Beta-ketothiolase deficiency: Difference between revisions
Ozzie10aaaa (talk | contribs) |
Ozzie10aaaa (talk | contribs) m Cleaned up using AutoEd |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Infobox medical condition (new) |
{{Infobox medical condition (new) |
||
| synonyms = 3-oxothiolase deficiency, Mitochondrial acetoacetyl-coenzyme A thiolase deficiency, Alpha-methyl-acetoacetyl-CoA thiolase deficiency |
| synonyms = 3-oxothiolase deficiency, Mitochondrial acetoacetyl-coenzyme A thiolase deficiency, Alpha-methyl-acetoacetyl-CoA thiolase deficiency |
||
| image = l-isoleucine.png |
| image = l-isoleucine.png |
||
| caption = [[Isoleucine]] |
| caption = [[Isoleucine]] |
||
| |
| |
||
| pronounce = |
| pronounce = |
||
| field = |
| field = |
||
| symptoms = |
| symptoms = |
||
| complications = |
| complications = |
||
| onset = |
| onset = |
||
| duration = |
| duration = |
||
| types = |
| types = |
||
| causes = |
| causes = |
||
| risks = |
| risks = |
||
| diagnosis = |
| diagnosis = |
||
| differential = |
| differential = |
||
| prevention = |
| prevention = |
||
| treatment = |
| treatment = |
||
| medication = |
| medication = |
||
| prognosis = |
| prognosis = |
||
| frequency = |
| frequency = |
||
| deaths = |
| deaths = |
||
}} |
}} |
||
'''Beta-ketothiolase deficiency''' is a rare, [[autosomal recessive]] [[metabolic disorder]] in which the body cannot properly process the [[amino acid]] [[isoleucine]] or the products of [[lipid]] breakdown.<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.orpha.net/consor/cgi-bin/OC_Exp.php?lng=en&Expert=134|title=Orphanet: Beta ketothiolase deficiency|last=RESERVED|first=INSERM US14 -- ALL RIGHTS|website=www.orpha.net|language=en|access-date=2017-07-02}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=https://omim.org/entry/203750|title=OMIM Entry - # 203750 - ALPHA-METHYLACETOACETIC ACIDURIA|website=omim.org|language=en-us|access-date=2017-07-02}}</ref> |
'''Beta-ketothiolase deficiency''' is a rare, [[autosomal recessive]] [[metabolic disorder]] in which the body cannot properly process the [[amino acid]] [[isoleucine]] or the products of [[lipid]] breakdown.<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.orpha.net/consor/cgi-bin/OC_Exp.php?lng=en&Expert=134|title=Orphanet: Beta ketothiolase deficiency|last=RESERVED|first=INSERM US14 -- ALL RIGHTS|website=www.orpha.net|language=en|access-date=2017-07-02}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=https://omim.org/entry/203750|title=OMIM Entry - # 203750 - ALPHA-METHYLACETOACETIC ACIDURIA|website=omim.org|language=en-us|access-date=2017-07-02}}</ref> |
||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
The signs and symptoms of beta-ketothiolase deficiency include [[vomiting]], [[dehydration]], trouble breathing, extreme tiredness, and occasionally [[convulsion]]s. These episodes are called ketoacidotic attacks and can sometimes lead to [[coma]]. Attacks occur when compounds called [[organic acids]] (which are formed as products of amino acid and fat breakdown) build up to toxic levels in the blood. These attacks are often triggered by an infection, fasting (not eating), or in some cases, other types of stress.{{citation needed|date=July 2017}} |
The signs and symptoms of beta-ketothiolase deficiency include [[vomiting]], [[dehydration]], trouble breathing, extreme tiredness, and occasionally [[convulsion]]s. These episodes are called ketoacidotic attacks and can sometimes lead to [[coma]]. Attacks occur when compounds called [[organic acids]] (which are formed as products of amino acid and fat breakdown) build up to toxic levels in the blood. These attacks are often triggered by an infection, fasting (not eating), or in some cases, other types of stress.{{citation needed|date=July 2017}} |
||
==Genetic |
==Genetic== |
||
[[Image:autorecessive.svg|thumb|100 px|Beta-ketothiolase deficiency is autosomal recessive]] |
[[Image:autorecessive.svg|thumb|100 px|Beta-ketothiolase deficiency is autosomal recessive]] |
||
This condition is inherited in an [[autosomal recessive]] pattern and is extremely rare having only been reported in 50 to 60 individuals throughout the world.{{citation needed}} |
This condition is inherited in an [[autosomal recessive]] pattern and is extremely rare having only been reported in 50 to 60 individuals throughout the world.{{citation needed}} |
||
| Line 47: | Line 47: | ||
== External links == |
== External links == |
||
{{Medical resources |
{{Medical resources |
||
| DiseasesDB = 29824 |
| DiseasesDB = 29824 |
||
| ICD10 = E71.1 |
| ICD10 = E71.1 |
||
| ICD9 = |
| ICD9 = |
||
| ICDO = |
| ICDO = |
||
| OMIM = 203750 |
| OMIM = 203750 |
||
| MedlinePlus = |
| MedlinePlus = |
||
| eMedicineSubj = |
| eMedicineSubj = |
||
| eMedicineTopic = |
| eMedicineTopic = |
||
| MeshID = |
| MeshID = |
||
| Orphanet = 134 |
| Orphanet = 134 |
||
}} |
}} |
||
{{Amino acid metabolic pathology}} |
{{Amino acid metabolic pathology}} |
||
Revision as of 10:42, 21 September 2020
| Beta-ketothiolase deficiency | |
|---|---|
| Other names | 3-oxothiolase deficiency, Mitochondrial acetoacetyl-coenzyme A thiolase deficiency, Alpha-methyl-acetoacetyl-CoA thiolase deficiency |
| File:L-isoleucine.png | |
| Isoleucine | |
Beta-ketothiolase deficiency is a rare, autosomal recessive metabolic disorder in which the body cannot properly process the amino acid isoleucine or the products of lipid breakdown.[1][2]
The typical age of onset for this disorder is between 6 months and 24 months.
Symptoms and signs
The signs and symptoms of beta-ketothiolase deficiency include vomiting, dehydration, trouble breathing, extreme tiredness, and occasionally convulsions. These episodes are called ketoacidotic attacks and can sometimes lead to coma. Attacks occur when compounds called organic acids (which are formed as products of amino acid and fat breakdown) build up to toxic levels in the blood. These attacks are often triggered by an infection, fasting (not eating), or in some cases, other types of stress.[citation needed]
Genetic
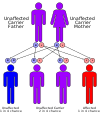
This condition is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern and is extremely rare having only been reported in 50 to 60 individuals throughout the world.[citation needed]
Mutations in the ACAT1 gene cause beta-ketothiolase deficiency. The enzyme made by the ACAT1 gene plays an essential role in breaking down proteins and fats in the diet. Specifically, the enzyme is responsible for processing isoleucine, an amino acid that is part of many proteins. This enzyme also processes ketones, which are produced during the breakdown of fats. If a mutation in the ACAT1 gene reduces or eliminates the activity of this enzyme, the body is unable to process isoleucine and ketones properly. As a result, harmful compounds can build up and cause the blood to become too acidic (ketoacidosis), which impairs tissue function, especially in the central nervous system.[citation needed]
Diagnosis
This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (July 2017) |
Treatment
This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (July 2017) |
References
- ^ RESERVED, INSERM US14 -- ALL RIGHTS. "Orphanet: Beta ketothiolase deficiency". www.orpha.net. Retrieved 2017-07-02.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ "OMIM Entry - # 203750 - ALPHA-METHYLACETOACETIC ACIDURIA". omim.org. Retrieved 2017-07-02.
This article incorporates public domain text from The U.S. National Library of Medicine
