1135: Difference between revisions
Appearance
Content deleted Content added
Added details Albert of Chiatina (Italian archpriest |
m Disambiguating links to Magnus Haraldsson (link changed to Magnus Haraldsson (son of Harald Gille)) using DisamAssist. |
||
| (37 intermediate revisions by 10 users not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
{{Year nav|1135}} |
{{Year nav|1135}} |
||
{{C12 year in topic}} |
{{C12 year in topic}} |
||
[[File:Map Crusader states 1135-en.svg| |
[[File:Map Crusader states 1135-en.svg|upright=1.35|thumb|The [[Near East]] with the [[Crusader states]]]] |
||
Year '''1135''' ('''[[Roman numerals|MCXXXV]]''') was a [[common year starting on Tuesday]] (link will display the full calendar) of the [[Julian calendar]]. |
Year '''1135''' ('''[[Roman numerals|MCXXXV]]''') was a [[common year starting on Tuesday]] (link will display the full calendar) of the [[Julian calendar]]. |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
<onlyinclude> |
<onlyinclude> |
||
=== By place === |
=== By place === |
||
[[File:Anonymous - Death of the Abbasid Caliph, Al-Mustarshid bi-llah, Assassinated During the Reign of Sultan Mas’ud, - 1965.51.6 - Yale University Art Gallery.jpg|thumb|200px|right|Assassination of [[Al-Mustarshid]] in 1135]] |
|||
==== Levant ==== |
==== Levant ==== |
||
* Spring – [[Shams al-Mulk Isma'il]], Seljuk ruler of [[Damascus]], sends envoys to [[Imad al-Din Zengi]], Seljuk ruler of [[Mosul]], to seek his protection in exchange of Damascus. Zengi crosses the [[Euphrates]], receiving the surrender of the city of [[Hama]]. He besieges Damascus |
* Spring – [[Shams al-Mulk Isma'il]], Seljuk ruler of [[Damascus]], sends envoys to [[Imad al-Din Zengi]], Seljuk ruler of [[Mosul]], to seek his protection in exchange of Damascus. Zengi crosses the [[Euphrates]], receiving the surrender of the city of [[Hama]]. He besieges Damascus but, due to a shortage of supplies, is forced to abandon the siege. Zengi extricates himself from Damascus, his Seljuk forces capture the fortresses at [[Ma'arrat al-Nu'man|Ma'arrat]] and [[Atharib]].<ref>[[Steven Runciman]] (1952). ''A History of The Crusades. Vol II: The Kingdom of Jerusalem'', p. 158. {{ISBN|978-0-241-29876-3}}.</ref> |
||
* Queen [[Melisende, Queen of Jerusalem|Melisende]] of [[Kingdom of Jerusalem|Jerusalem]] reconciles with her husband [[Fulk, King of Jerusalem|Fulk V]], after a period of estrangement occasioned by her growing power and rumors that she has had an affair with [[Hugh II of Jaffa|Hugh II]] ( |
* Queen [[Melisende, Queen of Jerusalem|Melisende]] of [[Kingdom of Jerusalem|Jerusalem]] reconciles with her husband [[Fulk, King of Jerusalem|Fulk V]], after a period of estrangement occasioned by her growing power, and rumors that she has had an affair with [[Hugh II of Jaffa|Hugh II]] (''du Puiset''), former count of [[County of Jaffa and Ascalon|Jaffa]]. |
||
==== Europe ==== |
==== Europe ==== |
||
* [[January 7]] – King [[Harald Gille|Harald IV]] returns with Danish reinforcements and the support of King [[Eric II of Denmark|Eric II]] ( |
* [[January 7]] – King [[Harald Gille|Harald IV]] returns with Danish reinforcements and the support of King [[Eric II of Denmark|Eric II]] ("the Memorable"). He captures his nephew and joint ruler [[Magnus IV of Norway|Magnus IV]] (Sigurdsson), who is blinded, castrated – and confined in [[Nidarholm Abbey]] (located on the island of [[Munkholmen]]). |
||
* [[May 26]] – King [[Alfonso VII of León and Castile|Alfonso VII]] is crowned as "Emperor of All Spain" (''[[Imperator totius Hispaniae]]'') in the [[León Cathedral|Cathedral of León]]. The coronation is attended by [[Ramon Berenguer IV, Count of Barcelona|Ramon Berenguer IV]] (his brother-in-law), [[Raymond V, Count of Toulouse|Raymond V]] and other Spanish nobles who have recognize him as their [[overlord]]. |
* [[May 26]] – King [[Alfonso VII of León and Castile|Alfonso VII]] is crowned as "Emperor of All Spain" (''[[Imperator totius Hispaniae]]'') in the [[León Cathedral|Cathedral of León]]. The coronation is attended by [[Ramon Berenguer IV, Count of Barcelona|Ramon Berenguer IV]] (his brother-in-law), [[Raymond V, Count of Toulouse|Raymond V]] and other Spanish nobles who have recognize him as their [[overlord]]. |
||
* Summer – King [[Roger II of Sicily|Roger II]] lands with |
* Summer – King [[Roger II of Sicily|Roger II]] lands with a Sicilian expeditionary force in [[Salerno]]. He splits his army, and conquers the cities of [[Aversa]] and [[Alife, Campania|Alife]]. Roger besieges [[Naples]] – but despite poor health conditions within the city, he is not able to take it, and returns again to [[Messina]]. |
||
* [[August 15]] – Emperor [[Lothair III, Holy Roman Emperor|Lothair III]] receives homage from Eric II, and makes him an imperial prince at the [[Imperial Diet (Holy Roman Empire)|Reichstag]]. His diplomatic missions to [[Kingdom of Hungary (1000–1301)|Hungary]] and [[Greater Poland|Poland]] |
* [[August 15]] – Emperor [[Lothair III, Holy Roman Emperor|Lothair III]] receives homage from Eric II, and makes him an imperial prince at the [[Imperial Diet (Holy Roman Empire)|Reichstag]]. His diplomatic missions to [[Kingdom of Hungary (1000–1301)|Hungary]] and [[Greater Poland|Poland]] result in a tribute payment. Duke [[Bolesław III Wrymouth]] is given [[Duchy of Pomerania|Pomerania]] and [[Principality of Rügen|Rügen]] as German fiefs. |
||
* Lothair III receives a [[Byzantine Empire|Byzantine]] embassy at his court, on behalf of Emperor [[John II Komnenos]]. It offers large financial subsidies for Lothair to start a campaign against Roger II. The negotiations will last for some months.<ref>Steven Runciman (1952). ''A History of the Crusades. Vol II: The Kingdom of Jerusalem'', p. 170. {{ISBN|978-0-241-29876--3}}.</ref> |
|||
* September – King [[García Ramírez of Navarre|García IV]] ( |
* [[September]] – King [[García Ramírez of Navarre|García IV]] ("the Restorer") breaks with Alfonso VII, and makes common cause with the [[County of Portugal]] against [[Kingdom of Castile|Castile]] and [[Kingdom of León|León]]. |
||
* October – [[Conrad III of Germany|Conrad III]], duke of [[Duchy of Franconia|Franconia]], gives up his title as [[King of Italy]] in opposition with Lothair III. He receives a pardon and recovers his estates. |
* [[October]] – [[Conrad III of Germany|Conrad III]], duke of [[Duchy of Franconia|Franconia]], gives up his title as [[King of Italy]] in opposition with Lothair III. He receives a pardon and recovers his estates. |
||
* [[Republic of Pisa|Pisa]]ns in the service of the [[Holy See]] ([[Diocese of Rome]]) sack the city of [[Republic of Amalfi|Amalfi]]. |
* [[Republic of Pisa|Pisa]]ns in the service of the [[Holy See]] ([[Diocese of Rome]]) sack the city of [[Republic of Amalfi|Amalfi]]. |
||
* A [[Moors|Moorish]] fleet raids the [[County of Barcelona|Catalan]] port-town of [[Elne|Elna]] (Southern [[France]]).{{sfn|McGrank|1981}} |
* A [[Moors|Moorish]] fleet raids the [[County of Barcelona|Catalan]] port-town of [[Elne|Elna]] (Southern [[France]]).{{sfn|McGrank|1981}} |
||
| Line 26: | Line 27: | ||
==== England ==== |
==== England ==== |
||
* [[December 1]] – King [[Henry I of England|Henry I]] dies at [[Lyons-la-Forêt]] in [[Duchy of Normandy|Normandy]] after a 35-year reign. He is succeeded by his nephew [[Stephen, King of England|Stephen of Blois]] (grandson of [[William the Conqueror]]), who asserts his claim to the throne in opposition to claims by Henry's daughter [[Empress Matilda|Matilda]] (prolonged in a civil war known as [[The Anarchy]]). |
* [[December 1]] – King [[Henry I of England|Henry I]] dies at [[Lyons-la-Forêt]] in [[Duchy of Normandy|Normandy]] after a 35-year reign. He is succeeded by his nephew [[Stephen, King of England|Stephen of Blois]] (grandson of [[William the Conqueror]]), who asserts his claim to the throne in opposition to claims by Henry's daughter [[Empress Matilda|Matilda]] (prolonged in a civil war known as [[The Anarchy]]). |
||
* [[December 26]] – Stephen of Blois is crowned at [[Westminster Abbey]] in [[London]] by Archbishop [[William de Corbeil]]. Matilda (pregnant with child) and her husband [[Geoffrey Plantagenet, Count of Anjou|Geoffrey V]] ( |
* [[December 26]] – Stephen of Blois is crowned at [[Westminster Abbey]] in [[London]] by Archbishop [[William de Corbeil]]. Matilda (pregnant with child) and her husband [[Geoffrey Plantagenet, Count of Anjou|Geoffrey V]] ("the Fair") leave for their own safety to Normandy, where she plans how to overthrow Stephen and claim the English throne for her own. |
||
==== |
==== Middle East ==== |
||
* [[August 29]] – Caliph [[Al-Mustarshid]] is assassinated at [[Baghdad]] after a 17-year reign. He is succeeded by his son [[Al-Rashid Billah]] as ruler of the [[Abbasid dynasty|Abbasid]] Caliphate (until [[1138]]). |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
==== North Africa ==== |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
==== Asia ==== |
==== Asia ==== |
||
* [[Jin–Song Wars|Jin–Song War]] |
* [[Jin–Song Wars|Jin–Song War]] – Song forces under [[Yue Fei]] begin a counteroffensive against the [[Jurchen people|Jurchen]]-ruled [[Jin dynasty (1115–1234)|Jin dynasty]] in northern [[China]]. He defeats Jin forces, by entangling his [[Paddle steamer|paddle-wheel ships]] at the [[Huai River]]. |
||
* [[June 4]] – Emperor [[Emperor Huizong of Song|Hui Zong]] dies in exile in [[Heilongjiang]] ([[Manchuria]]), having been held prisoner with his son [[Emperor Qinzong|Qin Zong]] since their capture in [[1127]]. |
* [[June 4]] – Emperor [[Emperor Huizong of Song|Hui Zong]] dies in exile in [[Heilongjiang]] ([[Manchuria]]), having been held prisoner with his son [[Emperor Qinzong|Qin Zong]] since their capture in [[1127]]. |
||
| Line 40: | Line 44: | ||
==== Religion ==== |
==== Religion ==== |
||
* January – [[Byland Abbey]] is founded in [[Kingdom of England|England]] by the [[Congregation of Savigny]]. |
* January – [[Byland Abbey]] is founded in [[Kingdom of England|England]] by the [[Congregation of Savigny]]. |
||
* [[Buildwas Abbey]] is founded in England by [[Roger de Clinton]], bishop of [[Diocese of Coventry|Coventry]]. |
* [[Buildwas Abbey]] is founded in England by [[Roger de Clinton]], bishop of [[Diocese of Coventry|Coventry]].</onlyinclude> |
||
</onlyinclude> |
|||
== Births == |
== Births == |
||
* [[Abu Yaqub Yusuf]], caliph of the [[Almohad Caliphate]] (d. [[1184]]) |
* [[Abu Yaqub Yusuf]], caliph of the [[Almohad Caliphate]] (d. [[1184]]) |
||
| Line 47: | Line 51: | ||
* [[Albert of Chiatina]], Italian [[archpriest]] and saint (d. [[1202]]) |
* [[Albert of Chiatina]], Italian [[archpriest]] and saint (d. [[1202]]) |
||
* [[André of Brienne]], French [[Nobility|nobleman]] (approximate date) |
* [[André of Brienne]], French [[Nobility|nobleman]] (approximate date) |
||
* [[Bogumilus]], archbishop of [[Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Gniezno|Gniezno]] (approximate date) |
|||
* [[Burhan al-Din al-Marghinani]], Arabic [[Hanafi]] jurist (d. [[1197]]) |
* [[Burhan al-Din al-Marghinani]], Arabic [[Hanafi]] jurist (d. [[1197]]) |
||
* [[Conrad, Count Palatine of the Rhine|Conrad of Hohenstaufen]], German nobleman (d. [[1195]]) |
|||
* [[Fernando Afonso of Portugal|Fernando Afonso]], Portuguese [[Grand Master (order)|Grand Master]] (d. [[1207]]) |
|||
* [[Gertrude of Flanders, Countess of Savoy|Gertrude of Flanders]], countess of [[Savoy]] (d. [[1186]]) |
|||
* [[Hafsa bint al-Hajj al-Rukuniyya]], Andalusian poet (d. [[1190]]) |
* [[Hafsa bint al-Hajj al-Rukuniyya]], Andalusian poet (d. [[1190]]) |
||
* [[Henry fitz Ailwin|Henry Fitz Eylwin]], 1st [[Lord Mayor of London]] (d. [[1212]]) |
|||
* [[Herman IV, Margrave of Baden|Herman IV]], margrave of [[Margraviate of Baden|Baden]] and [[March of Verona|Verona]] (d. 1190) |
* [[Herman IV, Margrave of Baden|Herman IV]], margrave of [[Margraviate of Baden|Baden]] and [[March of Verona|Verona]] (d. 1190) |
||
* [[Hugh de Willoughby (1135–1205)|Hugh de Willoughby]], English nobleman (d. [[1205]]) |
|||
* [[Inge I of Norway|Inge I]] ( |
* [[Inge I of Norway|Inge I]] ("the Hunchback"), king of [[Kingdom of Norway (872–1397)|Norway]] (d. [[1161]]) |
||
* [[Joachim of Fiore]], Italian theologian and mystic (d. 1202) |
* [[Joachim of Fiore]], Italian theologian and mystic (d. 1202) |
||
* [[Karl Jónsson]], Icelandic clergyman and poet (d. [[1213]]) |
|||
* [[Magnus Haraldsson (son of Harald Gille)|Magnus Haraldsson]], king of [[Kingdom of Norway (872–1397)|Norway]] (approximate date) |
|||
* [[Maimonides]], Almoravid philosopher and physician (d. [[1204]]) |
* [[Maimonides]], Almoravid philosopher and physician (d. [[1204]]) |
||
* [[Margaret of Navarre]], queen of [[Kingdom of Sicily|Sicily]] (approximate date) |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
* [[Minamoto no Yoshishige]], Japanese [[samurai]] (d. 1202) |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
* [[Simone Doria (admiral)|Simone Doria]], Genoese admiral (approximate date) |
|||
* [[Roger de Newburgh]], English nobleman (d. [[1192]]) |
|||
* [[Rudolf of Zähringen]], German archbishop (d. [[1191]]) |
|||
* [[Samson of Tottington]], English monk and [[abbot]] (d. [[1211]]) |
|||
* [[Walkelin de Derby]] (or Ferrers), Norman nobleman (d. 1190) |
|||
* [[William of the White Hands]], French archbishop (d. 1202) |
* [[William of the White Hands]], French archbishop (d. 1202) |
||
* [[Empress Xie (Xiaozong)|Xie]] (Xiaozong), Chinese empress of the [[Song dynasty]] (d. 1207) |
|||
== Deaths == |
== Deaths == |
||
* [[February 1]] – [[Shams al-Mulk Isma'il]], Seljuk ruler (b. [[1113]]) |
* [[February 1]] – [[Shams al-Mulk Isma'il]], Seljuk ruler (b. [[1113]]) |
||
* [[February 6]] – [[Elvira of Castile, Queen of Sicily|Elvira of Castile]], queen of [[Kingdom of Sicily|Sicily]] (b. [[1100]]) |
* [[February 6]] – [[Elvira of Castile, Queen of Sicily|Elvira of Castile]], queen of [[Kingdom of Sicily|Sicily]] (b. [[1100]]) |
||
* [[February 9]] – [[Emperor Taizong of Jin| |
* [[February 9]] – [[Emperor Taizong of Jin|Taizong]], emperor of the [[Jin dynasty (1115–1234)|Jin dynasty]] (b. [[1075]]) |
||
* |
* May – [[Rainier, Marquess of Montferrat|Rainier]] (or Renier), marquess of [[Montferrat]] (b. [[1084]]) |
||
* [[June 4]] – [[Emperor Huizong of Song|Huizong]], emperor of the [[Song dynasty]] (b. [[1082]]) |
|||
* [[August 9]] – [[Wartislaw I]], duke of [[Duchy of Pomerania|Pomerania]] (b. [[1091]]) |
* [[August 9]] – [[Wartislaw I]], duke of [[Duchy of Pomerania|Pomerania]] (b. [[1091]]) |
||
* [[August 29]] – [[Al-Mustarshid]], Abbasid caliph (b. [[1092]]) |
* [[August 29]] – [[Al-Mustarshid]], Abbasid caliph (b. [[1092]]) |
||
| Line 66: | Line 87: | ||
* [[Abd al-Majid ibn Abdun]], Andalusian poet (b. [[1050]]) |
* [[Abd al-Majid ibn Abdun]], Andalusian poet (b. [[1050]]) |
||
* [[Gerald de Windsor]], English nobleman (b. 1075) |
* [[Gerald de Windsor]], English nobleman (b. 1075) |
||
* [[Gisela of Burgundy, Marchioness of Montferrat|Gisela of Burgundy]], French noblewoman (b. 1075) |
* [[Gisela of Burgundy, Marchioness of Montferrat|Gisela of Burgundy]], marchioness of Montferrat, French noblewoman (b. 1075) |
||
* [[Harald Kesja]] ( |
* [[Harald Kesja]] ("the Spear"), king of [[Denmark]] (b. [[1080]]) |
||
* [[Liang Hongyu]] ( |
* [[Liang Hongyu]] ("Red Jade"), Chinese female general (b. [[1102]]) |
||
* [[Meginhard I, Count of Sponheim |
* [[Meginhard I, Count of Sponheim]], German nobleman (approximate date) |
||
* [[Rainier, Marquess of Montferrat|Rainier]] (or '''Renier'''), marquess of [[Montferrat]] (b. [[1084]]) |
|||
* [[Yuanwu Keqin]], Chinese [[Chan Buddhism|Chan Buddhist]] monk (b. [[1063]]) |
* [[Yuanwu Keqin]], Chinese [[Chan Buddhism|Chan Buddhist]] monk (b. [[1063]]) |
||
| Line 84: | Line 104: | ||
| first = Jeremy |
| first = Jeremy |
||
| title = Arabic Administration in Norman Sicily: The Royal Diwan |
| title = Arabic Administration in Norman Sicily: The Royal Diwan |
||
| url = https://archive.org/details/arabicadministra00john |
|||
| url-access = limited |
|||
| series = Cambridge Studies in Islamic Civilization |
| series = Cambridge Studies in Islamic Civilization |
||
| date = 2002 |
| date = 2002 |
||
| publisher = Cambridge University Press |
| publisher = Cambridge University Press |
||
| isbn = 978-0521816922 |
| isbn = 978-0521816922 |
||
| page = 85 |
| page = [https://archive.org/details/arabicadministra00john/page/n104 85] |
||
| ref = harv |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
| Line 102: | Line 123: | ||
| pages = 67–82 |
| pages = 67–82 |
||
| doi = 10.1016/0304-4181(81)90036-1 |
| doi = 10.1016/0304-4181(81)90036-1 |
||
| ref = harv |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
* {{cite book |
* {{cite book |
||
| title = La mer et les musulmans d'occident au Moyen Âge, VIIIe-XIIIe siècle |
| title = La mer et les musulmans d'occident au Moyen Âge, VIIIe-XIIIe siècle |
||
| language = |
| language = fr |
||
| first1 = Christophe |
| first1 = Christophe |
||
| last1 = Picard |
| last1 = Picard |
||
| Line 113: | Line 133: | ||
| publisher = Presses Universitaires de France |
| publisher = Presses Universitaires de France |
||
| isbn = 978-2130488101 |
| isbn = 978-2130488101 |
||
| ref = harv |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
Latest revision as of 18:23, 17 January 2024
| Millennium: | 2nd millennium |
|---|---|
| Centuries: | |
| Decades: | |
| Years: |
| 1135 by topic |
|---|
| Leaders |
| Birth and death categories |
| Births – Deaths |
| Establishments and disestablishments categories |
| Establishments – Disestablishments |
| Art and literature |
| 1135 in poetry |
| Gregorian calendar | 1135 MCXXXV |
| Ab urbe condita | 1888 |
| Armenian calendar | 584 ԹՎ ՇՁԴ |
| Assyrian calendar | 5885 |
| Balinese saka calendar | 1056–1057 |
| Bengali calendar | 542 |
| Berber calendar | 2085 |
| English Regnal year | 35 Hen. 1 – 1 Ste. 1 |
| Buddhist calendar | 1679 |
| Burmese calendar | 497 |
| Byzantine calendar | 6643–6644 |
| Chinese calendar | 甲寅年 (Wood Tiger) 3832 or 3625 — to — 乙卯年 (Wood Rabbit) 3833 or 3626 |
| Coptic calendar | 851–852 |
| Discordian calendar | 2301 |
| Ethiopian calendar | 1127–1128 |
| Hebrew calendar | 4895–4896 |
| Hindu calendars | |
| - Vikram Samvat | 1191–1192 |
| - Shaka Samvat | 1056–1057 |
| - Kali Yuga | 4235–4236 |
| Holocene calendar | 11135 |
| Igbo calendar | 135–136 |
| Iranian calendar | 513–514 |
| Islamic calendar | 529–530 |
| Japanese calendar | Chōshō 4 / Hōen 1 (保延元年) |
| Javanese calendar | 1041–1042 |
| Julian calendar | 1135 MCXXXV |
| Korean calendar | 3468 |
| Minguo calendar | 777 before ROC 民前777年 |
| Nanakshahi calendar | −333 |
| Seleucid era | 1446/1447 AG |
| Thai solar calendar | 1677–1678 |
| Tibetan calendar | 阳木虎年 (male Wood-Tiger) 1261 or 880 or 108 — to — 阴木兔年 (female Wood-Rabbit) 1262 or 881 or 109 |
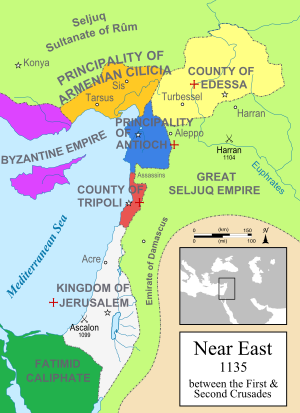
Year 1135 (MCXXXV) was a common year starting on Tuesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar.
Events
[edit]By place
[edit]
Levant
[edit]- Spring – Shams al-Mulk Isma'il, Seljuk ruler of Damascus, sends envoys to Imad al-Din Zengi, Seljuk ruler of Mosul, to seek his protection in exchange of Damascus. Zengi crosses the Euphrates, receiving the surrender of the city of Hama. He besieges Damascus but, due to a shortage of supplies, is forced to abandon the siege. Zengi extricates himself from Damascus, his Seljuk forces capture the fortresses at Ma'arrat and Atharib.[1]
- Queen Melisende of Jerusalem reconciles with her husband Fulk V, after a period of estrangement occasioned by her growing power, and rumors that she has had an affair with Hugh II (du Puiset), former count of Jaffa.
Europa
[edit]- January 7 – King Harald IV returns with Danish reinforcements and the support of King Eric II ("the Memorable"). He captures his nephew and joint ruler Magnus IV (Sigurdsson), who is blinded, castrated – and confined in Nidarholm Abbey (located on the island of Munkholmen).
- May 26 – King Alfonso VII is crowned as "Emperor of All Spain" (Imperator totius Hispaniae) in the Cathedral of León. The coronation is attended by Ramon Berenguer IV (his brother-in-law), Raymond V and other Spanish nobles who have recognize him as their overlord.
- Summer – King Roger II lands with a Sicilian expeditionary force in Salerno. He splits his army, and conquers the cities of Aversa and Alife. Roger besieges Naples – but despite poor health conditions within the city, he is not able to take it, and returns again to Messina.
- August 15 – Emperor Lothair III receives homage from Eric II, and makes him an imperial prince at the Reichstag. His diplomatic missions to Hungary and Poland result in a tribute payment. Duke Bolesław III Wrymouth is given Pomerania and Rügen as German fiefs.
- Lothair III receives a Byzantine embassy at his court, on behalf of Emperor John II Komnenos. It offers large financial subsidies for Lothair to start a campaign against Roger II. The negotiations will last for some months.[2]
- September – King García IV ("the Restorer") breaks with Alfonso VII, and makes common cause with the County of Portugal against Castile and León.
- October – Conrad III, duke of Franconia, gives up his title as King of Italy in opposition with Lothair III. He receives a pardon and recovers his estates.
- Pisans in the service of the Holy See (Diocese of Rome) sack the city of Amalfi.
- A Moorish fleet raids the Catalan port-town of Elna (Southern France).[3]
England
[edit]- December 1 – King Henry I dies at Lyons-la-Forêt in Normandy after a 35-year reign. He is succeeded by his nephew Stephen of Blois (grandson of William the Conqueror), who asserts his claim to the throne in opposition to claims by Henry's daughter Matilda (prolonged in a civil war known as The Anarchy).
- December 26 – Stephen of Blois is crowned at Westminster Abbey in London by Archbishop William de Corbeil. Matilda (pregnant with child) and her husband Geoffrey V ("the Fair") leave for their own safety to Normandy, where she plans how to overthrow Stephen and claim the English throne for her own.
Middle East
[edit]- August 29 – Caliph Al-Mustarshid is assassinated at Baghdad after a 17-year reign. He is succeeded by his son Al-Rashid Billah as ruler of the Abbasid Caliphate (until 1138).
North Africa
[edit]- Summer – A Sicilian expeditionary force led by Roger II embarks from Messina and takes the island of Djerba (modern Tunisia).[4]
- The Hammadid Emirate (modern Algeria) launches an assault against the city of Mahdia (modern Tunisia).[5]
Asia
[edit]- Jin–Song War – Song forces under Yue Fei begin a counteroffensive against the Jurchen-ruled Jin dynasty in northern China. He defeats Jin forces, by entangling his paddle-wheel ships at the Huai River.
- June 4 – Emperor Hui Zong dies in exile in Heilongjiang (Manchuria), having been held prisoner with his son Qin Zong since their capture in 1127.
By topic
[edit]Religion
[edit]- January – Byland Abbey is founded in England by the Congregation of Savigny.
- Buildwas Abbey is founded in England by Roger de Clinton, bishop of Coventry.
Births
[edit]- Abu Yaqub Yusuf, caliph of the Almohad Caliphate (d. 1184)
- Adachi Morinaga, Japanese warrior monk (d. 1200)
- Albert of Chiatina, Italian archpriest and saint (d. 1202)
- André of Brienne, French nobleman (approximate date)
- Bogumilus, archbishop of Gniezno (approximate date)
- Burhan al-Din al-Marghinani, Arabic Hanafi jurist (d. 1197)
- Conrad of Hohenstaufen, German nobleman (d. 1195)
- Fernando Afonso, Portuguese Grand Master (d. 1207)
- Gertrude of Flanders, countess of Savoy (d. 1186)
- Hafsa bint al-Hajj al-Rukuniyya, Andalusian poet (d. 1190)
- Henry Fitz Eylwin, 1st Lord Mayor of London (d. 1212)
- Herman IV, margrave of Baden and Verona (d. 1190)
- Hugh de Willoughby, English nobleman (d. 1205)
- Inge I ("the Hunchback"), king of Norway (d. 1161)
- Joachim of Fiore, Italian theologian and mystic (d. 1202)
- Karl Jónsson, Icelandic clergyman and poet (d. 1213)
- Magnus Haraldsson, king of Norway (approximate date)
- Maimonides, Almoravid philosopher and physician (d. 1204)
- Margaret of Navarre, queen of Sicily (approximate date)
- Minamoto no Yoshishige, Japanese samurai (d. 1202)
- Sharaf al-Dīn al-Tūsī, Persian mathematician (d. 1213)
- Simone Doria, Genoese admiral (approximate date)
- Roger de Newburgh, English nobleman (d. 1192)
- Rudolf of Zähringen, German archbishop (d. 1191)
- Samson of Tottington, English monk and abbot (d. 1211)
- Walkelin de Derby (or Ferrers), Norman nobleman (d. 1190)
- William of the White Hands, French archbishop (d. 1202)
- Xie (Xiaozong), Chinese empress of the Song dynasty (d. 1207)
Deaths
[edit]- February 1 – Shams al-Mulk Isma'il, Seljuk ruler (b. 1113)
- February 6 – Elvira of Castile, queen of Sicily (b. 1100)
- February 9 – Taizong, emperor of the Jin dynasty (b. 1075)
- May – Rainier (or Renier), marquess of Montferrat (b. 1084)
- June 4 – Huizong, emperor of the Song dynasty (b. 1082)
- August 9 – Wartislaw I, duke of Pomerania (b. 1091)
- August 29 – Al-Mustarshid, Abbasid caliph (b. 1092)
- December 1 – Henry I, king of England (b. 1068)
- Abd al-Majid ibn Abdun, Andalusian poet (b. 1050)
- Gerald de Windsor, English nobleman (b. 1075)
- Gisela of Burgundy, marchioness of Montferrat, French noblewoman (b. 1075)
- Harald Kesja ("the Spear"), king of Denmark (b. 1080)
- Liang Hongyu ("Red Jade"), Chinese female general (b. 1102)
- Meginhard I, Count of Sponheim, German nobleman (approximate date)
- Yuanwu Keqin, Chinese Chan Buddhist monk (b. 1063)
References
[edit]- ^ Steven Runciman (1952). A History of The Crusades. Vol II: The Kingdom of Jerusalem, p. 158. ISBN 978-0-241-29876-3.
- ^ Steven Runciman (1952). A History of the Crusades. Vol II: The Kingdom of Jerusalem, p. 170. ISBN 978-0-241-29876--3.
- ^ McGrank 1981.
- ^ Picard 1997.
- ^ Johns 2002.
Sources
[edit]- Johns, Jeremy (2002). Arabic Administration in Norman Sicily: The Royal Diwan. Cambridge Studies in Islamic Civilization. Cambridge University Press. p. 85. ISBN 978-0521816922.
- McGrank, Lawrence (1981). "Norman crusaders in the Catalan reconquest: Robert Burdet and the principality of Tarragona, 1129-55". Journal of Medieval History. 7 (1): 67–82. doi:10.1016/0304-4181(81)90036-1.
- Picard, Christophe (1997). La mer et les musulmans d'occident au Moyen Âge, VIIIe-XIIIe siècle (in French). Presses Universitaires de France. ISBN 978-2130488101.
