List of countries without rivers: Difference between revisions
Appearance
Content deleted Content added
→External links: fix ref |
LucasBrown (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| (20 intermediate revisions by 12 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|none}} <!-- "none" is preferred when the title is sufficiently descriptive; see [[WP:SDNONE]] --> |
|||
{{Short description|Wikimedia list article}} |
|||
[[File:Map of countries without rivers.png|thumb|529x529px|Map of countries without rivers]] |
|||
There are currently |
There are currently 20 countries and 22 territories that do not have a permanent natural [[river]] flowing within them, though some of them have [[stream]]s or seasonal watercourses such as [[wadi]]s.<ref>[https://www.graphicmaps.com/countries-with-no-rivers Which Countries Don't Have Rivers?]</ref> |
||
The [[Arabian Peninsula]] is the largest [[subregion]] in the world without any permanent natural river. Countries in this subregion have wadis instead. |
The [[Arabian Peninsula]] is the largest [[subregion]] in the world without any permanent natural river. Countries in this subregion have wadis instead. |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
==Sovereign states== |
==Sovereign states== |
||
===Africa=== |
===Africa=== |
||
*{{Flag|Comoros}}<ref>{{citation |title=[[Aquastat]] |chapter=Comoros |chapter-url=http://www.fao.org/nr/water/aquastat/data/wbsheets/aquastat_water_balance_sheet_com_en.pdf |publisher=[[Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations]] |date=April 10, 2012 |access-date=April 24, 2012}}.</ref> |
|||
*{{Flag|Djibouti}} (See [[List of wadis of Djibouti]]) |
*{{Flag|Djibouti}} (See [[List of wadis of Djibouti]]) |
||
*{{Flag|Libya}} (See [[List of wadis of Libya]]) |
*{{Flag|Libya}} (See [[List of wadis of Libya]]) |
||
| ⚫ | |||
*{{Flag|Bahamas}} |
|||
===Asia=== |
===Asia=== |
||
| Line 39: | Line 35: | ||
==Dependencies and other territories== |
==Dependencies and other territories== |
||
=== |
===Asia=== |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
===North America=== |
|||
*{{Flag|Anguilla}}<ref>{{citation |title=The Commonwealth Yearbook 2006 |first=Richard |last=Green |author2=[[Commonwealth Secretariat]] |publisher=Nexus Strategic Partnerships Ltd. |year=2006 |isbn=978-0-9549629-4-4 |page=404}}.</ref> |
*{{Flag|Anguilla}}<ref>{{citation |title=The Commonwealth Yearbook 2006 |first=Richard |last=Green |author2=[[Commonwealth Secretariat]] |publisher=Nexus Strategic Partnerships Ltd. |year=2006 |isbn=978-0-9549629-4-4 |page=404}}.</ref> |
||
*{{Flag|Aruba}} |
*{{Flag|Aruba}} |
||
| Line 48: | Line 51: | ||
*{{Flag|Saba}} |
*{{Flag|Saba}} |
||
*{{Flag|Saint Barthélemy|local}} |
*{{Flag|Saint Barthélemy|local}} |
||
*{{Flagicon image|Local flag of the Collectivity of Saint Martin.svg}} [[Collectivity of Saint Martin|Saint Martin]] |
|||
*{{Flag|Saint Martin}} |
|||
*{{Flag|Sint Eustatius}} |
*{{Flag|Sint Eustatius}} |
||
*{{Flag|Sint Maarten}} |
*{{Flag|Sint Maarten}} |
||
| ⚫ | |||
===Asia=== |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
===Europe=== |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
===Oceania=== |
===Oceania=== |
||
| Line 67: | Line 64: | ||
*{{Flag|Pitcairn Islands}}<ref>{{citation |title=Pub. 120 Sailing Directions (Planning Guide) Pacific Ocean and Southeast Ocean |author=[[National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency]] |edition=4 |publisher=ProStar Publications |year=2006 |isbn=1-57785-663-5 |page=307}}.</ref> |
*{{Flag|Pitcairn Islands}}<ref>{{citation |title=Pub. 120 Sailing Directions (Planning Guide) Pacific Ocean and Southeast Ocean |author=[[National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency]] |edition=4 |publisher=ProStar Publications |year=2006 |isbn=1-57785-663-5 |page=307}}.</ref> |
||
*{{Flag|Tokelau}} |
*{{Flag|Tokelau}} |
||
| ⚫ | |||
== See also == |
== See also == |
||
| Line 76: | Line 72: | ||
==External links== |
==External links== |
||
*{{ |
* {{Cite web|url=https://geonames.nga.mil/namesgaz/|title=GEONet Names Server|website=[[National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency]]|access-date=June 25, 2021}}, [[GEOnet Names Server]] |
||
{{Rivers, streams and springs|state=collapsed}} |
{{Rivers, streams and springs|state=collapsed}} |
||
Latest revision as of 19:32, 12 June 2024
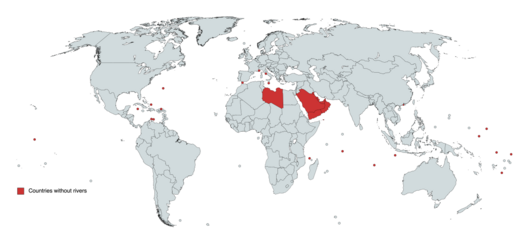
There are currently 20 countries and 22 territories that do not have a permanent natural river flowing within them, though some of them have streams or seasonal watercourses such as wadis.[1]
The Arabian Peninsula is the largest subregion in the world without any permanent natural river. Countries in this subregion have wadis instead.
The Chinese special administrative region of Macau has no permanent natural rivers other than a small man-made canal named Canal Dos Patos (鴨涌河). Due to environment issues, this small canal is currently being backfilled with land by the local government. Eventually, this small canal will cease to exist.[2]
Sovereign states
[edit]Africa
[edit] Djibouti (See List of wadis of Djibouti)
Djibouti (See List of wadis of Djibouti) Libya (See List of wadis of Libya)
Libya (See List of wadis of Libya)
Asia
[edit] Bahrain[3]
Bahrain[3] Kuwait (See List of wadis of Kuwait)
Kuwait (See List of wadis of Kuwait) Maldives[4]
Maldives[4] Oman (See List of wadis of Oman)
Oman (See List of wadis of Oman) Qatar (See List of wadis of Qatar)
Qatar (See List of wadis of Qatar) Saudi Arabia[5] (See List of wadis of Saudi Arabia)
Saudi Arabia[5] (See List of wadis of Saudi Arabia) United Arab Emirates (See List of wadis of the United Arab Emirates)
United Arab Emirates (See List of wadis of the United Arab Emirates) Yemen (See List of wadis of Yemen)
Yemen (See List of wadis of Yemen)
Europe
[edit]Oceania
[edit]Dependencies and other territories
[edit]Asia
[edit]Europe
[edit]North America
[edit] Anguilla[12]
Anguilla[12] Aruba
Aruba Bermuda[13]
Bermuda[13] Bonaire
Bonaire Cayman Islands[14]
Cayman Islands[14] Curaçao
Curaçao Saba
Saba Saint Barthélemy
Saint Barthélemy Saint Martin
Saint Martin Sint Eustatius
Sint Eustatius Sint Maarten
Sint Maarten Turks and Caicos Islands
Turks and Caicos Islands
Oceania
[edit] Christmas Island
Christmas Island Cocos (Keeling) Islands
Cocos (Keeling) Islands Easter Island
Easter Island Niue
Niue Norfolk Island
Norfolk Island Pitcairn Islands[15]
Pitcairn Islands[15] Tokelau
Tokelau
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Which Countries Don't Have Rivers?
- ^ a b 臭水鴨涌河掃進歷史垃圾箱 – 青茂口岸 帶動景觀交通大變革 (in Chinese)
- ^ Creative Media Applications, Inc. (2004), The Middle East: Bahrain, Cyprus, Egypt, vol. 1, Greenwood Press, p. 7, ISBN 0-313-32923-0.
- ^ Weightman, Barbara A. (2011), Dragons and Tigers: A Geography of South, East, and Southeast Asia (3 ed.), John Wiley & Sons, p. 266, ISBN 978-0-470-87628-2.
- ^ Oxford Business Group (2007), The Report: Emerging Saudi Arabia 2007, Oxford Business Group, p. 114, ISBN 978-1-902339-66-5
{{citation}}:|author=has generic name (help) ("The Kingdom has no rivers, lakes or any permanent body of standing water..."). - ^ Lal, Brij V.; Fortune, Kate (2000), The Pacific Islands: An Encyclopedia, vol. 1, University of Hawaii Press, p. 582, ISBN 978-0-8248-2265-1.
- ^ Ridgell, Reilly (1995), Pacific Nations and Territories: the Islands of Micronesia, Melanesia, and Polynesia (3 ed.), Bess Press, p. 79, ISBN 1-57306-006-2.
- ^ Ridgell 1995, p. 92.
- ^ Encyclopædia Britannica – Tonga
- ^ "Tuvalu", The World Factbook, Central Intelligence Agency, May 26, 2011, retrieved June 27, 2011.
- ^ Green & Commonwealth Secretariat 2006, p. 414.
- ^ Green, Richard; Commonwealth Secretariat (2006), The Commonwealth Yearbook 2006, Nexus Strategic Partnerships Ltd., p. 404, ISBN 978-0-9549629-4-4.
- ^ Green & Commonwealth Secretariat 2006, p. 405.
- ^ "Water Suppliers in the Cayman Islands – Water Authority Cayman". waterauthority.ky. Retrieved 13 April 2018.
- ^ National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency (2006), Pub. 120 Sailing Directions (Planning Guide) Pacific Ocean and Southeast Ocean (4 ed.), ProStar Publications, p. 307, ISBN 1-57785-663-5.
External links
[edit]- "GEONet Names Server". National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency. Retrieved June 25, 2021., GEOnet Names Server
