Trochlea of humerus: Difference between revisions
Fama Clamosa (talk | contribs) reword |
Fama Clamosa (talk | contribs) +ref; -{{Gray's}} |
||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
It presents a deep depression between two well-marked borders; it is convex from before backward, concave from side to side, and occupies the anterior, lower, and posterior parts of the extremity. |
It presents a deep depression between two well-marked borders; it is convex from before backward, concave from side to side, and occupies the anterior, lower, and posterior parts of the extremity. |
||
It is directly inferior to the [[coronoid fossa]] anteriorly and to the [[olecranon fossa]] posteriorly. In humans, these two fossae, the most prominent in the humerus, are occasionally transformed into a hole, the [[supratrochlear foramen]], |
It is directly inferior to the [[coronoid fossa]] anteriorly and to the [[olecranon fossa]] posteriorly. In humans, these two fossae, the most prominent in the humerus, are occasionally transformed into a hole, the [[supratrochlear foramen]],<ref>{{cite book |
||
| last = Platzer | first = Werner |
|||
| title = Color Atlas of Human Anatomy, Vol. 1: Locomotor System |
|||
| publisher = [[Thieme Medical Publishers|Thieme]] | isbn = 3-13-533305-1<!---US: 1-58890-159-9---> |
|||
| year = 2004 | edition = 5th | page = 114 |
|||
}}</ref> which is regularly present in, for example, dogs. |
|||
The trochlea has the [[capitulum of the humerus|capitulum]] located on its lateral side and the [[Medial epicondyle of the humerus|medial epidcondyle]] on its medial. |
The trochlea has the [[capitulum of the humerus|capitulum]] located on its lateral side and the [[Medial epicondyle of the humerus|medial epidcondyle]] on its medial. |
||
==References== |
|||
{{Reflist}} |
|||
==External links== |
==External links== |
||
* {{SUNYAnatomyFigs|07|02|04}} |
* {{SUNYAnatomyFigs|07|02|04}} |
||
{{Gray's}} |
|||
{{Bones of upper extremity}} |
{{Bones of upper extremity}} |
||
Revision as of 08:52, 5 February 2012
| Trochlea of humerus | |
|---|---|
 Anterior view of distal part of left humerus | |
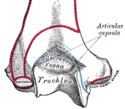 Posterior view of distal part of left humerus | |
| Identifiers | |
| TA98 | A02.4.04.023 |
| TA2 | 1203 |
| FMA | 23370 |
| Anatomical terms of bone | |
In the human arm, the humeral trochlea is the medial portion of the articular surface of the elbow joint which articulates with the trochlear notch on the ulna in the forearm.
It presents a deep depression between two well-marked borders; it is convex from before backward, concave from side to side, and occupies the anterior, lower, and posterior parts of the extremity.
It is directly inferior to the coronoid fossa anteriorly and to the olecranon fossa posteriorly. In humans, these two fossae, the most prominent in the humerus, are occasionally transformed into a hole, the supratrochlear foramen,[1] which is regularly present in, for example, dogs.
The trochlea has the capitulum located on its lateral side and the medial epidcondyle on its medial.
References
- ^ Platzer, Werner (2004). Color Atlas of Human Anatomy, Vol. 1: Locomotor System (5th ed.). Thieme. p. 114. ISBN 3-13-533305-1.
External links
- Anatomy figure: 07:02-04 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center
