2-Pyrone: Difference between revisions
Appearance
Content deleted Content added
Citation bot (talk | contribs) m [364]Misc citation tidying. |
Script assisted update of identifiers for the Chem/Drugbox validation project (updated: 'ChEBI'). |
||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
| CASNo=504-31-4 |
| CASNo=504-31-4 |
||
| PubChem=68154 |
| PubChem=68154 |
||
| SMILES = O=C\1O\C=C/C=C/1 |
| ChEBI = 37965 |
||
| SMILES = O=C\1O\C=C/C=C/1 |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
|Section2= {{Chembox Properties |
|Section2= {{Chembox Properties |
||
Revision as of 08:55, 6 August 2011

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Pyran-2-one
| |
| Other names
α-Pyrone
2-Pyranone 2H-Pyran-2-one | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.264 |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H4O2 | |
| Molar mass | 96.08 |
| Density | 1.197 g/mL |
| Boiling point | 102-103 °C at 20 mmHg |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
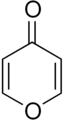
2-Pyrone (α-pyrone or pyran-2-one) is an unsaturated cyclic chemical compound with the molecular formula C5H4O2. It is isomeric with 4-pyrone.
2-Pyrone is used in organic synthesis as a building block for more complex chemical structures because it may participate in a variety of cycloaddition reactions to form bicyclic lactones. For example, it readily undergoes Diels-Alder reactions with alkynes producing, upon loss of carbon dioxide, substituted benzenes.[2] The Gogte Synthesis (1938) is a method for the alkylation of certain pyrones with acid chlorides.[citation needed]
-
4-Pyrone
The most common natural products containing a 2-pyrone are the bufanolides and kavalactones.
References
- ^ 2H-Pyran-2-one at Sigma-Aldrich
- ^ Woodard BT, Posner G H (1999). "Recent Advances in Diels-Alder Cycloadditions Using 2-Pyrones". Advances in Cycloaddition. 5: 47–83.