Thenar eminence: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
{{Anatomy terms}} Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit Advanced mobile edit |
||
| (18 intermediate revisions by 15 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Mound at the base of the thumb formed by the intrinsic group of muscles}} |
|||
{{Anatomy terms}} |
|||
{{Multiple issues| |
{{Multiple issues| |
||
{{Disputed|Innervation by deep branch of Ulnar nerve of Flexor Pollicis brevis (medial head) is not clearly stated|date=December 2015}} |
{{Disputed|Innervation by deep branch of Ulnar nerve of Flexor Pollicis brevis (medial head) is not clearly stated|date=December 2015}} |
||
| Line 6: | Line 8: | ||
{{Infobox muscle |
{{Infobox muscle |
||
| Name = Thenar eminence |
| Name = Thenar eminence |
||
| Latin = |
| Latin = eminentia thenaris |
||
| Image = Gray423.png |
| Image = Gray423.png |
||
| Caption = The mucous sheaths of the tendons on the anterior surface of the [[wrist]] and [[finger|digits]] |
| Caption = The mucous sheaths of the tendons on the anterior surface of the [[wrist]] and [[finger|digits]] |
||
| Line 20: | Line 22: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
The '''thenar eminence''' |
The '''thenar eminence''' is the mound formed at the base of the [[thumb]] on the palm of the hand by the [[muscles of the thumb#Intrinsic|intrinsic group]] of [[muscles of the thumb]].<ref name="Gupta">{{cite journal |last1=Gupta |first1=S |last2=Michelsen-Jost |first2=H |title=Anatomy and function of the thenar muscles. |journal=Hand Clinics |date=February 2012 |volume=28 |issue=1 |pages=1–7 |doi=10.1016/j.hcl.2011.09.006 |pmid=22117918}}</ref> The skin overlying this region is the area stimulated when trying to elicit a [[palmomental reflex]]. The word thenar comes {{ety|grc|''θέναρ'' (thenar)|palm of the hand}}.<ref>[https://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/text?doc=Perseus%3Atext%3A1999.04.0057%3Aentry%3Dqe%2Fnar θέναρ]</ref> |
||
==Structure== |
==Structure== |
||
The following three muscles are considered part of the thenar eminence:<ref name="titleIntrinsic Muscles of the Hand — Wheeless Textbook of Orthopaedics">{{cite web |url=http://www.wheelessonline.com/ortho/intrinsic_muscles_of_the_hand |title=Intrinsic Muscles of the Hand — Wheeless' Textbook of Orthopaedics | |
The following three muscles are considered part of the thenar eminence:<ref name="titleIntrinsic Muscles of the Hand — Wheeless Textbook of Orthopaedics">{{cite web |url=http://www.wheelessonline.com/ortho/intrinsic_muscles_of_the_hand |title=Intrinsic Muscles of the Hand — Wheeless' Textbook of Orthopaedics |access-date=2008-01-16 }}</ref> |
||
* [[Abductor pollicis brevis]] [[abduction (anatomy)|abducts]] the thumb. This muscle is the most [[superficial (anatomy)|superficial]] of the thenar group. |
* [[Abductor pollicis brevis]] [[abduction (anatomy)|abducts]] the thumb. This muscle is the most [[superficial (anatomy)|superficial]] of the thenar group. |
||
* [[Flexor pollicis brevis]], which lies next to the abductor, will [[flexion|flex]] the thumb, curling it up in the palm. |
* [[Flexor pollicis brevis]], which lies next to the abductor, will [[flexion|flex]] the thumb, curling it up in the palm. (The [[flexor pollicis longus]], which is inserted into the distal phalanx of the thumb, is not considered part of the thenar eminence.) |
||
* [[Opponens pollicis]] lies deep to abductor pollicis brevis. As its name suggests it [[Anatomical terms of motion|opposes]] the thumb, bringing it against the fingers. This is a very important movement, as most of human hand dexterity comes from this action. |
* [[Opponens pollicis]] lies deep to abductor pollicis brevis. As its name suggests it [[Anatomical terms of motion|opposes]] the thumb, bringing it against the fingers. This is a very important movement, as most of human hand dexterity comes from this action. |
||
Another muscle that controls movement of the thumb is [[adductor pollicis]]. It lies deeper and more [[distal]] to flexor pollicis brevis. Despite |
Another muscle that controls movement of the thumb is [[adductor pollicis]]. It lies deeper and more [[distal]] to flexor pollicis brevis. Despite the name, adductor pollicis is chiefly responsible for rotation and opposition. This muscle is not in the thenar group of muscles, and is supplied by the [[ulnar nerve]] instead.<ref name="titleApplied MSK anatomy of the hand">{{cite web |url=http://www.med.mun.ca/anatomyts/msk/hand.htm |title=Applied MSK anatomy of the hand |access-date=2008-01-16 |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20080101140737/http://www.med.mun.ca/anatomyts/msk/hand.htm <!-- Bot retrieved archive --> |archive-date = 2008-01-01}}</ref> |
||
===Nerve supply=== |
===Nerve supply=== |
||
The opponens pollicis and abductor pollicis brevis are normally innervated by the [[median nerve]]. |
The opponens pollicis and abductor pollicis brevis are normally innervated by the [[median nerve]]. |
||
The flexor pollicis brevis has two heads a superficial and a deep. |
The flexor pollicis brevis has two heads a superficial and a deep. The flexor pollicis brevis (FPB) is typically an ulnar-innervated muscle. Due to a common interconnection between the median and ulnar nerves in the hand (Riche-Cannieu interconnection), the Median nerve may innervate the FPB in 35% of people. It is innervated by the Ulnar nerve in 50% of people and by both the median and ulnar nerves in 15%. |
||
The adductor pollicis is typically innervated by the [[ulnar nerve]]. |
The adductor pollicis is typically innervated by the [[ulnar nerve]]. There are normal variations. In a [[Cannieu-Riche anastomosis]], fibers from the [[Deep branch of ulnar nerve|deep palmar branch of the ulnar nerve]] innervate the opponens pollicis and/or abductor pollicis brevis. Regardless of their final innervation, the nerves that reach the thenar muscles arise from the [[Cervical spinal nerve 8|C8]] and [[Thoracic spinal nerve 1|T1 roots]], pass through the lower trunk of the plexus, and then through the medial cord of the plexus. |
||
The ulnar nerve is exclusively responsible for the innervations of the [[hypothenar eminence]]. Both nerves contribute to the innervations of the [[midpalmar group]].<ref name="test">{{cite book |
The ulnar nerve is exclusively responsible for the innervations of the [[hypothenar eminence]]. Both nerves contribute to the innervations of the [[midpalmar group]].<ref name="test">{{cite book |
||
| Line 52: | Line 54: | ||
File:Slide8PPP.JPG|Thenar eminence |
File:Slide8PPP.JPG|Thenar eminence |
||
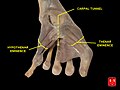
File:Hand dissection 5.jpg|Carpal tunnel and thenar and hypothenar eminences |
File:Hand dissection 5.jpg|Carpal tunnel and thenar and hypothenar eminences |
||
File:Thenar eminence comparison anterior.jpg|Comparison, anterior |
|||
File:Thenar eminence comparison posterior.jpg|Comparison, posterior |
|||
File:Thenar eminence comparison thumbs.jpg|Comparison facing thumbs |
|||
</gallery> |
</gallery> |
||
Latest revision as of 18:57, 17 April 2024
This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages)
|
| Thenar eminence | |
|---|---|
 | |
 | |
| Details | |
| Artery | Superficial palmar arch |
| Nerve | Median nerve |
| Actions | Control movement of the thumb |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | eminentia thenaris |
| TA98 | A01.2.07.023 |
| TA2 | 306 |
| FMA | 61520 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
The thenar eminence is the mound formed at the base of the thumb on the palm of the hand by the intrinsic group of muscles of the thumb.[1] The skin overlying this region is the area stimulated when trying to elicit a palmomental reflex. The word thenar comes from Ancient Greek θέναρ (thenar) 'palm of the hand'.[2]
Structure
[edit]The following three muscles are considered part of the thenar eminence:[3]
- Abductor pollicis brevis abducts the thumb. This muscle is the most superficial of the thenar group.
- Flexor pollicis brevis, which lies next to the abductor, will flex the thumb, curling it up in the palm. (The flexor pollicis longus, which is inserted into the distal phalanx of the thumb, is not considered part of the thenar eminence.)
- Opponens pollicis lies deep to abductor pollicis brevis. As its name suggests it opposes the thumb, bringing it against the fingers. This is a very important movement, as most of human hand dexterity comes from this action.
Another muscle that controls movement of the thumb is adductor pollicis. It lies deeper and more distal to flexor pollicis brevis. Despite the name, adductor pollicis is chiefly responsible for rotation and opposition. This muscle is not in the thenar group of muscles, and is supplied by the ulnar nerve instead.[4]
Nerve supply
[edit]The opponens pollicis and abductor pollicis brevis are normally innervated by the median nerve.
The flexor pollicis brevis has two heads a superficial and a deep. The flexor pollicis brevis (FPB) is typically an ulnar-innervated muscle. Due to a common interconnection between the median and ulnar nerves in the hand (Riche-Cannieu interconnection), the Median nerve may innervate the FPB in 35% of people. It is innervated by the Ulnar nerve in 50% of people and by both the median and ulnar nerves in 15%.
The adductor pollicis is typically innervated by the ulnar nerve. There are normal variations. In a Cannieu-Riche anastomosis, fibers from the deep palmar branch of the ulnar nerve innervate the opponens pollicis and/or abductor pollicis brevis. Regardless of their final innervation, the nerves that reach the thenar muscles arise from the C8 and T1 roots, pass through the lower trunk of the plexus, and then through the medial cord of the plexus.
The ulnar nerve is exclusively responsible for the innervations of the hypothenar eminence. Both nerves contribute to the innervations of the midpalmar group.[5]
The muscles in this location are usually innervated by the recurrent branch of the median nerve. They all control movement of the thumb.
The innervation of these muscles by the median nerve is unusual, as most of the intrinsic muscles on the palm of the hand are supplied by the ulnar nerve. The lateral two lumbrical muscles are the other exception.
Additional images
[edit]-
Thenar eminence
-
Carpal tunnel and thenar and hypothenar eminences
-
Comparison, anterior
-
Comparison, posterior
-
Comparison facing thumbs
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Gupta, S; Michelsen-Jost, H (February 2012). "Anatomy and function of the thenar muscles". Hand Clinics. 28 (1): 1–7. doi:10.1016/j.hcl.2011.09.006. PMID 22117918.
- ^ θέναρ
- ^ "Intrinsic Muscles of the Hand — Wheeless' Textbook of Orthopaedics". Retrieved 2008-01-16.
- ^ "Applied MSK anatomy of the hand". Archived from the original on 2008-01-01. Retrieved 2008-01-16.
- ^ Van De Graaff, Kent M. (1992). Human Anatomy (3rd ed.). Dubuque: Wm C Brown. ISBN 0-697-09716-1. Print.
External links
[edit]- lesson5mus&tendonsofhand at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University)