Neurilemma: Difference between revisions
Appearance
Content deleted Content added
No edit summary |
m Bot: Migrating 4 interwiki links, now provided by Wikidata on d:q3184389 (Report Errors) |
||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
{{neuroanatomy-stub}} |
{{neuroanatomy-stub}} |
||
{{Nervous tissue}} |
{{Nervous tissue}} |
||
[[es:Neurilema]] |
|||
[[fr:Neurolemme]] |
|||
[[pt:Neurilema]] |
|||
[[ro:Teaca Schwann]] |
|||
Revision as of 10:17, 28 February 2013
| Neurolemma | |
|---|---|
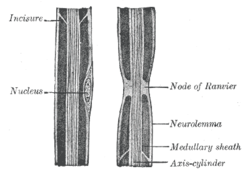 Diagram of longitudinal sections of medullated nerve fibers. | |
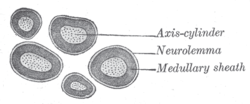 Transverse sections of medullated nerve fibers. | |
| Identifiers | |
| MeSH | D009441 |
| TH | H2.00.06.1.00002 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
Neurolemma (also known as neurilemma[1] or sheath of Schwann (Schwann's Sheath)) is the outermost nucleated cytoplasmic layer of Schwann cells that surrounds the axon of the neuron. It forms the outermost layer of the nerve fiber in the peripheral nervous system.[2]
The neurolemma is underlain by the basal lamina (referred to as the medullary sheath in the included illustrations). In CNS, axons are myelinated by oligodendrocytes, thus lack neurolemma. The myelin sheaths of Oligodendrocytes do not have neurolemma because excess cytoplasm is directed centrally toward the Oligodendrocyte cell body.
A neurilemoma is a tumor of the neurilemma.[3]
References
- ^ "neurilemma" at Dorland's Medical Dictionary
- ^ Elaine N. Marieb and Katja Hoehn (2007). Human Anatomy & Physiology (7th Ed.). Pearson. pp. 394–5. ISBN 0-8053-5909-5.
- ^ "neurilemoma" at Dorland's Medical Dictionary
