Retroreflector: Difference between revisions
Wingman4l7 (talk | contribs) fixed dead reference link to go to archived copy on Archive.org |
|||
| Line 62: | Line 62: | ||
[[Image:Apollo AS11-40-5952HR.jpg|thumb|200px|The Apollo 11 Lunar Laser Ranging Experiment]] |
[[Image:Apollo AS11-40-5952HR.jpg|thumb|200px|The Apollo 11 Lunar Laser Ranging Experiment]] |
||
[[Astronaut]]s on the ''[[Apollo 11]]'', ''[[Apollo 14|14]]'', and ''[[Apollo 15|15]]'' missions left retroreflectors on the [[Moon]] as part of the [[Lunar Laser Ranging Experiment]]. They are considered to conclusively prove that man-made equipment is present on the moon<ref>[http://home.austin.rr.com/broadb/chris/Using_Lunar_Retroreflectors.html |
[[Astronaut]]s on the ''[[Apollo 11]]'', ''[[Apollo 14|14]]'', and ''[[Apollo 15|15]]'' missions left retroreflectors on the [[Moon]] as part of the [[Lunar Laser Ranging Experiment]]. They are considered to conclusively prove that man-made equipment is present on the moon<ref>[http://web.archive.org/web/20080414163245/http://home.austin.rr.com/broadb/chris/Using_Lunar_Retroreflectors.html]{{Using Lunar Retroreflectors -- original page link dead, using most recent copy from Archive.org|date=April 14 2008}}</ref> and thus disprove some [[Apollo moon landing hoax accusations|Moon landing hoax accusations]]. Additionally the Soviet ''[[Lunokhod 1]]'' and ''[[Lunokhod 2]]'' rovers carried smaller arrays. Reflected signals were initially received from ''Lunokhod 1'', but no return signals have been detected since 1971, at least in part due to some uncertainty in its location on the Moon. ''Lunokhod 2's'' array continues to return signals to Earth.<ref>http://ilrs.gsfc.nasa.gov/docs/williams_lw13.pdf</ref> Even under good viewing conditions, only a single reflected photon is received every few seconds. This makes the job of filtering laser-generated photons from naturally-occurring photons challenging.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://sunearth.gsfc.nasa.gov/eclipse/SEhelp/ApolloLaser.html |title=NASA - Accuracy of Eclipse Predictions |publisher=Sunearth.gsfc.nasa.gov |date= |accessdate=2009-12-08}}</ref> |
||
===Retroreflectors in Earth orbit=== |
===Retroreflectors in Earth orbit=== |
||
Revision as of 05:13, 2 June 2010
 A gold corner cube retroreflector | |
| Uses | Distance measurement by optical delay line |
|---|---|
A retroreflector (sometimes called a retroflector or cataphote) is a device or surface that reflects light back to its source with a minimum scattering of light. An electromagnetic wave front is reflected back along a vector that is parallel to but opposite in direction from the wave's source. The device or surface's angle of incidence is greater than zero. This is unlike a planar mirror, which does this only if the mirror is exactly perpendicular to the wave front, having a zero angle of incidence.
Types of retroreflectors

Retroreflection is usually obtained in the following ways:[1]
- with a set of three mutually perpendicular mirrors that form a corner (a corner reflector or corner cube)
- with reflecting and refracting optical elements arranged so that the focal surface of the refractive element coincides with the reflective surface, typically a transparent sphere and a spherical mirror. This same effect can be achieved with a single transparent sphere provided that the refractive index of the material is exactly two times the refractive index of the medium from which the radiation is incident. In that case, the sphere surface behaves as a concave spherical mirror with the required curvature for retroreflection. This is conventionally known as a cat's eye retroreflector in either configuration.
The term cat's eye derives from the resemblance of the cat's eye retroreflector to the optical system that produces the well-known phenomenon of "glowing eyes" or eyeshine in cats and other vertebrates (which are only reflecting light, rather than actually glowing). The combination of the eye's lens and the aqueous humor form the refractive converging system, while the tapetum lucidum behind the retina forms the spherical concave mirror. Because the function of the eye is to form an image on the retina, an eye focused on a distant object has a focal surface that approximately follows the reflective tapetum lucidum structure,[citation needed] which is the condition required to form a good retroreflection.
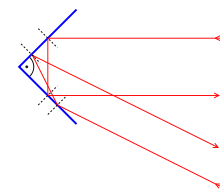
Corner retroreflectors occur in two varieties. In the more common form, the corner is literally the truncated corner of a cube of transparent material such as conventional optical glass. In this structure, the reflection is achieved either by total internal reflection or silvering of the outer cube surfaces. The second form uses mutually perpendicular flat mirrors bracketing an air space. These two types have similar optical properties.
A retroreflector can consist of many small versions of these structures incorporated in a thin sheet or in paint. In the case of paint containing glass beads, the paint glues the beads to the surface where retroreflection is required and the beads protrude, their diameter being about twice the thickness of the paint.
A third, much less common way of producing a retroreflector is to use the nonlinear optical phenomenon of phase conjugation. This technique is used in advanced optical systems such as high-power lasers and optical transmission lines. Phase conjugate mirrors require a comparatively expensive and complex apparatus, as well as large quantities of power (as nonlinear optical processes can be efficient only at high enough intensities). However, phase conjugate mirrors have an inherently much greater accuracy in the direction of the retroreflection, which in passive elements is limited by the mechanical accuracy of the construction.
Operation
Retroreflectors are devices that operate by returning light back to the light source along the same light direction. The coefficient of luminous intensity, RI, is the measure of a reflector performance, which is defined as the ratio of the strength of the reflected light (luminous intensity) to the amount of light that falls on the reflector (normal illuminance). A reflector will appear brighter as its RI value increases.[1]
The RI value of the reflector is a function of the color, size, and condition of the reflector. Clear or white reflectors are the most efficient, and appear brighter than other colors. The surface area of the reflector is proportional to the RI value and increases as the reflective surface increases.[1]


The RI value is also a function of the spatial geometry between the observer, light source, and reflector. Figures 1 and 2 show the observation angle and entrance angle between the automobile's headlights, bicycle, and driver. The observation angle is the angle formed by the light beam and the driver's line of sight. Observation angle is a function of the distance between the headlights and the driver's eye, and the distance to the reflector. Traffic engineers use an observation angle of 0.2 degrees to simulate a reflector target about 800 feet in front of a passenger automobile. As the observation angle increases, the reflector performance decreases. For example, a truck has a large separation between the headlight and the driver's eye compared to a passenger vehicle. A bicycle reflector appears brighter to the passenger car driver than to the truck driver at the same distance from the vehicle to the reflector.[1]
The light beam and the normal axis of the reflector as shown in Figure 2 form the entrance angle. The entrance angle is a function of the orientation of the reflector to the light source. For example, the entrance angle between an automobile approaching a bicycle at an intersection 90 degrees apart is larger than the entrance angle for a bicycle directly in front of an automobile on a straight road. The reflector appears brightest to the observer when it is directly in line with the light source.[1]
The brightness of a reflector is also a function of the distance between the light source and the reflector. At a given observation angle, as the distance between the light source and the reflector decreases, the light that falls on the reflector increases. This increases the amount of light returned to the observer and the reflector appears brighter.[1]
Applications
Retroreflectors on roads

Retroreflection (sometimes called retroflection) is used on road surfaces, road signs, vehicles, and clothing (large parts of the surface of special safety clothing, less on regular coats). When the headlights of a car illuminate a retroreflective surface, the reflected light is directed towards the car and its driver (rather than in all directions as with diffuse reflection). However, a pedestrian can see retroreflective surfaces in the dark only if there is a light source directly between them and the reflector (e.g., via a flashlight they carry) or directly behind them (e.g., via a car approaching from behind). "Cat's eyes" are a particular type of retroreflector embedded in the road surface and are used mostly in the UK and parts of the United States.
Corner reflectors are better at sending the light back to the source over long distances, while spheres are better at sending the light to a receiver somewhat off-axis from the source, as when the light from headlights is reflected into the driver's eyes.
Retroreflectors can be embedded in the road (level with the road surface), or they can be raised above the road surface. Raised reflectors are visible for very long distances (typically 0.5-1 kilometer or more), while sunken reflectors are visible only at very close ranges due to the higher angle required to properly reflect the light. Raised reflectors are generally not used in areas that regularly experience snow during winter, as passing snowplows can tear them off of the roadways. Stress on roadways caused by cars running over embedded objects also contributes to accelerated wear and pothole formation.
Retroreflective road paint is thus very popular in Canada and parts of the United States, as it is not affected by the passage of snowplows and does not affect the interior of the roadway. Where weather permits, embedded or raised retroreflectors are preferred as they last much longer than road paint, which is weathered by the elements, can be obscured by sediment or rain, and is ground away by the passage of vehicles.
Retroreflectors on the Moon

Astronauts on the Apollo 11, 14, and 15 missions left retroreflectors on the Moon as part of the Lunar Laser Ranging Experiment. They are considered to conclusively prove that man-made equipment is present on the moon[2] and thus disprove some Moon landing hoax accusations. Additionally the Soviet Lunokhod 1 and Lunokhod 2 rovers carried smaller arrays. Reflected signals were initially received from Lunokhod 1, but no return signals have been detected since 1971, at least in part due to some uncertainty in its location on the Moon. Lunokhod 2's array continues to return signals to Earth.[3] Even under good viewing conditions, only a single reflected photon is received every few seconds. This makes the job of filtering laser-generated photons from naturally-occurring photons challenging.[4]
Retroreflectors in Earth orbit
LAGEOS, or Laser Geodynamics Satellites, are a series of scientific research satellites designed to provide an orbiting laser ranging benchmark for geodynamical studies of the Earth. There are two LAGEOS spacecraft: LAGEOS-1 (launched in 1976), and LAGEOS-2 (launched in 1992). They use cube-corner retroreflectors made of fused silica glass. As of 2004, both LAGEOS spacecraft are still in service.
Retroreflectors and invisibility
Retroreflective clothing, combined with a properly set up camera and projector, can be used to achieve the effect of partial invisibility when viewed from a single direction.[5][6] Reflectin is a retroreflective material with potential for use in this application.
Retroreflectors and communications
Modulated retroreflectors, in which the reflectance is changed over time by some means, are the subject of research and development for free-space optical communications networks. The basic concept of such systems is that a low-power remote system, such as a sensor mote, can receive an optical signal from a base station and reflect the modulated signal back to the base station. Since the base station supplies the optical power, this allows the remote system to communicate without excessive power consumption. Modulated retroreflectors also exist in the form of modulated phase-conjugate mirrors (PCMs). In the latter case, a "time-reversed" wave is generated by the PCM with temporal encoding of the phase-conjugate wave (see, e.g., SciAm, Oct. 1990, "The Photorefractive Effect," David M. Pepper, et. al).
Inexpensive corner-aiming retroreflectors are used in user-controlled technology as optical datalink devices. Aiming is done at night, and the necessary retroreflector area depends on aiming distance and ambient lighting from street lamps. The optical receiver itself behaves as a weak retroreflector because it contains a large, precisely focused lens that detects illuminated objects in its focal plane. This allows aiming without a retroreflector for short ranges.
A single biological instance of this is known: in flashlight fish of the family Anomalopidae (see Tapetum lucidum).
Retroreflectors and ships, boats, emergency gear
Retroflective tape is recognized and recommended by the International Convention for the Safety of Life at Sea (SOLAS) because of its high reflectivity of both light and radar signals. Application to life rafts, personal flotation devices, and other safety gear makes it easy to locate people and objects in the water at night. When applied to boat surfaces it creates a much larger radar signature, particularly for fiberglass boats which produce very little radar reflection on their own. It conforms to International Maritime Organization regulation, IMO Res. A.658 (16) and meets U.S. Coast Guard specification 46 CFR Part 164, Subpart 164.018/5/0. Examples of commercially available products are 3M part numbers 3150A and 6750I.
Other uses
Retroreflectors are used in the following example applications:
- In surveying with a total station or robot, the instrument man or robot aims a laser beam at a corner cube retroreflector held by the rodman. The instrument measures the propagation time of the light and converts it to a distance.
- In common (non-SLR) digital cameras, where the sensor system is retroreflective. Researchers have used this property to demonstrate a system to prevent unauthorized photographs by detecting digital cameras and beaming a highly-focused beam of light into the lens.[7]
- In movie screens to allow for high brilliance under dark conditions.[8]
- Digital compositing programs and chroma environments use retroreflection to replace traditional lit backdrops in composite work as they provide a more solid colour without requiring the backdrop to be lit separately.[9]
See also
- Bicycle reflector
- Free space optical communication
- Scotchlite
- Modulating retro-reflector
- GPS modernization
- Corner reflector
- Pentaprism
References
- ^ a b c d e f U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission Bicycle Reflector Project report
- ^ [1]Template:Using Lunar Retroreflectors -- original page link dead, using most recent copy from Archive.org
- ^ http://ilrs.gsfc.nasa.gov/docs/williams_lw13.pdf
- ^ "NASA - Accuracy of Eclipse Predictions". Sunearth.gsfc.nasa.gov. Retrieved 2009-12-08.
- ^ "Inventor plans 'invisible walls'". BBC News. 2004-06-14. Retrieved 2010-05-22.
- ^ [2][dead link]
- ^ ABC News: Device Seeks to Jam Covert Digital Photographers
- ^ Howstuffworks "Altered Reality"
- ^ "Changing the art of chroma key". Reflecmedia. Retrieved 2009-12-08.
This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations. (February 2008) |
- Optics Letters, Vol. 4, pp. 190-192 (1979), "Retroreflective Arrays as Approximate Phase Conjugators," by H.H. Barrett and S.F. Jacobs.
- Optical Engineering, Vol. 21, pp. 281-283 (March/April 1982), "Experiments with Retrodirective Arrays," by Stephen F. Jacobs.
- Scientific American, December 1985, "Phase Conjugation," by Vladimir Shkunov and Boris Zel'dovich.
- Scientific American, January 1986, "Applications of Optical Phase Conjugation," by David M. Pepper.
- Scientific American, April 1986, "The Amateur Scientist" ('Wonders with the Retroreflector'), by Jearl Walker.
- Scientific American, October 1990, "The Photorefractive Effect," by David M. Pepper, Jack Feinberg, and Nicolai V. Kukhtarev.
