Numbers in Germanic paganism
Appearance
A request that this article title be changed to Numbers in Germanic paganism is under discussion. Please do not move this article until the discussion is closed. |
This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages)
|
The numbers three and nine are significant numbers in Norse mythology and Germanic paganism. Both numbers (and multiples thereof) appear throughout surviving attestations of Norse mythology, in both mythology and Germanic paganism.[1]
While the number three appears significant in many cultures, Norse mythology appears to put special emphasis on the number nine. Along with the number 27, both numbers also figure into the lunar Germanic calendar.[1]

Three
Groupings and lists
- There were three original beings: the primordial cow Auðhumla, Ymir the first jötunn, and Búri the first god and grandfather of Odin.
- There are three named Norns.
- Odin had two brothers, Vili and Vé (or Lodur and Hoenir according to Völuspá), numbering three sons of Borr who created the world and gave life to the first human beings.
- The World Tree Yggdrasil has three roots. Under the three roots are three sacred wells, one for each, including the Well of Urd in Asgard, the Well of Mimir located among the Hrímþursar, and Hvergelmir in Niflheim.
- Odin endured three hardships upon the World Tree in his quest for the runes: he hanged himself, wounded himself with a spear, and suffered from hunger and thirst.
- In the Gylfaginning section of the Prose Edda, King Gylfi is confronted by a triple throne at the home of the gods, one being seated and occupied atop another.
- Loki has three malign progeny by the gýgr Angrboða: the wolf Fenrir, Jörmungandr the World Serpent, and Hel.
- Odin has three special possessions: His spear Gungnir, his golden ring Draupnir and his eight-legged horse Sleipnir.
- Thor has three main weapons for use against the jötnar: his hammer Mjolnir, a magical belt that doubles his strength and a pair of iron gauntlets that allow him to wield the hammer.
- Freyr has three magical items, including the ship Skiðblaðnir, his boar Gullinbursti and a sword with the ability to fight on its own which he gave to Skirnir in return for his role in the courtship of Gerðr.
- Freyja has three special artefacts, including the priceless necklace Brisingamen, a cloak that allows her to assume the form of a falcon and a chariot drawn by a pair of great cats.
- There were three statues of Odin, Thor and Freyr in the Temple at Uppsala.
- Three of Odin's sons remain after Ragarök: Vidar, Baldr and Hǫðr.
- Ymir had three direct offspring: a boy and girl who grew from beneath his arms and a six-headed son who sprang from the coupling of his feet.
- The wolf Fenrir was bound by three fetters: Loeding, Drómi, and Gleipnir, of which only the last held him.
- Loki is bound with three bonds made from the entrails of his son through holes in three upright slabs of rock, the first under his shoulders, the second under his loins and the third under the backs of his knees.
- During the onset of Ragnarök three cockerels will begin to crow, heralding the final conflict: Gullinkambi for the gods, Fjalar for the jötnar and an unnamed third for the dead.
- The group of dwarves known only as the sons of Ivaldi fashioned three wondrous artefacts, including the ship of Freyr, the spear of Odin and the golden hair of Sif. The dwarf brothers Eitri and Brokk also created three items, including the boar of Freyr, the golden ring of Odin and the hammer of Thor.
Events and time
- For three days Auðhumla licked the ice of Ginnungagap until Búri was freed.
- There were three generations of jötnar before the race as a whole was destroyed by the deluge of Ymir's blood, after which time his grandson Bergelmir became the progenitor of a new line.
- Odin is the ruler of the third generation of gods as the son of Borr and grandson of Búri.
- Prior to Ragnarök, there will be three hard winters without an intervening summer, the Fimbulwinter.
- There are three main events leading up to Ragnarök itself: the birth of Loki's three monstrous children, the death of Baldr and subsequent punishment of Loki, and the onset of Fimbulwinter.
- In the poem Völuspá from the Poetic Edda, the monstrous hound Garmr howls three times at the Gnipa-cave (or at least, the description of his howling is repeated three times).
- In Völuspá, the gods burn Gullveig three times and three times she is reborn.
- In the stronghold of the jötunn Útgarda-Loki, Thor drank three mighty draughts from a horn during a drinking contest but gave up when he was unable to empty the horn of its contents; this was also one of three tasks he did -and failed- during his stay, the other two being to lift a cat (he made it lift a paw, leaving three on ground) and to defeat an old woman; it is later revealed that the horn was connected to the sea (which he leveled down by three fingers), the cat was the World Serpent and the old woman, the Old Age itself. Previous to this, Thor and his companions had met the jötunn, who was under the assumed name Skrýmir, in the forest outside the castle. When Skrymir had gone to sleep during their journey together, Thor became annoyed by his loud snoring and struck at him three times with his hammer, but in each case the blow was misdirected through magic and illusion.
- Odin spent three nights with the gýgr Gunnlöð in order to obtain the mead of poetry. She then allowed him to take three drinks of the mead, one from each of three vessels.
- The builder of the walls of Asgard offered to build them in three seasons in return for three prizes: the sun and moon and the hand of Freyja in marriage.
Other
- The heart of the jötunn Hrungnir was triangular and made of stone.
- The rainbow bridge Bifröst has three colours. It also has two other names, Ásbrú and Bilröst, thus having three names.
- Heimdall has three special powers in his role as guardian of the rainbow bridge. He needs less sleep than a bird, can see at night for a hundred leagues and is able to hear grass growing on the earth.
Nine

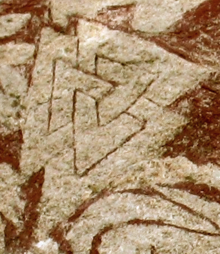
The number nine is also a significant number:
Cosmology
- The Norse cosmology knows nine worlds that are supported by Yggdrasil.
- At the end of Skáldskaparmál is a list of nine heavenly realms provided by Snorri, including, from the nethermost to the highest, Vindblain (also Heidthornir or Hregg-Mimir), Andlang, Vidblain, Vidfedmir, Hrjod, Hlyrnir, Gimir, Vet-Mimir and Skatyrnir which "stands higher than the clouds, beyond all worlds."
Religious practice
- The syncretic Anglo-Saxon nine-herbs charm, as the name implies, invokes nine herbs, and also contains a rare mention of Woden.
- Every ninth year, people from all over Sweden assembled at the Temple at Uppsala. There was feasting for nine days and sacrifices of both men and male animals according to Adam of Bremen.
- The 600s Stentoften Runestone mentions a sacrifice of nine he-goats and nine stallions, very similar to Adam's account.
- According to the very late Trollkyrka poem, the fire for the blót was lit with nine kinds of wood.
Mythology
- In Skírnismál, Freyr is obliged to wait nine nights to consummate his union with Gerðr.
- In Svipdagsmál, the völva Gróa grants nine charms to her son Svipdag. In the same poem there are nine maidens who sit at the knees of Menglod.
- In Fjölsvinnsmál, Laegjarn's chest is fastened with nine locks.
- During Ragnarök, Thor kills Jörmungandr but staggers back nine steps before falling dead himself, poisoned by the venom that the Serpent spewed over him and after that, he resurrected himself.
- Odin's ring Draupnir releases eight golden drops every ninth night, forming rings of equal worth for a total of nine rings.
- In the guise of Grímnir in the poem Grímnismál, Odin allows himself to be held by King Geirröd for eight days and nights and kills him on the ninth after revealing his true identity.
- There are nine daughters of Ægir.
- There are nine mothers of Heimdall.
- There are nine great worms: Jörmungandr, Níðhöggr, Grábakr, Grafvölluðr, Ofnir, Svafnir, Grafvitni and his sons Góinn and Móinn.
- The god Hermóðr rode Sleipnir for nine nights on his quest to free Baldr from the underworld.
- The jötunn Baugi had nine thralls who killed each other in their desire to possess Odin's magical sharpening stone.
- The god Njörð and his wife Skaði decided to settle their argument over where to live by agreeing to spend nine nights in Þrymheimr and nine nights at Nóatún.
- The jötunn Þrívaldi has nine heads.
- The clay jötunn Mokkurkalfi measured nine leagues high and three broad beneath the arms.
- When Odin sacrificed himself to himself, he hung upon the gallows of Yggdrasil for nine days and nights. In return, he secured rúnar 'runes, secret knowledge'.
- There are nine surviving deities of Ragnarök, including Baldr and Hödr, Magni and Modi, Vidar and Váli, Hoenir, the daughter of Sól and a ninth "powerful, mighty one, he who rules over everything".[2]
Other
- The valknut symbol is three interlocking triangles forming nine points.
See also
Notes
- ^ a b Simek (2007), pp. 232–233.
- ^ This last being from Völuspá, who will "come from on high", is found only in the Hauksbók manuscript. Some scholars, including Lindow (2001), p. [page needed], consider this to be a later Christian interpolation and a reference to the Last Judgment.
References
- Lindow, John (2001). Handbook of Norse Mythology. Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-515382-0.
- Simek, Rudolf (2007). Dictionary of Northern Mythology. Translated by Angela Hall. D.S. Brewer. ISBN 978-0-85991-513-7.
