Rectus femoris muscle: Difference between revisions
Kamal mezian (talk | contribs) m Just text flow adjustment |
capitalized #article-section-source-editor Tags: Mobile edit Mobile app edit iOS app edit |
||
| (27 intermediate revisions by 24 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{short description|Muscle in the quad}} |
|||
{{Infobox muscle |
{{Infobox muscle |
||
| Name = Rectus femoris muscle |
| Name = Rectus femoris muscle |
||
| Latin = |
| Latin = musculus rectus femoris |
||
| GraySubject = 128 |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| Image = Rectus femoris.png |
| Image = Rectus femoris.png |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| Caption = Muscles of the iliac and anterior femoral regions. (Rectus femoris visible near center.) |
| Caption = Muscles of the iliac and anterior femoral regions. (Rectus femoris visible near center.) |
||
| Image2 = |
| Image2 = |
||
| Caption2 = |
| Caption2 = |
||
| Origin = [[ |
| Origin = [[Anterior inferior iliac spine]] and the exterior surface of the bony ridge which forms the groove on the iliac portion of the [[acetabulum]] |
||
| Insertion = |
| Insertion = Inserts into the [[patellar ligament|patellar tendon]] as one of the four [[quadriceps femoris muscle|quadriceps muscles]] |
||
| Blood = |
| Blood = Descending branch of the [[lateral circumflex femoral artery|lateral femoral circumflex artery]] |
||
| Nerve = [[ |
| Nerve = [[Femoral nerve]] |
||
| Action = [[ |
| Action = [[Knee]] [[Anatomical terms of motion#Flexion and extension|extension]]; [[hip]] [[Anatomical terms of motion#Flexion and extension|flexion]] |
||
| Antagonist = [[Hamstring]] |
| Antagonist = [[Hamstring]] |
||
| Pronunciation = {{IPAc-en|ˈ|r|ɛ|k|t|ə|s|_|ˈ|f|ɛ|m|ər|ᵻ|s}} |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
The '''rectus femoris muscle''' |
The '''rectus femoris muscle''' is one of the four [[quadriceps femoris muscle|quadriceps muscles]] of the [[human body]]. The others are the [[vastus medialis]], the [[vastus intermedius muscle|vastus intermedius]] (deep to the rectus femoris), and the [[vastus lateralis muscle|vastus lateralis]]. All four parts of the quadriceps muscle attach to the [[patella]] (knee cap) by the [[quadriceps tendon]]. |
||
The rectus femoris is situated in the middle of the front of the [[thigh]]; it is [[wikt:fusiform|fusiform]] in shape, and its superficial fibers are arranged in a [[ |
The rectus femoris is situated in the middle of the front of the [[thigh]]; it is [[wikt:fusiform|fusiform]] in shape, and its superficial fibers are arranged in a [[Anatomical terms of muscle#Muscle fibres|bipenniform]] manner, the deep fibers running straight ({{lang-la|rectus}}) down to the deep [[aponeurosis]]. Its functions are to [[Anatomical terms of motion#Flexion and extension|flex]] the thigh at the [[hip]] joint and to [[Anatomical terms of motion#Flexion and extension|extend]] the [[leg]] at the [[knee]] joint.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Function of the Rectus Femoris Muscle |author = Elizabeth Quinn| url=https://www.verywellfit.com/rectus-femoris-definition-3120373 |access-date=2022-07-23 |website=Verywell Fit |language=en}}</ref> |
||
==Structure== |
==Structure== |
||
It arises by two tendons: one, the anterior or straight, from the [[anterior inferior iliac spine]]; the other, the posterior or reflected, from a groove above the rim of the [[acetabulum]]. |
It arises by two tendons: one, the anterior or straight, from the [[anterior inferior iliac spine]]; the other, the posterior or reflected, from a groove above the rim of the [[acetabulum]]. |
||
The two unite at an acute angle |
The two unite at an acute angle and spread into an aponeurosis that is prolonged downward on the anterior surface of the muscle, and from this the muscular fibers arise. |
||
The muscle ends in a broad and thick aponeurosis |
The muscle ends in a broad and thick aponeurosis that occupies the lower two-thirds of its posterior surface, and, gradually becoming narrowed into a flattened tendon, is inserted into the base of the [[patella]]. |
||
===Nerve supply=== |
===Nerve supply=== |
||
The neurons for voluntary thigh contraction originate near the summit of the medial side of the precentral gyrus (the primary motor area of the brain). These neurons send a nerve signal that is carried by the corticospinal tract down the brainstem and spinal cord. The signal starts with the upper motor neurons carrying the signal from the precentral gyrus down through the internal capsule, through the cerebral peduncle, and into the medulla. In the medullary pyramid, the corticospinal tract decussates and becomes the lateral corticospinal tract. The nerve signal will continue down the lateral corticospinal tract until it reaches spinal nerve L4. At this point, the nerve signal will synapse from the upper motor neurons to the lower motor neurons. The signal will travel through the anterior root of L4 and into the anterior rami of the L4 nerve, leaving the spinal cord through the lumbar plexus. The posterior division of the L4 root is the |
The neurons for voluntary thigh contraction originate near the summit of the medial side of the precentral gyrus (the primary motor area of the brain). These neurons send a nerve signal that is carried by the corticospinal tract down the brainstem and spinal cord. The signal starts with the upper motor neurons carrying the signal from the precentral gyrus down through the internal capsule, through the cerebral peduncle, and into the medulla. In the medullary pyramid, the corticospinal tract decussates and becomes the lateral corticospinal tract. The nerve signal will continue down the lateral corticospinal tract until it reaches spinal nerve L4. At this point, the nerve signal will synapse from the upper motor neurons to the lower motor neurons. The signal will travel through the anterior root of L4 and into the anterior rami of the L4 nerve, leaving the spinal cord through the lumbar plexus. The posterior division of the L4 root is the femoral nerve. The femoral nerve innervates the quadriceps femoris, a fourth of which is the rectus femoris. When the rectus femoris receives the signal that has traveled all the way from the medial side of the precentral gyrus, it contracts, extending the knee and flexing the thigh at the hip.<ref>''Anatomy and Physiology: The Unity of Form and Function'', Saladin, 5th ed.</ref> |
||
==Function== |
==Function== |
||
The rectus femoris, [[Sartorius muscle|sartorius]], and [[iliopsoas]] are the flexors of the thigh at the hip. |
The rectus femoris, [[Sartorius muscle|sartorius]], and [[iliopsoas]] are the flexors of the thigh at the hip. |
||
The rectus femoris is a weaker hip flexor when the knee is extended because it is already shortened and thus suffers from [[active insufficiency]]; the action will recruit more [[iliacus muscle|iliacus]], [[psoas major muscle|psoas major]], [[tensor fasciae latae muscle|tensor fasciae latae]], and the remaining [[hip flexors]] than it will the rectus femoris. |
The rectus femoris is a weaker hip flexor when the knee is extended because it is already shortened and thus suffers from [[Anatomical terms of muscle|active insufficiency]]; the action will recruit more [[iliacus muscle|iliacus]], [[psoas major muscle|psoas major]], [[tensor fasciae latae muscle|tensor fasciae latae]], and the remaining [[List of flexors of the human body#Hip|hip flexors]] than it will the rectus femoris. |
||
Similarly, the rectus femoris is not dominant in knee extension when the hip is flexed since it is already shortened and thus suffers from active insufficiency. In essence: the action of extending the knee from a seated position is primarily driven by the [[vastus lateralis muscle|vastus lateralis]], [[vastus medialis]], and [[vastus intermedius muscle|vastus intermedius]], and less by the rectus femoris. |
Similarly, the rectus femoris is not dominant in knee extension when the hip is flexed since it is already shortened and thus suffers from active insufficiency. In essence: the action of extending the knee from a seated position is primarily driven by the [[vastus lateralis muscle|vastus lateralis]], [[vastus medialis]], and [[vastus intermedius muscle|vastus intermedius]], and less by the rectus femoris. |
||
In the other extreme, the muscle's ability to flex the hip and extend the knee can be compromised in a position of full hip extension and knee flexion, due to [[passive insufficiency]]. |
In the other extreme, the muscle's ability to flex the hip and extend the knee can be compromised in a position of full hip extension and knee flexion, due to [[Anatomical terms of muscle|passive insufficiency]]. |
||
The rectus femoris is a direct [[ |
The rectus femoris is a direct [[Anatomical terms of muscle#Agonist|antagonist]] to the [[hamstring]]s, at the hip and at the knee. |
||
==Clinical significance== |
==Clinical significance== |
||
===Strain=== |
===Strain=== |
||
Rectus femoris strain, referred to as hip flexor strain,<ref>Geier, David (2011-01-18) [http://www.drdavidgeier.com/injuries/rectus-femoris-strain/ Rectus Femoris Strain (“Hip Flexor Strain”) | Dr. David Geier – Sports Medicine Simplified]. drdavidgeier.com.</ref> is an injury commonly at the tendon that attaches to the patella or in the muscle itself. The injury is usually a partial tear but could be a full tear. The injury is caused by a forceful movement related to sprinting, jumping, or kicking and is common in sports like football or soccer. The rectus femoris is prone to injury since it crosses both the knee and the hip. Symptoms include a sudden sharp pain at the front of the hip or in the groin, swelling and bruising, and an inability to contract the rectus femoris with a full tear.<ref>[http://orthopaedic.com.sg/a-rare-form-of-soccer-injury-rectus-femoris-tendon-rupture/ A Rare Form of Soccer Injury – Rectus Femoris Tendon Rupture – Orthopaedic Information | Singapore]. Orthopaedic.com.sg. Retrieved on 2015-09-30.</ref> |
Rectus femoris strain, referred to as hip flexor strain,<ref>Geier, David (2011-01-18) [http://www.drdavidgeier.com/injuries/rectus-femoris-strain/ Rectus Femoris Strain (“Hip Flexor Strain”) | Dr. David Geier – Sports Medicine Simplified]. drdavidgeier.com.</ref> is an injury commonly at the tendon that attaches to the patella or in the muscle itself. The injury is usually a partial tear, but could be a full tear. The injury is caused by a forceful movement related to sprinting, jumping, or kicking and is common in sports like football or soccer. The rectus femoris is prone to injury, since it crosses both the knee and the hip. Symptoms include a sudden sharp pain at the front of the hip or in the groin, swelling and bruising, and an inability to contract the rectus femoris with a full tear.<ref>[http://orthopaedic.com.sg/a-rare-form-of-soccer-injury-rectus-femoris-tendon-rupture/ A Rare Form of Soccer Injury – Rectus Femoris Tendon Rupture – Orthopaedic Information | Singapore]. Orthopaedic.com.sg. Retrieved on 2015-09-30.</ref> |
||
=== Avulsion fracture === |
|||
The Rectus femoris tendon can cause a fragment of [[Anterior inferior iliac spine|anterior inferior ilac spine]] of the hip (AIIS) to avulse in what is known as an [[Avulsion fracture]]. This is due to forceful contraction of the muscle that generates a force greater than that which holds the bone together. This is a well recognized, but unusual [[sports injury]] that can affect young athletes.<ref>{{Cite journal|last1=Esser|first1=Stephan|last2=Jantz|first2=David|last3=Hurdle|first3=Mark F.|last4=Taylor|first4=Walter|date=July 2015|title=Proximal Rectus Femoris Avulsion: Ultrasonic Diagnosis and Nonoperative Management|journal=Journal of Athletic Training|volume=50|issue=7|pages=778–780|doi=10.4085/1052-6050-50.2.13|issn=1062-6050|pmc=4532190|pmid=25978099}}</ref> |
|||
==References== |
==References== |
||
| Line 49: | Line 53: | ||
==External links== |
==External links== |
||
{{Commons}} |
{{Commons}} |
||
*[http://www.ptcentral.com/muscles/musclelegs.html#rectus%20femoris PTCentral] |
*[https://web.archive.org/web/20100715211225/http://www.ptcentral.com/muscles/musclelegs.html#rectus%20femoris PTCentral] |
||
{{Muscles of lower limb}} |
{{Muscles of lower limb}} |
||
{{Portal bar|Anatomy}} |
|||
{{Authority control}} |
|||
[[Category:Hip flexors]] |
[[Category:Hip flexors]] |
||
Latest revision as of 18:26, 4 May 2024
| Rectus femoris muscle | |
|---|---|
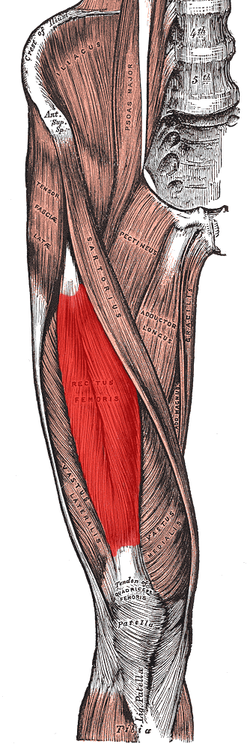 Muscles of the iliac and anterior femoral regions. (Rectus femoris visible near center.) | |
| Details | |
| Pronunciation | /ˈrɛktəs ˈfɛmərɪs/ |
| Origin | Anterior inferior iliac spine and the exterior surface of the bony ridge which forms the groove on the iliac portion of the acetabulum |
| Insertion | Inserts into the patellar tendon as one of the four quadriceps muscles |
| Artery | Descending branch of the lateral femoral circumflex artery |
| Nerve | Femoral nerve |
| Actions | Knee extension; hip flexion |
| Antagonist | Hamstring |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus rectus femoris |
| TA98 | A04.7.02.018 |
| TA2 | 2614 |
| FMA | 22430 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
The rectus femoris muscle is one of the four quadriceps muscles of the human body. The others are the vastus medialis, the vastus intermedius (deep to the rectus femoris), and the vastus lateralis. All four parts of the quadriceps muscle attach to the patella (knee cap) by the quadriceps tendon.
The rectus femoris is situated in the middle of the front of the thigh; it is fusiform in shape, and its superficial fibers are arranged in a bipenniform manner, the deep fibers running straight (Latin: rectus) down to the deep aponeurosis. Its functions are to flex the thigh at the hip joint and to extend the leg at the knee joint.[1]
Structure
[edit]It arises by two tendons: one, the anterior or straight, from the anterior inferior iliac spine; the other, the posterior or reflected, from a groove above the rim of the acetabulum.
The two unite at an acute angle and spread into an aponeurosis that is prolonged downward on the anterior surface of the muscle, and from this the muscular fibers arise.
The muscle ends in a broad and thick aponeurosis that occupies the lower two-thirds of its posterior surface, and, gradually becoming narrowed into a flattened tendon, is inserted into the base of the patella.
Nerve supply
[edit]The neurons for voluntary thigh contraction originate near the summit of the medial side of the precentral gyrus (the primary motor area of the brain). These neurons send a nerve signal that is carried by the corticospinal tract down the brainstem and spinal cord. The signal starts with the upper motor neurons carrying the signal from the precentral gyrus down through the internal capsule, through the cerebral peduncle, and into the medulla. In the medullary pyramid, the corticospinal tract decussates and becomes the lateral corticospinal tract. The nerve signal will continue down the lateral corticospinal tract until it reaches spinal nerve L4. At this point, the nerve signal will synapse from the upper motor neurons to the lower motor neurons. The signal will travel through the anterior root of L4 and into the anterior rami of the L4 nerve, leaving the spinal cord through the lumbar plexus. The posterior division of the L4 root is the femoral nerve. The femoral nerve innervates the quadriceps femoris, a fourth of which is the rectus femoris. When the rectus femoris receives the signal that has traveled all the way from the medial side of the precentral gyrus, it contracts, extending the knee and flexing the thigh at the hip.[2]
Function
[edit]The rectus femoris, sartorius, and iliopsoas are the flexors of the thigh at the hip. The rectus femoris is a weaker hip flexor when the knee is extended because it is already shortened and thus suffers from active insufficiency; the action will recruit more iliacus, psoas major, tensor fasciae latae, and the remaining hip flexors than it will the rectus femoris.
Similarly, the rectus femoris is not dominant in knee extension when the hip is flexed since it is already shortened and thus suffers from active insufficiency. In essence: the action of extending the knee from a seated position is primarily driven by the vastus lateralis, vastus medialis, and vastus intermedius, and less by the rectus femoris.
In the other extreme, the muscle's ability to flex the hip and extend the knee can be compromised in a position of full hip extension and knee flexion, due to passive insufficiency.
The rectus femoris is a direct antagonist to the hamstrings, at the hip and at the knee.
Clinical significance
[edit]Strain
[edit]Rectus femoris strain, referred to as hip flexor strain,[3] is an injury commonly at the tendon that attaches to the patella or in the muscle itself. The injury is usually a partial tear, but could be a full tear. The injury is caused by a forceful movement related to sprinting, jumping, or kicking and is common in sports like football or soccer. The rectus femoris is prone to injury, since it crosses both the knee and the hip. Symptoms include a sudden sharp pain at the front of the hip or in the groin, swelling and bruising, and an inability to contract the rectus femoris with a full tear.[4]
Avulsion fracture
[edit]The Rectus femoris tendon can cause a fragment of anterior inferior ilac spine of the hip (AIIS) to avulse in what is known as an Avulsion fracture. This is due to forceful contraction of the muscle that generates a force greater than that which holds the bone together. This is a well recognized, but unusual sports injury that can affect young athletes.[5]
References
[edit]![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 470 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 470 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ^ Elizabeth Quinn. "Function of the Rectus Femoris Muscle". Verywell Fit. Retrieved 2022-07-23.
- ^ Anatomy and Physiology: The Unity of Form and Function, Saladin, 5th ed.
- ^ Geier, David (2011-01-18) Rectus Femoris Strain (“Hip Flexor Strain”) | Dr. David Geier – Sports Medicine Simplified. drdavidgeier.com.
- ^ A Rare Form of Soccer Injury – Rectus Femoris Tendon Rupture – Orthopaedic Information | Singapore. Orthopaedic.com.sg. Retrieved on 2015-09-30.
- ^ Esser, Stephan; Jantz, David; Hurdle, Mark F.; Taylor, Walter (July 2015). "Proximal Rectus Femoris Avulsion: Ultrasonic Diagnosis and Nonoperative Management". Journal of Athletic Training. 50 (7): 778–780. doi:10.4085/1052-6050-50.2.13. ISSN 1062-6050. PMC 4532190. PMID 25978099.
