Imidazolidine: Difference between revisions
Appearance
Content deleted Content added
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Chembox |
{{Chembox |
||
| Verifiedfields = |
| Verifiedfields = correct |
||
| Watchedfields = |
| Watchedfields = correct |
||
| verifiedrevid = 419241295 |
| verifiedrevid = 419241295 |
||
| ImageFile = Imidazolidine numbering.png |
| ImageFile = Imidazolidine numbering.png |
||
Revision as of 00:44, 10 August 2013

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Imidazolidine
| |
| Other names
Tetrahydroimidazole
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C3H8N2 | |
| Molar mass | 72.109 |
| Supplementary data page | |
| Imidazolidine (data page) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Imidazolidine is a heterocyclic compound formally derived by the addition of four hydrogen atoms to imidazole. The intermediate, resulting from the addition of only two hydrogen atoms is called dihydroimidazole (imidazoline). The connection of imidazolidine to related compounds is indicated in the Figure.
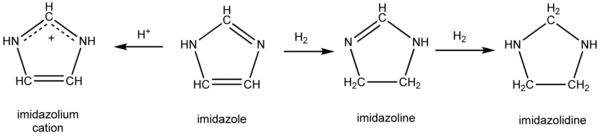
Formally, removal of the two hydrogens at carbon 2 (between the two nitrogens) would yield the carbene dihydroimidazol-2-ylidene. Derivatives of the latter comprise an important class of persistent carbenes.[1]
References
- ^
A. J. Arduengo, H. V. R. Dias, R. L. Harlow, and M. Kline (1992). "Electronic stabilization of nucleophilic carbenes". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 114 (14): 5530. doi:10.1021/ja00040a007.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
