T-slot structural framing: Difference between revisions
Re-add relevant removed content from revision 1143923302; change media order; rewrite language to be less hostile; add citations for history. |
m nits: style/grammar |
||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
While the precise history of the T-slot framing system is not known, advancement in extrusion press technology in the early 1950s allowed for economic production of aluminium profiles,<ref>{{cite book |last1=Bauser |first1=M |last2=Sauer |first2=G |last3=Siegert |first3=K |title=Extrusion |date=2006 |publisher=ASM International |location=Materials Park, Ohio |isbn=978-0-87170-837-3 |pages=6 |edition=2}}</ref> and examples of use can be found from the early 1960s.<ref>{{cite patent |country=US |number=US3143981A |inventor=Leslie E Tassell |status=patent |title=Demountable partition |pubdate=1964-08-11 |gdate=1964-08-11 |fdate=1962-03-23 |pridate=1962-03-23 |assign1=Tassell Hardware Co |url=https://patents.google.com/patent/US3143981A/en?oq=US3143981}}</ref> |
While the precise history of the T-slot framing system is not known, advancement in extrusion press technology in the early 1950s allowed for economic production of aluminium profiles,<ref>{{cite book |last1=Bauser |first1=M |last2=Sauer |first2=G |last3=Siegert |first3=K |title=Extrusion |date=2006 |publisher=ASM International |location=Materials Park, Ohio |isbn=978-0-87170-837-3 |pages=6 |edition=2}}</ref> and examples of use can be found from the early 1960s.<ref>{{cite patent |country=US |number=US3143981A |inventor=Leslie E Tassell |status=patent |title=Demountable partition |pubdate=1964-08-11 |gdate=1964-08-11 |fdate=1962-03-23 |pridate=1962-03-23 |assign1=Tassell Hardware Co |url=https://patents.google.com/patent/US3143981A/en?oq=US3143981}}</ref> |
||
Although no published standard defines the system, it is produced in a series of conventional sizes which allows for compatibility between manufacturers. |
|||
There is a variation on T-slot profiles known as '''V-slot rails''' where V-slot wheels are slotted into the V-shaped channels of the framing for [[Linear stage|linear motion]] in a [[ |
There is a variation on T-slot profiles known as '''V-slot rails''' where V-slot wheels are slotted into the V-shaped channels of the framing for [[Linear stage|linear motion]] in a [[3D printer]] or other [[CNC machine]]. |
||
==Profiles== |
==Profiles== |
||
T-slot framing is divided into metric and fractional (imperial) categories. The T-slot is always centered along the long-axis of the piece. Pieces are available in each series with a square cross-section. Rectangular cross sections are available |
T-slot framing is divided into metric and fractional (imperial) categories. The T-slot is always centered along the long-axis of the piece. Pieces are available in each series with a square cross-section. Rectangular cross sections are also available which measure ''x'' by ''2x'' (where ''x'' is the defined width) - e.g. 40mm by 80mm for 40 series. |
||
{|class="wikitable" |
{|class="wikitable" |
||
Revision as of 20:47, 11 August 2023
This article needs additional citations for verification. (April 2022) |



T-slot structural framing, sometimes known as aluminum extrusion, or 2020 extrusion when the cross-section is 20x20 mm, is a framing system consisting of lengths of square or rectangular extruded aluminum, typically 6105-T5 aluminium alloy, with a T-slot down the centerline of one or more sides. It is also known as 80/20 framing, after the company 80/20, Inc., one of the prominent T-slot framing brands, the name of which is based on the 80/20 or "Pareto" principle.[1]
While the precise history of the T-slot framing system is not known, advancement in extrusion press technology in the early 1950s allowed for economic production of aluminium profiles,[2] and examples of use can be found from the early 1960s.[3]
Although no published standard defines the system, it is produced in a series of conventional sizes which allows for compatibility between manufacturers.
There is a variation on T-slot profiles known as V-slot rails where V-slot wheels are slotted into the V-shaped channels of the framing for linear motion in a 3D printer or other CNC machine.
Profiles
T-slot framing is divided into metric and fractional (imperial) categories. The T-slot is always centered along the long-axis of the piece. Pieces are available in each series with a square cross-section. Rectangular cross sections are also available which measure x by 2x (where x is the defined width) - e.g. 40mm by 80mm for 40 series.
| Profile type |
Profile name |
Profile size |
|---|---|---|
| fractional | 10 series | 1" |
| 15 series | 1.5" | |
| metric | 20 series | 20 mm |
| 25 series | 25 mm | |
| 30 series | 30 mm | |
| 40 series | 40 mm | |
| 45 series | 45 mm |
-
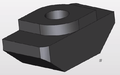
CAD model of a rotating T-slot nut used with aluminium T-slots/ T-track/ extrusions
-
T-nut (red) installed in a T-slot
See also
References
- ^ "Find out About Our Mission and Vision Here at 80/20". 8020.net. Archived from the original on 2022-03-06. Retrieved 2022-05-15.
- ^ Bauser, M; Sauer, G; Siegert, K (2006). Extrusion (2 ed.). Materials Park, Ohio: ASM International. p. 6. ISBN 978-0-87170-837-3.
- ^ US patent US3143981A, Leslie E Tassell, "Demountable partition", published 1964-08-11, issued 1964-08-11, assigned to Tassell Hardware Co