrin solution absorbs waste products from the blood, and is removed from the peritoneum after a few hours together with the waste.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Frampton JE, Plosker GL | title = Icodextrin: a review of its use in peritoneal dialysis | journal = Drugs | volume = 63 | issue = 19 | pages = 2079–105 | year = 2003 | pmid = 12962523 | doi = 10.2165/00003495-200363190-00011 }}</ref> |
||
==Pharmacokinetics== |
==Pharmacokinetics== |
||
Icodextrin is not significantly metabolised inside the peritoneum. Instead, it is absorbed slowly (40% after 12 hours) into the bloodstream via the [[lymph vessel]]s. There it is broken down into [[oligosaccharide]]s by the enzyme [[alpha-amylase]]. In patients with intact kidney function, both icodextrin and its fragments are excreted via the kidney by [[glomerular filtration]].<ref name="RxList">RxList.com |
Icodextrin is not significantly metabolised inside the peritoneum. Instead, it is absorbed slowly (40% after 12 hours) into the bloodstream via the [[lymph vessel]]s. There it is broken down into [[oligosaccharide]]s by the enzyme [[alpha-amylase]]. In patients with intact kidney function, both icodextrin and its fragments are excreted via the kidney by [[glomerular filtration]].<ref name="RxList">{{cite web | work = RxList.com | url = http://www.rxlist.com/extraneal-drug.htm | title = Extraneal }}</ref><ref name="FDA">{{cite web | work = FDA | url = http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/cdrh_docs/pdf5/P050011c.pdf | title = Adept (4% Icodextrin) Adhesion Reduction Solution }}</ref> |
||
==Contraindications== |
==Contraindications== |
||
Icodextrin is contraindicated in patients with cornstarch allergy, [[maltose]] or [[isomaltose]] intolerance, [[glycogen storage disease]], or severe [[lactic acidosis]].<ref name="Drugs.com">Drugs.com |
Icodextrin is contraindicated in patients with cornstarch allergy, [[maltose]] or [[isomaltose]] intolerance, [[glycogen storage disease]], or severe [[lactic acidosis]].<ref name="Drugs.com">{{cite web | work = Drugs.com | url = https://www.drugs.com/pro/extraneal.html | title = Extraneal }}</ref> |
||
==Adverse effects== |
==Adverse effects== |
||
Adverse effects include [[peritonitis]], [[respiratory infection]], [[hypertension]] (high blood pressure), [[rash]]es, and headache. Of these side effects, only hypertension and rashes occurred significantly more often than under glucose solution; the other events seem to be related to peritoneal dialysis in general.<ref name="Drugs.com" /> |
Adverse effects include [[peritonitis]], [[respiratory infection]], [[hypertension]] (high blood pressure), [[rash]]es, and headache. Of these side effects, only hypertension and rashes occurred significantly more often than under glucose solution; the other events seem to be related to peritoneal dialysis in general.<ref name="Drugs.com" /> |
||
==Interactions== |
== Interactions == |
||
Icodextrin can mimic increased [[blood glucose]] levels, depending on the used testing system. Specifically, glucose dehydrogenase pyrroloquinolinequinone (GDH-PQQ) or glucose-dye-oxidoreductase (GDO) based tests can erroneously show high blood glucose in patients that have been treated with icodextrin.<ref name="Drugs.com" /> |
Icodextrin can mimic increased [[blood glucose]] levels, depending on the used testing system. Specifically, glucose dehydrogenase pyrroloquinolinequinone (GDH-PQQ) or glucose-dye-oxidoreductase (GDO) based tests can erroneously show high blood glucose in patients that have been treated with icodextrin.<ref name="Drugs.com" /> |
||
==References== |
== References == |
||
{{reflist}} |
{{reflist}} |
||
{{Blood substitutes and perfusion solutions}} |
|||
{{B03, B05, B06}} |
|||
[[Category:Renal dialysis]] |
[[Category:Renal dialysis]] |
||
Latest revision as of 16:02, 21 November 2023
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Intraperitoneal |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 40% in 12 hours |
| Metabolism | Alpha-amylase |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem SID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | (C6H10O5)n |
| Molar mass | 13–19 kg/mol |
| | |
Icodextrin (INN, USAN) is a colloid osmotic agent, derived from maltodextrin,[1] used in form of an aqueous solution for peritoneal dialysis under the trade name Extraneal,[2] and after gynecological laparoscopic surgery for the reduction of post-surgical adhesions (fibrous bands that form between tissues and organs) under the trade name Adept.[3]
Chemistry
[edit]Icodextrin is a starch-derived, branched, water-soluble glucose polymer linked by α-(1→4) and less than 10% α-(1→6) glycosidic bonds, making it a type of dextrin. Its weight-average molecular weight is between 13,000 and 19,000 daltons and its number-average molecular weight between 5,000 and 6,500 daltons. The substance is a white to off-white solid, and the solution is clear and colourless to pale yellow.[3]
Mechanism of action
[edit]The osmotic activity of icodextrin keeps the solution inside the peritoneum for three to four days, separating tissues and thus reducing adhesion between them when fibrin is formed after a surgery. In other words, the tissues are kept from gluing together.[3]

When used for peritoneal dialysis, the icodextrin solution absorbs waste products from the blood, and is removed from the peritoneum after a few hours together with the waste.[4]
Pharmacokinetics
[edit]Icodextrin is not significantly metabolised inside the peritoneum. Instead, it is absorbed slowly (40% after 12 hours) into the bloodstream via the lymph vessels. There it is broken down into oligosaccharides by the enzyme alpha-amylase. In patients with intact kidney function, both icodextrin and its fragments are excreted via the kidney by glomerular filtration.[2][3]
Contraindications
[edit]Icodextrin is contraindicated in patients with cornstarch allergy, maltose or isomaltose intolerance, glycogen storage disease, or severe lactic acidosis.[5]
Adverse effects
[edit]Adverse effects include peritonitis, respiratory infection, hypertension (high blood pressure), rashes, and headache. Of these side effects, only hypertension and rashes occurred significantly more often than under glucose solution; the other events seem to be related to peritoneal dialysis in general.[5]
Interactions
[edit]Icodextrin can mimic increased blood glucose levels, depending on the used testing system. Specifically, glucose dehydrogenase pyrroloquinolinequinone (GDH-PQQ) or glucose-dye-oxidoreductase (GDO) based tests can erroneously show high blood glucose in patients that have been treated with icodextrin.[5]
References
[edit]- ^ American College of Physicians--American Society of Internal Medicine (2005). Clinical evidence, Issue 14. BMJ Pub. Group. p. 1046.
- ^ a b "Extraneal". RxList.com.
- ^ a b c d "Adept (4% Icodextrin) Adhesion Reduction Solution" (PDF). FDA.
- ^ Frampton JE, Plosker GL (2003). "Icodextrin: a review of its use in peritoneal dialysis". Drugs. 63 (19): 2079–105. doi:10.2165/00003495-200363190-00011. PMID 12962523.
- ^ a b c "Extraneal". Drugs.com.
