Cefoperazone: Difference between revisions
m oops |
→Mechanism of action: Removing unsourced content |
||
| (95 intermediate revisions by 66 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{short description|Antibiotic}} |
|||
{{drugbox |
|||
{{Drugbox |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| Watchedfields = changed |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| verifiedrevid = 443509478 |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| image2 = Cefoperazone ball-and-stick.png |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
<!--Clinical data--> |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| |
| tradename = |
||
| Drugs.com = {{drugs.com|CONS|cefoperazone}} |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| MedlinePlus = a601206 |
|||
| molecular_weight = 645.67 g/mol |
|||
| pregnancy_AU = <!-- A / B1 / B2 / B3 / C / D / X --> |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| |
| pregnancy_category = |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| |
| legal_UK = <!-- GSL / P / POM / CD / Class A, B, C --> |
||
| |
| legal_US = <!-- OTC / Rx-only / Schedule I, II, III, IV, V --> |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| pregnancy_category= |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| legal_US = <!-- OTC / Rx-only / Schedule I, II, III, IV, V --> |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| routes_of_administration = |
| routes_of_administration = |
||
<!--Pharmacokinetic data--> |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| metabolism = |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
<!--Identifiers--> |
|||
| CAS_number_Ref = {{cascite|correct|??}} |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| DrugBank_Ref = {{drugbankcite|correct|drugbank}} |
|||
| DrugBank = DB01329 |
|||
| ChemSpiderID_Ref = {{chemspidercite|correct|chemspider}} |
|||
| ChemSpiderID = 40206 |
|||
| UNII_Ref = {{fdacite|correct|FDA}} |
|||
| UNII = 7U75I1278D |
|||
| KEGG_Ref = {{keggcite|correct|kegg}} |
|||
| KEGG = D07645 |
|||
| ChEMBL_Ref = {{ebicite|correct|EBI}} |
|||
| ChEMBL = 507674 |
|||
<!--Chemical data--> |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| smiles = O=C2N1/C(=C(\CS[C@@H]1[C@@H]2NC(=O)[C@@H](c3ccc(O)cc3)NC(=O)N4C(=O)C(=O)N(CC)CC4)CSc5nnnn5C)C(=O)O |
|||
| StdInChI_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} |
|||
| StdInChI = 1S/C25H27N9O8S2/c1-3-32-8-9-33(21(39)20(32)38)24(42)27-15(12-4-6-14(35)7-5-12)18(36)26-16-19(37)34-17(23(40)41)13(10-43-22(16)34)11-44-25-28-29-30-31(25)2/h4-7,15-16,22,35H,3,8-11H2,1-2H3,(H,26,36)(H,27,42)(H,40,41)/t15-,16-,22-/m1/s1 |
|||
| StdInChIKey_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} |
|||
| StdInChIKey = GCFBRXLSHGKWDP-XCGNWRKASA-N |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
<!-- Definition and medical uses --> |
|||
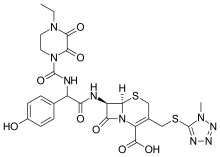
'''Cefoperazone''' is a third generation [[cephalosporin]] [[antibiotic]]. |
|||
'''Cefoperazone''' is a third-generation [[cephalosporin]] [[antibiotic]], marketed by [[Pfizer]] under the name '''Cefobid'''. It is one of few cephalosporin antibiotics effective in treating ''[[Pseudomonas]]'' bacterial infections which are otherwise resistant to these antibiotics. |
|||
<!-- Society and culture --> |
|||
''Cefina-SB'' is a combination of [[sulbactam]] and cefoperazone. Cefoperazone exerts its bactericidal effect by inhibiting the [[bacterial]] [[cell wall]] synthesis, and sulbactam acts as a beta-lactamase inhibitor, to increase the antibacterial activity of cefoperazone against beta-lactamase producing organisms. Cefina-SB is available as injection for the treatment of bacterial infections. |
|||
It was patented in 1974 and approved for medical use in 1981.<ref name=Fis2006>{{cite book | vauthors = Fischer J, Ganellin CR |title=Analogue-based Drug Discovery |date=2006 |publisher=John Wiley & Sons |isbn=9783527607495 |page=494 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=FjKfqkaKkAAC&pg=PA494 |language=en}}</ref> [[Cefoperazone/sulbactam]] (Sulperazon) is a co-formulation with [[sulbactam]]. |
|||
==Spectrum of bacterial susceptibility== |
|||
{{pharm-stub}} |
|||
Cefoperazone has a broad spectrum of activity and has been used to target bacteria responsible for causing infections of the respiratory and urinary tract, skin, and the female genital tract. The following represents MIC susceptibility data for a few medically significant microorganisms. |
|||
* ''Haemophilus influenzae'': 0.12 - 0.25 μg/ml |
|||
* ''Staphylococcus aureus'': 0.125 - 32 μg/ml |
|||
* ''Streptococcus pneumoniae'': ≤0.007 - 1 μg/ml<ref>{{cite web|url=http://antibiotics.toku-e.com/antimicrobial_462_1.html|title=Cefoperazone (Cefobid) - The Antimicrobial Index Knowledgebase - TOKU-E|website=antibiotics.toku-e.com}}</ref> |
|||
==Adverse effects== |
|||
Cefoperazone contains an ''N''-methylthiotetrazole (NMTT or 1-MTT) [[side chain]]. As the antibiotic is broken down in the body, it releases free NMTT, which can cause [[hypoprothrombinemia]] (likely due to [[enzyme inhibitor|inhibition]] of the [[enzyme]] [[vitamin K epoxide reductase]]) and a reaction with ethanol similar to that produced by [[disulfiram]] ([[Antabuse effect]]), due to inhibition of [[aldehyde dehydrogenase]].<ref name=Goldfrank>{{cite book | vauthors = Stork CM |veditors=Nelson LH, Flomenbaum N, Goldfrank LR, Hoffman RL, Howland MD, Lewin NA |title=Goldfrank's toxicologic emergencies |chapter=Antibiotics, antifungals, and antivirals |chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=cvJuLqBxGUcC&pg=PA847 |publisher=McGraw-Hill |location=New York |year=2006 |pages=847 |isbn=0-07-143763-0 |access-date=2009-07-03 }}</ref> |
|||
==Mechanism of action== |
|||
{{Empty section|date=August 2024}} |
|||
==References== |
|||
{{Reflist}} |
|||
{{CephalosporinAntiBiotics}} |
{{CephalosporinAntiBiotics}} |
||
[[Category:Acetaldehyde dehydrogenase inhibitors]] |
|||
[[Category:Cephalosporin antibiotics]] |
|||
[[Category:Tetrazoles]] |
|||
[[Category:Piperazines]] |
|||
[[Category:Phenols]] |
|||
[[Category:Acetamides]] |
|||
[[Category:Lactams]] |
|||
[[Category:Drugs developed by Pfizer]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 12:57, 10 August 2024
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information |
| MedlinePlus | a601206 |
| ATC code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Excretion | Hepatic |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.057.936 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C25H27N9O8S2 |
| Molar mass | 645.67 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Cefoperazone is a third-generation cephalosporin antibiotic, marketed by Pfizer under the name Cefobid. It is one of few cephalosporin antibiotics effective in treating Pseudomonas bacterial infections which are otherwise resistant to these antibiotics.
It was patented in 1974 and approved for medical use in 1981.[1] Cefoperazone/sulbactam (Sulperazon) is a co-formulation with sulbactam.
Spectrum of bacterial susceptibility
[edit]Cefoperazone has a broad spectrum of activity and has been used to target bacteria responsible for causing infections of the respiratory and urinary tract, skin, and the female genital tract. The following represents MIC susceptibility data for a few medically significant microorganisms.
- Haemophilus influenzae: 0.12 - 0.25 μg/ml
- Staphylococcus aureus: 0.125 - 32 μg/ml
- Streptococcus pneumoniae: ≤0.007 - 1 μg/ml[2]
Adverse effects
[edit]Cefoperazone contains an N-methylthiotetrazole (NMTT or 1-MTT) side chain. As the antibiotic is broken down in the body, it releases free NMTT, which can cause hypoprothrombinemia (likely due to inhibition of the enzyme vitamin K epoxide reductase) and a reaction with ethanol similar to that produced by disulfiram (Antabuse effect), due to inhibition of aldehyde dehydrogenase.[3]
Mechanism of action
[edit]This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (August 2024) |
References
[edit]- ^ Fischer J, Ganellin CR (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 494. ISBN 9783527607495.
- ^ "Cefoperazone (Cefobid) - The Antimicrobial Index Knowledgebase - TOKU-E". antibiotics.toku-e.com.
- ^ Stork CM (2006). "Antibiotics, antifungals, and antivirals". In Nelson LH, Flomenbaum N, Goldfrank LR, Hoffman RL, Howland MD, Lewin NA (eds.). Goldfrank's toxicologic emergencies. New York: McGraw-Hill. p. 847. ISBN 0-07-143763-0. Retrieved 2009-07-03.
