Tobelo language: Difference between revisions
template |
No edit summary Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
||
| (42 intermediate revisions by 28 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ |
{{Short description|North Halmahera language spoken in Indonesia}} |
||
{{For|the town in North Halmahera, Indonesia|Tobelo}} |
|||
{{Infobox language |
{{Infobox language |
||
|name=Tobelo |
|name=Tobelo |
||
| Line 8: | Line 9: | ||
|ref=e18 |
|ref=e18 |
||
|familycolor=Papuan |
|familycolor=Papuan |
||
|fam1=[[West Papuan languages|West Papuan]] |
|fam1=[[West Papuan languages|West Papuan]]? |
||
|fam2=[[Halmahera languages|Halmahera]] |
|fam2=[[North Halmahera languages|North Halmahera]] |
||
|fam3= |
|fam3=Northern |
||
|fam4=Mainland |
|||
|fam5=Tobelo–Tugutil |
|||
|lc1=tlb|ld1=Tobelo |
|lc1=tlb|ld1=Tobelo |
||
|lc2=tuj|ld2=Tugutil |
|lc2=tuj|ld2=Tugutil |
||
| Line 16: | Line 19: | ||
|glottorefname=Tobelo–Tugutil |
|glottorefname=Tobelo–Tugutil |
||
|map=halmahera tobelo.png |
|map=halmahera tobelo.png |
||
|mapscale=1.25 |
|||
|mapsize=frameless |
|||
|mapcaption=The Tobelo–Tugutil speaking region (grey) on Halmahera |
|||
|mapalt= |
|||
|mapcaption=The Tobelo speaking region (grey) on Halmahera |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
'''Tobelo''' ( |
'''Tobelo''' ({{lang-id|bahasa Tobelo}}) is a [[North Halmahera languages|North Halmahera language]] spoken on the eastern Indonesian island of [[Halmahera]] and on parts of several neighboring islands. The Tobelo-speaking heartland is in the six administrative districts ({{lang-id|kecamatan}}) of Tobelo, located on the western shore of [[Kao Bay]] and forming the central part of [[Halmahera Utara Regency]]. Other Tobelo speaking areas are the five districts of Wasile (the northwestern half of [[East Halmahera Regency]]; where they are actually speakers of the [[Tugutil language]] which is very related to Tobelo) on the south and east coast of Kao Bay, and the northern half of [[Morotai Island]]. The district capital, also known as [[Tobelo]], serves as a regional commercial and administrative center and is the largest settlement on Halmahera. |
||
<!-- Deleted image removed: [[File:tobleomarahai.jpg|frame|This sign posted in Tobelo village in 1995 combines Tobelo language (''marahai'') with Indonesian]] --> |
<!-- Deleted image removed: [[File:tobleomarahai.jpg|frame|This sign posted in Tobelo village in 1995 combines Tobelo language (''marahai'') with Indonesian]] --> |
||
| Line 35: | Line 36: | ||
*Popon |
*Popon |
||
The |
The last three dialects are also known as ''Tugutil''. The [[Tugutil language|Tugutil]] varieties may include additional dialectal variants, but this has not been satisfactorily documented (Voorhoeve 1988). Intelligibility is not great (Ethnologue). |
||
In addition, based on cognition percentages in a basic vocabulary list, Voorhoeve 1988 identifies five other North Halmaheran language varieties as dialects of the putative Northeast Halmaheran language. Together with Tobelo, these varieties are [[Galela language|Galela]], [[Loloda language|Loloda]], [[Modole language|Modole]], [[Pagu language|Pagu]] and [[Tabaru language|Tabaru]]. Most speakers consider these to be distinct languages from Tobelo, although they do acknowledge a certain degree of mutual intelligibility. |
In addition, based on cognition percentages in a basic vocabulary list, Voorhoeve 1988 identifies five other North Halmaheran language varieties as dialects of the putative Northeast Halmaheran language. Together with Tobelo, these varieties are [[Galela language|Galela]], [[Loloda language|Loloda]], [[Modole language|Modole]], [[Pagu language|Pagu]], and [[Tabaru language|Tabaru]]. Most speakers consider these to be distinct languages from Tobelo, although they do acknowledge a certain degree of mutual intelligibility. |
||
==Phonology== |
|||
=== Consonants === |
|||
{| class="wikitable" style="text-align:center;" |
|||
|- |
|||
! colspan="2" | |
|||
![[Bilabial consonant|Bilabial]] |
|||
![[Alveolar consonant|Alveolar]] |
|||
![[Palatal consonant|Palatal]] |
|||
![[Velar consonant|Velar]] |
|||
![[Glottal consonant|Glottal]] |
|||
|- |
|||
! colspan="2" | [[Nasal consonant|Nasal]] |
|||
| {{IPAlink|m}} |
|||
| {{IPAlink|n}} |
|||
| {{IPAlink|ɲ}} |
|||
| {{IPAlink|ŋ}} |
|||
| |
|||
|- |
|||
! rowspan="2" | [[Plosive]]/<br />[[Affricate]] |
|||
! {{small|voiceless}} |
|||
| {{IPAlink|p}} |
|||
| {{IPAlink|t}} |
|||
| ({{IPAlink|tʃ}}) |
|||
| {{IPAlink|k}} |
|||
| |
|||
|- |
|||
! {{small|voiced}} |
|||
| {{IPAlink|b}} |
|||
| {{IPAlink|d}} |
|||
| {{IPAlink|dʒ}} |
|||
| {{IPAlink|ɡ}} |
|||
| |
|||
|- |
|||
! colspan="2" | [[Fricative]] |
|||
| ({{IPAlink|f}}) |
|||
| |
|||
| {{IPAlink|ɕ}} |
|||
| |
|||
| {{IPAlink|h}} |
|||
|- |
|||
! rowspan="2" | [[Liquid consonant|Liquid]] |
|||
! {{small|[[Lateral consonant|lateral]]}} |
|||
| |
|||
| {{IPAlink|l}} |
|||
| {{IPAlink|ʎ}} |
|||
| |
|||
| |
|||
|- |
|||
! {{small|[[Rhotic consonant|rhotic]]}} |
|||
| |
|||
| {{IPAlink|r}} |
|||
| |
|||
| |
|||
| |
|||
|- |
|||
! colspan="2" | [[Semivowel]] |
|||
| {{IPAlink|w}} |
|||
| |
|||
| ({{IPAlink|j}}) |
|||
| |
|||
| |
|||
|} |
|||
Consonant sounds in parentheses only occur in loan words or in other Tobelo dialects. |
|||
=== Vowels === |
|||
====Tobelo==== |
|||
{| class="wikitable" style="text-align:center;" |
|||
! |
|||
![[Front vowel|Front]] |
|||
![[Central vowel|Central]] |
|||
![[Back vowel|Back]] |
|||
|- |
|||
![[Close vowel|Close]] |
|||
|{{IPAlink|i}} |
|||
| |
|||
|{{IPAlink|u}} |
|||
|- |
|||
![[Mid vowel|Mid]] |
|||
|{{IPAlink|e}}~{{IPAlink|ɛ}} |
|||
| |
|||
|{{IPAlink|o}} |
|||
|- |
|||
![[Open vowel|Open]] |
|||
| |
|||
|{{IPAlink|a}} |
|||
| |
|||
|} |
|||
Mid front vowels can range from /e/ to /ɛ/.<ref>{{Cite book|title=Tobelo|last=Holton|first=Gary|year=2003}}</ref> |
|||
====Togutil<ref name="o860">{{cite journal | last=Taha | first=Mujahid | title=Vokal Bahasa Togutil | journal=Gramatika: Jurnal Ilmiah Kebahasaan dan Kesastraan | publisher=Kantor Bahasa Maluku Utara | volume=4 | issue=1 | date=2016-06-01 | issn=2599-3283 | doi=10.31813/gramatika/4.1.2016.49.59--64 | pages=59–64 | doi-access=free | language = id }}</ref>==== |
|||
{| class="wikitable" style="text-align:center;" |
|||
! |
|||
![[Front vowel|Front]] |
|||
![[Central vowel|Central]] |
|||
![[Back vowel|Back]] |
|||
|- |
|||
![[Close vowel|Close]] |
|||
|{{IPAlink|i}} |
|||
| |
|||
|{{IPAlink|u}} |
|||
|- |
|||
![[Close-mid vowel|Close-mid]] |
|||
|{{IPAlink|e}} |
|||
| |
|||
|{{IPAlink|o}} |
|||
|- |
|||
![[Open-mid vowel|Low-mid]] |
|||
|{{IPAlink|ɛ}} |
|||
| |
|||
|{{IPAlink|ɔ}} |
|||
|- |
|||
![[Near-open vowel|Near-open]] |
|||
|{{IPAlink|æ}} |
|||
| |
|||
| |
|||
|- |
|||
![[Open vowel|Open]] |
|||
| |
|||
|{{IPAlink|a}} |
|||
| |
|||
|} |
|||
==Directionals== |
==Directionals== |
||
Most all of the 50 languages of Maluku have some sort of directional system. At the least the up/down distinction seems to be an areal feature. But this brings up the chicken and the egg phenomenon. |
Most all of the 50 languages of Maluku have some sort of [[Directionality (grammar)|directional system]]. At the least the up/down distinction seems to be an [[areal feature]]. But this brings up the chicken and the egg phenomenon. |
||
Is this directional system of AN or NAN origin? Or is it a mixture? |
Is this directional system of AN or NAN origin? Or is it a mixture? |
||
| Line 46: | Line 170: | ||
because Malay as spoken in Western Indonesia does not use these directionals whereas Moluccan Malay uses direct calques of the Tobelo terms: |
because Malay as spoken in Western Indonesia does not use these directionals whereas Moluccan Malay uses direct calques of the Tobelo terms: |
||
''bawah'', ''atas'', ''darat'', ''laut''. |
:''bawah'', ''atas'', ''darat'', ''laut''. |
||
Tobelo directionals are described in Taylor (1984). |
Tobelo directionals are described in Taylor (1984). |
||
| Line 55: | Line 179: | ||
Thus, interpretation of directional adverbs is entirely context-dependent. For example, |
Thus, interpretation of directional adverbs is entirely context-dependent. For example, |
||
{| class="toccolours" |
|||
{{interlinear|indent=3|glossing=no abbr |
|||
|<poem> |
|||
| o tau t-oiki |
|||
| NM house 1AGT-go |
|||
| 'I'm going to the house'}} |
|||
</poem> |
|||
|} |
|||
If I meet you landwards of the house, this means that I'm headed inland from my house. |
If I meet you landwards of the house, this means that I'm headed inland from my house. |
||
If I meet you seawards of the house, then it means I'm headed inland to the house. |
If I meet you seawards of the house, then it means I'm headed inland to the house. |
||
| Line 86: | Line 209: | ||
|} |
|} |
||
[[File:Tobelo directionals.gif]] |
[[File:Tobelo directionals.gif|thumb|Directionals in Tobelo, including village names near the Gogaili river]] |
||
==References== |
==References== |
||
{{Reflist}} |
{{Reflist}} |
||
== External links == |
|||
* [https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.tobelo.maluku.alkitab&hl=de Tobelo Bible App] |
|||
==Further reading== |
==Further reading== |
||
*Holton, Gary. 2003. Tobelo. (Languages of the World/Materials 328). Munich: LINCOM Europa. ISBN |
*Holton, Gary. 2003. Tobelo. (Languages of the World/Materials 328). Munich: LINCOM Europa. {{ISBN|3-89586-706-3}} |
||
*Hueting, Anton. 1908. Tobeloreesch-Hollandsch woordenboek met Hollandsch-Tobeloreesch inhoudsopgave. 's-Gravenhage: Nijhoff. |
*Hueting, Anton. 1908. Tobeloreesch-Hollandsch woordenboek met Hollandsch-Tobeloreesch inhoudsopgave. 's-Gravenhage: Nijhoff. |
||
*Hueting, Anton. 1908. O Tobelohoka manga totoade: verhalen en vertellingen in de Tobeloreesche taal. Bijdragen tot de Taal, Land en Volkenkunde 61.1-318. |
*Hueting, Anton. 1908. O Tobelohoka manga totoade: verhalen en vertellingen in de Tobeloreesche taal. Bijdragen tot de Taal-, Land- en Volkenkunde van Nederlandsch-Indië 61.1-318. {{doi|10.1163/22134379-90001891|doi-access=free}} {{JSTOR|20769537}} |
||
*Hueting, Anton. 1936. Iets over de spaakkunst van de Tobeloreesche taal. Bijdragen tot de Taal, Land en Volkenkunde 94.295-407. |
*Hueting, Anton. 1936. Iets over de spaakkunst van de Tobeloreesche taal. Bijdragen tot de Taal-, Land- en Volkenkunde van Nederlandsch-Indië 94.295-407. {{doi|10.1163/22134379-90001374|doi-access=free}} {{JSTOR|20770352}} |
||
*Taylor, Paul Michael. 1984. Tobelorese deixis. Anthropological Linguistics 26.102-22. |
*Taylor, Paul Michael. 1984. Tobelorese deixis. Anthropological Linguistics 26.102-22. |
||
*{{cite journal |title=The Folk Biology of the Tobelo People: A Study in Folk Classification |last=Taylor |first=Paul Michael |journal=Smithsonian Contributions to Anthropology |publisher=Smithsonian Institution Press |location=Washington, D.C. |date=1990 |issue=34 |pages=1–187 |url=https://repository.si.edu/handle/10088/1341 |doi=10.5479/si.00810223.34.1}} |
|||
*Voorhoeve, C. L. 1988. The languages of the northern Halmaheran stock. Papers in New Guinea Linguistics, no. 26., 181-209. (Pacific Linguistics A-76). Canberra: Australian National University. |
*Voorhoeve, C. L. 1988. The languages of the northern Halmaheran stock. Papers in New Guinea Linguistics, no. 26., 181-209. (Pacific Linguistics A-76). Canberra: Australian National University. |
||
{{West Papuan languages}} |
{{West Papuan languages}} |
||
{{Languages of Indonesia}} |
{{Languages of Indonesia}} |
||
{{Authority control}} |
|||
[[Category:Languages of Indonesia]] |
[[Category:Languages of Indonesia]] |
||
[[Category: |
[[Category:North Halmahera languages]] |
||
Latest revision as of 19:40, 11 July 2024
| Tobelo | |
|---|---|
| Native to | Indonesien |
| Region | North Halmahera |
Native speakers | 30,000 (2000)[1] |
West Papuan?
| |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | Either:tlb – Tobelotuj – Tugutil |
| Glottolog | tobe1251 |
| ELP | Tobelo |
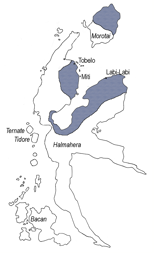 The Tobelo–Tugutil speaking region (grey) on Halmahera | |
Tobelo (Indonesian: bahasa Tobelo) is a North Halmahera language spoken on the eastern Indonesian island of Halmahera and on parts of several neighboring islands. The Tobelo-speaking heartland is in the six administrative districts (Indonesian: kecamatan) of Tobelo, located on the western shore of Kao Bay and forming the central part of Halmahera Utara Regency. Other Tobelo speaking areas are the five districts of Wasile (the northwestern half of East Halmahera Regency; where they are actually speakers of the Tugutil language which is very related to Tobelo) on the south and east coast of Kao Bay, and the northern half of Morotai Island. The district capital, also known as Tobelo, serves as a regional commercial and administrative center and is the largest settlement on Halmahera.
Dialects
[edit]Six principal dialects are generally recognized (Voorhoeve 1988):
- Heleworuru
- Boeng
- Dodinga
- Lake Paca
- Kukumutuk
- Popon
The last three dialects are also known as Tugutil. The Tugutil varieties may include additional dialectal variants, but this has not been satisfactorily documented (Voorhoeve 1988). Intelligibility is not great (Ethnologue).
In addition, based on cognition percentages in a basic vocabulary list, Voorhoeve 1988 identifies five other North Halmaheran language varieties as dialects of the putative Northeast Halmaheran language. Together with Tobelo, these varieties are Galela, Loloda, Modole, Pagu, and Tabaru. Most speakers consider these to be distinct languages from Tobelo, although they do acknowledge a certain degree of mutual intelligibility.
Phonology
[edit]Consonants
[edit]| Bilabial | Alveolar | Palatal | Velar | Glottal | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal | m | n | ɲ | ŋ | ||
| Plosive/ Affricate |
voiceless | p | t | (tʃ) | k | |
| voiced | b | d | dʒ | ɡ | ||
| Fricative | (f) | ɕ | h | |||
| Liquid | lateral | l | ʎ | |||
| rhotic | r | |||||
| Semivowel | w | (j) | ||||
Consonant sounds in parentheses only occur in loan words or in other Tobelo dialects.
Vowels
[edit]Tobelo
[edit]| Front | Central | Zurück | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Schließen Sie | i | u | |
| Mid | e~ɛ | o | |
| Öffnen Sie | a |
Mid front vowels can range from /e/ to /ɛ/.[2]
| Front | Central | Zurück | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Schließen Sie | i | u | |
| Close-mid | e | o | |
| Low-mid | ɛ | ɔ | |
| Near-open | æ | ||
| Öffnen Sie | a |
Directionals
[edit]Most all of the 50 languages of Maluku have some sort of directional system. At the least the up/down distinction seems to be an areal feature. But this brings up the chicken and the egg phenomenon. Is this directional system of AN or NAN origin? Or is it a mixture?
Perhaps it is not a coincidence that the Tobelo are the most widespread ethnic group in Maluku, with sizable emigrant population throughout the province. We can a least be sure that the Malay directionals are the "egg", because Malay as spoken in Western Indonesia does not use these directionals whereas Moluccan Malay uses direct calques of the Tobelo terms:
- bawah, atas, darat, laut.
Tobelo directionals are described in Taylor (1984). Tobelo directional adverbs occur:
- on motion verbs to specify direction of motion
- on nouns to specify motion away from or toward an object
Thus, interpretation of directional adverbs is entirely context-dependent. For example,
o
NM
tau
house
t-oiki
1AGT-go
'I'm going to the house'
If I meet you landwards of the house, this means that I'm headed inland from my house. If I meet you seawards of the house, then it means I'm headed inland to the house.
| Deictic | Adverb | |
|---|---|---|
| land | dina | -iha |
| sea | dai | -oko |
| up | daku | -ilye |
| down | dau | -uku |
| over | doka | -ika |

References
[edit]- ^ Tobelo at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
Tugutil at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required) - ^ Holton, Gary (2003). Tobelo.
- ^ Taha, Mujahid (2016-06-01). "Vokal Bahasa Togutil". Gramatika: Jurnal Ilmiah Kebahasaan dan Kesastraan (in Indonesian). 4 (1). Kantor Bahasa Maluku Utara: 59–64. doi:10.31813/gramatika/4.1.2016.49.59--64. ISSN 2599-3283.
External links
[edit]Further reading
[edit]- Holton, Gary. 2003. Tobelo. (Languages of the World/Materials 328). Munich: LINCOM Europa. ISBN 3-89586-706-3
- Hueting, Anton. 1908. Tobeloreesch-Hollandsch woordenboek met Hollandsch-Tobeloreesch inhoudsopgave. 's-Gravenhage: Nijhoff.
- Hueting, Anton. 1908. O Tobelohoka manga totoade: verhalen en vertellingen in de Tobeloreesche taal. Bijdragen tot de Taal-, Land- en Volkenkunde van Nederlandsch-Indië 61.1-318. doi:10.1163/22134379-90001891 JSTOR 20769537
- Hueting, Anton. 1936. Iets over de spaakkunst van de Tobeloreesche taal. Bijdragen tot de Taal-, Land- en Volkenkunde van Nederlandsch-Indië 94.295-407. doi:10.1163/22134379-90001374 JSTOR 20770352
- Taylor, Paul Michael. 1984. Tobelorese deixis. Anthropological Linguistics 26.102-22.
- Taylor, Paul Michael (1990). "The Folk Biology of the Tobelo People: A Study in Folk Classification". Smithsonian Contributions to Anthropology (34). Washington, D.C.: Smithsonian Institution Press: 1–187. doi:10.5479/si.00810223.34.1.
- Voorhoeve, C. L. 1988. The languages of the northern Halmaheran stock. Papers in New Guinea Linguistics, no. 26., 181-209. (Pacific Linguistics A-76). Canberra: Australian National University.
