Socket 7: Difference between revisions
Added a release date with reference |
Undid revision 1217644110 by 120.29.107.10 (talk) |
||
| (18 intermediate revisions by 14 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Physical and electrical specification for an x86-style CPU socket}} |
|||
{{Infobox CPU socket |
{{Infobox CPU socket |
||
|name = Socket 7 |
|name = Socket 7 |
||
| Line 9: | Line 10: | ||
|voltage = 2.5–3.5 V |
|voltage = 2.5–3.5 V |
||
|processors = 75–233 MHz Intel [[P5 (microarchitecture)|P5]] [[Pentium (brand)|Pentium]], AMD K5 through K6, Cyrix 6x86 (and 6x86MX) P120–P233 |
|processors = 75–233 MHz Intel [[P5 (microarchitecture)|P5]] [[Pentium (brand)|Pentium]], AMD K5 through K6, Cyrix 6x86 (and 6x86MX) P120–P233 |
||
|predecessor = [[Socket 5]] |
|||
|successor = [[Socket 8]] (Intel)<br/>[[Slot 1]] (Intel)<br/>[[Super Socket 7]] (AMD) |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
'''Socket 7''' is a physical and electrical specification for an [[x86]]-style [[Central processing unit|CPU]] socket on a personal computer [[motherboard]]. It was released June 1995<ref>{{cite web|last1=Torres|first1=Gabriel|title=A Complete List of CPU Sockets|url=http://www.hardwaresecrets.com/article/A-Complete-List-of-CPU-Sockets/373/2|website=Hardware Secrets| |
'''Socket 7''' is a physical and electrical specification for an [[x86]]-style [[Central processing unit|CPU]] socket on a personal computer [[motherboard]]. It was released in June 1995.<ref>{{cite web|last1=Torres|first1=Gabriel|title=A Complete List of CPU Sockets|url=http://www.hardwaresecrets.com/article/A-Complete-List-of-CPU-Sockets/373/2|website=Hardware Secrets|access-date=23 September 2014|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140924043456/http://www.hardwaresecrets.com/article/A-Complete-List-of-CPU-Sockets/373/2|archive-date=24 September 2014}}</ref> The socket supersedes the earlier [[Socket 5]], and accepts [[P5 (microarchitecture)|P5]] [[Pentium (brand)|Pentium]] [[microprocessor]]s manufactured by [[Intel]], as well as compatibles made by [[Cyrix]]/[[IBM]], [[AMD]], [[Integrated Device Technology|IDT]] and others.<ref>{{Citation |title=Intel Socket 7 Specification |publisher=pcguide.com |url=http://www.pcguide.com/ref/cpu/char/socketSocket7-c.html |access-date=2009-03-31}}</ref> Socket 7 was the only socket that supported a wide range of CPUs from different manufacturers and a wide range of speeds. |
||
| ⚫ | Differences between Socket 5 and Socket 7 are that Socket 7 has an extra pin and is designed to provide dual split rail voltage, as opposed to Socket 5's single voltage. However, not all motherboard manufacturers supported the dual voltage on their boards initially. Socket 7 is [[Backward compatibility|backwards compatible]]; a Socket 5 CPU can be inserted and used on a Socket 7 motherboard. |
||
Socket 7 was the only socket that supported a wide range of CPUs from different manufacturers and a wide range of speeds. |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | Differences between Socket 5 and Socket 7 are that Socket 7 has an extra pin and is designed to provide dual split rail voltage, as opposed to Socket 5's single voltage. |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | Processors that used Socket 7 are the [[AMD K5]] and [[AMD K6|K6]], the [[Cyrix 6x86]] and 6x86MX, the IDT [[WinChip]], the Intel |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
Socket 7 and [[Socket 8]] were replaced by [[Slot 1]] and [[Slot 2]] in 1999.[[File:Cyrix IBM CPU 6x86MX PR200 bottom.jpg|thumb|Bottom view of a socket 7, 321-pin SPGA CPU]] |
|||
The size is 1.95" x 1.95" (4.95 cm x 4.95 cm). |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
[[File:Cyrix_IBM_CPU_6x86MX_PR200_bottom.jpg|thumb|left|Bottom view of a socket 7, 321-pin SPGA CPU]] |
|||
{{clr}} |
|||
==See also== |
==See also== |
||
* [[List of Intel microprocessors]] |
* [[List of Intel microprocessors]] |
||
| Line 32: | Line 31: | ||
==References== |
==References== |
||
{{Reflist}} |
{{Reflist}} |
||
{{FOLDOC}} |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
{{earlysock}} |
{{earlysock}} |
||
{{intelsock}} |
{{intelsock}} |
||
| ⚫ | |||
Latest revision as of 02:22, 7 April 2024
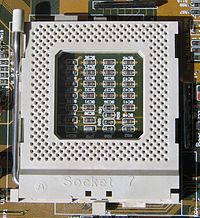 | |
| Typ | ZIF |
|---|---|
| Chip form factors | SPGA |
| Contacts | 321 |
| FSB protocol | P5 |
| FSB frequency | 66–83 MHz System Clock |
| Voltage range | 2.5–3.5 V |
| Processors | 75–233 MHz Intel P5 Pentium, AMD K5 through K6, Cyrix 6x86 (and 6x86MX) P120–P233 |
| Predecessor | Socket 5 |
| Successor | Socket 8 (Intel) Slot 1 (Intel) Super Socket 7 (AMD) |
This article is part of the CPU socket series | |
Socket 7 is a physical and electrical specification for an x86-style CPU socket on a personal computer motherboard. It was released in June 1995.[1] The socket supersedes the earlier Socket 5, and accepts P5 Pentium microprocessors manufactured by Intel, as well as compatibles made by Cyrix/IBM, AMD, IDT and others.[2] Socket 7 was the only socket that supported a wide range of CPUs from different manufacturers and a wide range of speeds.
Differences between Socket 5 and Socket 7 are that Socket 7 has an extra pin and is designed to provide dual split rail voltage, as opposed to Socket 5's single voltage. However, not all motherboard manufacturers supported the dual voltage on their boards initially. Socket 7 is backwards compatible; a Socket 5 CPU can be inserted and used on a Socket 7 motherboard.
Processors that used Socket 7 are the AMD K5 and K6, the Cyrix 6x86 and 6x86MX, the IDT WinChip, the Intel P5 Pentium (2.5–3.5 V, 75–200 MHz), the Pentium MMX (166–233 MHz), and the Rise Technology mP6.
Socket 7 typically uses a 321-pin (arranged as 19 by 19 pins) SPGA ZIF socket or the very rare 296-pin (arranged as 37 by 37 pins) SPGA LIF socket. The size is 1.95" x 1.95" (4.95 cm x 4.95 cm).
An extension of Socket 7, Super Socket 7, was developed by AMD for their K6-2 and K6-III processors to operate at a higher clock rate and use AGP.
Socket 7 and Socket 8 were replaced by Slot 1 and Slot 2 in 1999.

See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Torres, Gabriel. "A Complete List of CPU Sockets". Hardware Secrets. Archived from the original on 24 September 2014. Retrieved 23 September 2014.
- ^ Intel Socket 7 Specification, pcguide.com, retrieved 2009-03-31
