Gambia River: Difference between revisions
The Gambia River |
added wikidata map |
||
| (242 intermediate revisions by more than 100 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{short description|Major river in West Africa}} |
|||
'''The Gambia River''' is one of the smallest rivers in [[Africa]], running just 700 miles from the Fouta Djallon plateau in north Guinea to the Atlantic Ocean at the capital city, [[Banjul]]. It is navigable for about half that length. |
|||
{{Infobox river |
|||
| name = Gambia River |
|||
| name_native = |
|||
| name_native_lang = |
|||
| name_other = |
|||
| name_etymology = |
|||
<!---------------------- IMAGE & MAP --> |
|||
| image = River gambia Niokolokoba National Park.gif |
|||
| image_size = |
|||
| image_caption = Gambia River in the [[Niokolo-Koba National Park]] |
|||
| map = Gambiarivermap.png |
|||
| map_size = |
|||
| map_caption = Map of the Gambia River drainage basin |
|||
| pushpin_map = |
|||
| pushpin_map_size = |
|||
| pushpin_map_caption= |
|||
<!---------------------- LOCATION --> |
|||
| subdivision_type1 = Countries |
|||
| subdivision_name1 = {{hlist|[[Guinea]]|[[Senegal]]|[[The Gambia]]}} |
|||
| subdivision_type2 = |
|||
| subdivision_name2 = |
|||
| subdivision_type3 = |
|||
| subdivision_name3 = |
|||
| subdivision_type4 = |
|||
| subdivision_name4 = |
|||
| subdivision_type5 = |
|||
| subdivision_name5 = |
|||
<!---------------------- PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS --> |
|||
| length = {{convert|1120<ref>{{cite encyclopedia |title=Gambia River |encyclopedia=[[Encyclopædia Britannica]] |url=https://global.britannica.com/place/Gambia-River |access-date=30 October 2016}}</ref>|km|mi|abbr=on}} |
|||
| width_min = |
|||
| width_avg = |
|||
| width_max = |
|||
| depth_min = |
|||
| depth_avg = |
|||
| depth_max = |
|||
| discharge1_location= |
|||
| discharge1_min = |
|||
| discharge1_avg = |
|||
| discharge1_max = |
|||
<!---------------------- BASIN FEATURES --> |
|||
| source1 = [[Fouta Djallon]] |
|||
| source1_location = [[Labé Prefecture| Labé]], Guinea |
|||
| source1_coordinates= {{Coord|11.412|-12.226|format=dms|display=i}} |
|||
| source1_elevation = {{Convert|795|m|abbr=on}} |
|||
| mouth = [[Atlantic Ocean]] |
|||
| mouth_location = [[Banjul]], The Gambia |
|||
| mouth_coordinates = {{coord|13|28|N|16|34|W|display=inline,title}} |
|||
| mouth_elevation = {{Convert|0|m|abbr=on}} |
|||
| progression = |
|||
| river_system = |
|||
| basin_size = {{Convert|78000|km2|abbr=on}} |
|||
| tributaries_left = |
|||
| tributaries_right = |
|||
| custom_label = |
|||
| custom_data = |
|||
| extra = {{Infobox mapframe |wikidata=yes |zoom=5 |height=250 | stroke-width=1.5 |coord {{WikidataCoord|display=i}}}} |
|||
}} |
|||
The '''Gambia River''' (formerly known as the '''River Gambra''', [[French language|French]]: ''Fleuve Gambie'', [[Portuguese language|Portuguese]]: ''Rio Gâmbia'') is a major [[river]] in [[West Africa]], running {{convert|1120|km|mi}} from the [[Fouta Djallon]] plateau in north [[Guinea]] westward through [[Senegal]] and [[The Gambia]] to the [[Atlantic Ocean]] at the city of [[Banjul]]. It is [[navigability|navigable]] for about half that length. |
|||
The river is known largely because of [[Gambia]], the smallest country in Africa, which consists of little more than half the river and its two banks. |
|||
The river is strongly associated with The Gambia, the smallest country in mainland Africa, which occupies the downstream half of the river and its two banks. |
|||
==Geography== |
|||
The Gambia River runs a total length of {{convert|1120|km}}. From the Fouta Djallon, it runs northwest into the [[Tambacounda Region]] of Senegal, where it flows through the [[Parc National du Niokolo Koba]], then is joined by the [[Nieri Ko]] and {{ill|Koulountou|fr|Koulountou}} and passing through the [[Barrakunda Falls]] before entering the Gambia at Koina. At this point, the river runs generally west, but in a meandering course with a number of [[Oxbow lake|oxbows]], and about {{convert|100|km}} from its mouth it gradually widens, to over {{convert|10|km}} wide where it meets the sea. |
|||
===Crossings=== |
|||
There are several bridges crossing the river. The largest and furthest downriver is the [[Senegambia Bridge]] between the towns of [[Farafenni]] and [[Soma, Gambia|Soma]] in [[The Gambia]]. Opened in January 2019, it provides a link between the stretches of the [[Trans-Gambia Highway]] on the North and South Bank of the river. It also provides an expedited connection for Senegalese trucks traveling to and from [[Casamance]]. The bridge is {{convert|1.9 |km}} long and replaces a previously-unreliable vehicle ferry. A toll is levied on vehicle crossings. |
|||
There are also bridges in the [[Upper River Division|Upper River Region]] of The Gambia at [[Basse Santa Su]] and [[Fatoto]] that opened in October 2021,<ref>{{cite news |last1=Ma |first1=Jianchun |title=Building the Friendship Bridges towards a Shared Future of China and The Gambia |url=https://thepoint.gm/africa/gambia/opinion/commentary-building-the-friendship-bridges-towards-a-shared-future-of-china-and-the-gambia |access-date=3 August 2022 |agency=The Point |date=13 Oct 2021}}</ref> as well as a bridge in Senegal at Gouloumbou. |
|||
All other crossings are done by ferry, including a primary crossing between [[Banjul]] and [[Barra, Gambia|Barra]] at the mouth of the river, or by small boat. |
|||
===Bolongs=== |
|||
Small tributaries on the lower stretches of the river are commonly referred to as ''bolongs'' or ''bolons.'' These include Sami Bolong dividing the northern halves of the [[Central River Division]] and [[Upper River Division]], Bintang Bolong dividing the [[Lower River Division]] from the [[West Coast Division]], as well as smaller bodies of water such as the Sofancama, Jurunku, Kutang, Nianji, and Sandugu bolongs.<ref>Gailey.</ref> |
|||
==History== |
|||
The earliest known inhabitants of the area along the Gambia river include the [[Jola people|Jola]], the [[Balante]], the [[Bainuk]], and the [[Manjak people|Manjak]].<ref>Buhnen, 49.</ref> The [[Carthage|Carthaginian]] explorer [[Hanno the Navigator]] may have reached the Gambia during his expedition in the fifth century BC.<ref>"Kunta Kinteh Island and Related Sites". UNESCO World Heritage Centre. United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization. Accessed 14/8/22.</ref> |
|||
According to oral tradition, large numbers of [[Mandinka people|Mandinka]] immigrants from [[Mali]] led by [[Tiramakhan Traore]], one of [[Sundiata Keita|Sundiata]]'s top generals, came to the region in the 14th century. Some modern historians, however, posit that relatively few immigrants, primarily ''jula'' traders, instead led a gradual socio-cultural shift towards identification with the higher-status Mandinka ethnicity and the ruling [[Mali Empire]].<ref>Wright, "Beyond Migration", 385.</ref><ref>Buhnen, 51.</ref> These ''jula'' made the Gambia an important part of the wider West African trade network, where salt, shellfish, iron, cloth, ivory, beeswax, gold, slaves, leather and more were exchanged as far as the Niger River and beyond.<ref>Wright, "Darbo Jula", 33.</ref><ref>Van Hoven.</ref> |
|||
[[Alvise Cadamosto]], a [[Venice|Venetian]] explorer working for the [[Portugal|Portuguese]], became the first European to sail to the Gambia in 1455, referring to the river as the ''Gambra'' or ''Cambra''. Other sources from that period record names such as ''Guambea'', ''Guabu'', and ''Gambu'' (possibly a conflation, at the time or in later historiography, of the name of the river and the kingdom of [[Kaabu]]).<ref>Buhnen, 71.</ref> While merchants of various European countries traded on the Gambia river for two centuries after Cadamosto, the [[Duchy of Courland and Semigallia]] was the first to establish a permanent base, on what they called [[Kunta Kinteh Island|St Andrew's Island]] in 1651. After taking control of the island and renaming it 'St James' in 1661, the English vied with the French for commercial domination of the river for the next century and a half.<ref>Gailey, 3.</ref> |
|||
During this period, kingdoms along the river Gambia included [[Niumi]] (also known as [[Barra, Gambia|Barra]]), Niani, Kantora, Jimara, Kiang, Badibu, [[Fuladu]], Tumana, and [[Kingdom of Wuli|Wuli]], all of which have lent their names to districts of [[The Gambia]] today. Major trading posts on or near the river included [[Barra, Gambia|Barra]], [[Albreda]], [[Juffure]], [[Kunta Kinteh Island|James Island]] (now a [[UNESCO]] [[World Heritage Site]]), Tendeba, Joar, [[MacCarthy Island]], [[Fattatenda]], and [[Sutukoba]]. |
|||
Around the turn of the 18th century, the Scottish explorer [[Mungo Park (explorer)|Mungo Park]] traveled up the Gambia twice on his way to the Niger River.<ref>Capt. Washington. "Some Account of Mohammedu-Siseï, a Mandingo, of Nyáni-Marú on the Gambia." The Journal of the Royal Geographical Society of London, vol. 8, 1838, pp. 448–54. JSTOR, https://doi.org/10.2307/1797825. Accessed 27 Jul. 2022.</ref> |
|||
The [[Anglo-French Convention of 1889]] delimited the borders of the [[Gambia Protectorate]] and the colony of [[Senegal]] as being ten kilometers north and south of the river as far inland as Yarbutenda (near modern-day Koina), with a 10km radius to mark the eastern border measured from the center of town.<ref>Gailey, 27.</ref> The British therefore controlled the river as far as it was navigable by sea-going vessels. Though widely seen as temporary at the time, the borders set in 1889 have remained unchanged ever since.<ref>Gailey, 28.</ref> |
|||
==Flora and fauna== |
|||
The aquatic fauna in the Gambia River [[Drainage basin|basin]] is closely associated with that of the [[Senegal River]] basin, and the two are usually combined under a single [[ecoregion]] known as the [[List of freshwater ecoregions in Africa and Madagascar#Nilo-Sudan|Senegal-Gambia Catchments]]. Although the [[species richness]] is moderately high, only three species of frogs and one fish are [[Endemism|endemic]] to this ecoregion.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.feow.org/ecoregions/details/senegal_gambia |title=509: Senegal – Gambia |website=Freshwater Ecoregions of the World |access-date=30 October 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161030202252/http://www.feow.org/ecoregions/details/senegal_gambia |archive-date=30 October 2016 |url-status=dead }}</ref> |
|||
Oysters are harvested from the River Gambia by women and used to make [[oyster stew]], a traditional dish in the [[cuisine of Gambia]]. |
|||
==Gallery== |
|||
<gallery mode=packed heights= style="text-align:left"> |
|||
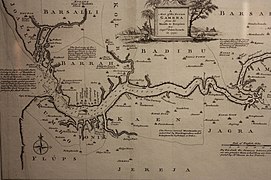
File:Map of the River Gambra (now the Gambia) 1732.JPG|Map of the River Gambra (now the Gambia) 1732 |
|||
File:Gambia satellite fires.jpeg|The western portion of the Gambia River, seen from space. The line shows the border of The Gambia. |
|||
File:RiverGambia_Janjanbureh_20190122_Upstream.jpg|Upstream view of the river, near [[Janjanbureh Island]] |
|||
File:RiverGambia_Janjanbureh_20190122_Riverbank.jpg|Bank of the river, near Janjanbureh |
|||
File:RiverGambia_Janjanbureh_20190122_Ferry.jpg|Ferry crossing of the river, at Janjanbureh |
|||
</gallery> |
|||
==References== |
|||
{{Reflist}} |
|||
==Bibliography== |
|||
* Bühnen, Stephan. "Place Names as an Historical Source: An Introduction with Examples from Southern Senegambia and Germany." History in Africa, vol. 19, 1992. JSTOR, https://doi.org/10.2307/3171995. |
|||
* {{cite book |last1=Gailey |first1=Harry |title=Historical dictionary of the Gambia |date=1987 |publisher=Scarecrow Press |location=Metuchen, N.J. |isbn=0810820013}} |
|||
* Gray, J.M. (1940). History of the Gambia. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. |
|||
* {{cite book|first=Arnold|last=Hughes|first2=David|last2=Perfect|title=Historical Dictionary of The Gambia|series=African Historical Dictionaries|volume=109|location=Metuchen, New Jersey|publisher=Scarecrow Press|edition=4th|year=2008|isbn=9781442265226|contribution=|pages=}} |
|||
* {{cite journal |last1=van Hoven |first1=Ed |title=Local Tradition or Islamic Precept? The Notion of zakāt in Wuli (Eastern Senegal) (La notion de "zakāt" au Wuli (Sénégal)) |journal=Cahiers d'Études Africaines |date=1996 |volume=36 |issue=144 |pages=703–722 |doi=10.3406/cea.1996.1863 |jstor=4392734 |url=https://www.jstor.org/stable/4392734 |access-date=2 December 2020}} |
|||
* Wright, Donald R. "Beyond Migration and Conquest: Oral Traditions and Mandinka Ethnicity in Senegambia." History in Africa, vol. 12, 1985. JSTOR, https://doi.org/10.2307/3171727. |
|||
* Wright, Donald R. "Darbo Jula: The Role of a Mandinka Jula Clan in the Long-Distance Trade of the Gambia River and Its Hinterland." African Economic History, no. 3, 1977, pp. 33–45. JSTOR, https://doi.org/10.2307/3601138. Accessed 27 Jul. 2022. |
|||
==External links== |
|||
*{{Commons category-inline}} |
|||
*[http://www.accessgambia.com/information/gambia-river-info.html Gambia River Information & Photos] |
|||
{{Authority control}} |
|||
[[Category:Gambia River| ]] |
|||
[[Category:Rivers of Guinea]] |
|||
[[Category:Rivers of the Gambia]] |
|||
[[Category:Rivers of Senegal]] |
|||
[[Category:International rivers of Africa]] |
|||
[[Category:Banjul]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 02:44, 4 September 2024
| Gambia River | |
|---|---|
 Gambia River in the Niokolo-Koba National Park | |
 Map of the Gambia River drainage basin | |
| Standort | |
| Countries | |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | Fouta Djallon |
| • location | Labé, Guinea |
| • coordinates | 11°24′43″N 12°13′34″W / 11.412°N 12.226°W |
| • elevation | 795 m (2,608 ft) |
| Mouth | Atlantic Ocean |
• location | Banjul, The Gambia |
• coordinates | 13°28′N 16°34′W / 13.467°N 16.567°W |
• elevation | 0 m (0 ft) |
| Length | 1,120[1] km (700 mi) |
| Basin size | 78,000 km2 (30,000 sq mi) |
 | |
The Gambia River (formerly known as the River Gambra, French: Fleuve Gambie, Portuguese: Rio Gâmbia) is a major river in West Africa, running 1,120 kilometres (700 mi) from the Fouta Djallon plateau in north Guinea westward through Senegal and The Gambia to the Atlantic Ocean at the city of Banjul. It is navigable for about half that length.
The river is strongly associated with The Gambia, the smallest country in mainland Africa, which occupies the downstream half of the river and its two banks.
Geography
[edit]The Gambia River runs a total length of 1,120 kilometres (700 mi). From the Fouta Djallon, it runs northwest into the Tambacounda Region of Senegal, where it flows through the Parc National du Niokolo Koba, then is joined by the Nieri Ko and Koulountou and passing through the Barrakunda Falls before entering the Gambia at Koina. At this point, the river runs generally west, but in a meandering course with a number of oxbows, and about 100 kilometres (62 mi) from its mouth it gradually widens, to over 10 kilometres (6.2 mi) wide where it meets the sea.
Crossings
[edit]There are several bridges crossing the river. The largest and furthest downriver is the Senegambia Bridge between the towns of Farafenni and Soma in The Gambia. Opened in January 2019, it provides a link between the stretches of the Trans-Gambia Highway on the North and South Bank of the river. It also provides an expedited connection for Senegalese trucks traveling to and from Casamance. The bridge is 1.9 kilometres (1.2 mi) long and replaces a previously-unreliable vehicle ferry. A toll is levied on vehicle crossings.
There are also bridges in the Upper River Region of The Gambia at Basse Santa Su and Fatoto that opened in October 2021,[2] as well as a bridge in Senegal at Gouloumbou.
All other crossings are done by ferry, including a primary crossing between Banjul and Barra at the mouth of the river, or by small boat.
Bolongs
[edit]Small tributaries on the lower stretches of the river are commonly referred to as bolongs or bolons. These include Sami Bolong dividing the northern halves of the Central River Division and Upper River Division, Bintang Bolong dividing the Lower River Division from the West Coast Division, as well as smaller bodies of water such as the Sofancama, Jurunku, Kutang, Nianji, and Sandugu bolongs.[3]
History
[edit]The earliest known inhabitants of the area along the Gambia river include the Jola, the Balante, the Bainuk, and the Manjak.[4] The Carthaginian explorer Hanno the Navigator may have reached the Gambia during his expedition in the fifth century BC.[5]
According to oral tradition, large numbers of Mandinka immigrants from Mali led by Tiramakhan Traore, one of Sundiata's top generals, came to the region in the 14th century. Some modern historians, however, posit that relatively few immigrants, primarily jula traders, instead led a gradual socio-cultural shift towards identification with the higher-status Mandinka ethnicity and the ruling Mali Empire.[6][7] These jula made the Gambia an important part of the wider West African trade network, where salt, shellfish, iron, cloth, ivory, beeswax, gold, slaves, leather and more were exchanged as far as the Niger River and beyond.[8][9]
Alvise Cadamosto, a Venetian explorer working for the Portuguese, became the first European to sail to the Gambia in 1455, referring to the river as the Gambra or Cambra. Other sources from that period record names such as Guambea, Guabu, and Gambu (possibly a conflation, at the time or in later historiography, of the name of the river and the kingdom of Kaabu).[10] While merchants of various European countries traded on the Gambia river for two centuries after Cadamosto, the Duchy of Courland and Semigallia was the first to establish a permanent base, on what they called St Andrew's Island in 1651. After taking control of the island and renaming it 'St James' in 1661, the English vied with the French for commercial domination of the river for the next century and a half.[11]
During this period, kingdoms along the river Gambia included Niumi (also known as Barra), Niani, Kantora, Jimara, Kiang, Badibu, Fuladu, Tumana, and Wuli, all of which have lent their names to districts of The Gambia today. Major trading posts on or near the river included Barra, Albreda, Juffure, James Island (now a UNESCO World Heritage Site), Tendeba, Joar, MacCarthy Island, Fattatenda, and Sutukoba.
Around the turn of the 18th century, the Scottish explorer Mungo Park traveled up the Gambia twice on his way to the Niger River.[12]
The Anglo-French Convention of 1889 delimited the borders of the Gambia Protectorate and the colony of Senegal as being ten kilometers north and south of the river as far inland as Yarbutenda (near modern-day Koina), with a 10km radius to mark the eastern border measured from the center of town.[13] The British therefore controlled the river as far as it was navigable by sea-going vessels. Though widely seen as temporary at the time, the borders set in 1889 have remained unchanged ever since.[14]
Flora and fauna
[edit]The aquatic fauna in the Gambia River basin is closely associated with that of the Senegal River basin, and the two are usually combined under a single ecoregion known as the Senegal-Gambia Catchments. Although the species richness is moderately high, only three species of frogs and one fish are endemic to this ecoregion.[15]
Oysters are harvested from the River Gambia by women and used to make oyster stew, a traditional dish in the cuisine of Gambia.
Gallery
[edit]-
Map of the River Gambra (now the Gambia) 1732
-
The western portion of the Gambia River, seen from space. The line shows the border of The Gambia.
-
Upstream view of the river, near Janjanbureh Island
-
Bank of the river, near Janjanbureh
-
Ferry crossing of the river, at Janjanbureh
References
[edit]- ^ "Gambia River". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 30 October 2016.
- ^ Ma, Jianchun (13 Oct 2021). "Building the Friendship Bridges towards a Shared Future of China and The Gambia". The Point. Retrieved 3 August 2022.
- ^ Gailey.
- ^ Buhnen, 49.
- ^ "Kunta Kinteh Island and Related Sites". UNESCO World Heritage Centre. United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization. Accessed 14/8/22.
- ^ Wright, "Beyond Migration", 385.
- ^ Buhnen, 51.
- ^ Wright, "Darbo Jula", 33.
- ^ Van Hoven.
- ^ Buhnen, 71.
- ^ Gailey, 3.
- ^ Capt. Washington. "Some Account of Mohammedu-Siseï, a Mandingo, of Nyáni-Marú on the Gambia." The Journal of the Royal Geographical Society of London, vol. 8, 1838, pp. 448–54. JSTOR, https://doi.org/10.2307/1797825. Accessed 27 Jul. 2022.
- ^ Gailey, 27.
- ^ Gailey, 28.
- ^ "509: Senegal – Gambia". Freshwater Ecoregions of the World. Archived from the original on 30 October 2016. Retrieved 30 October 2016.
Bibliography
[edit]- Bühnen, Stephan. "Place Names as an Historical Source: An Introduction with Examples from Southern Senegambia and Germany." History in Africa, vol. 19, 1992. JSTOR, https://doi.org/10.2307/3171995.
- Gailey, Harry (1987). Historical dictionary of the Gambia. Metuchen, N.J.: Scarecrow Press. ISBN 0810820013.
- Gray, J.M. (1940). History of the Gambia. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Hughes, Arnold; Perfect, David (2008). Historical Dictionary of The Gambia. African Historical Dictionaries. Vol. 109 (4th ed.). Metuchen, New Jersey: Scarecrow Press. ISBN 9781442265226.
- van Hoven, Ed (1996). "Local Tradition or Islamic Precept? The Notion of zakāt in Wuli (Eastern Senegal) (La notion de "zakāt" au Wuli (Sénégal))". Cahiers d'Études Africaines. 36 (144): 703–722. doi:10.3406/cea.1996.1863. JSTOR 4392734. Retrieved 2 December 2020.
- Wright, Donald R. "Beyond Migration and Conquest: Oral Traditions and Mandinka Ethnicity in Senegambia." History in Africa, vol. 12, 1985. JSTOR, https://doi.org/10.2307/3171727.
- Wright, Donald R. "Darbo Jula: The Role of a Mandinka Jula Clan in the Long-Distance Trade of the Gambia River and Its Hinterland." African Economic History, no. 3, 1977, pp. 33–45. JSTOR, https://doi.org/10.2307/3601138. Accessed 27 Jul. 2022.
External links
[edit] Media related to Gambia River at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Gambia River at Wikimedia Commons- Gambia River Information & Photos