2-Pyrone
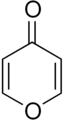
2-Pyrone (α-pyrone or pyran-2-one) is an unsaturated cyclic chemical compound with the molecular formula C5H4O2. It is isomeric with 4-pyrone.
2-Pyrone is used in organic synthesis as a building block for more complex chemical structures because it may participate in a variety of cycloaddition reactions to form bicyclic lactones. For example, it readily undergoes Diels-Alder reactions with alkynes producing, upon loss of carbon dioxide, substituted benzenes.[1]. The Gogte Synthesis (1938) is a method for the alkylation of certain pyrones with acid chlorides [citation needed].
2-Pyrone also forms the core structure of a variety of natural organic compounds. For example, the coumarins are an important class of compounds which are benzo-fused derivatives of 2-pyrone.
-
4-Pyrone
-
Coumarin
References
- ^ Woodard BT, Posner G H. "Recent Advances in Diels-Alder Cycloadditions Using 2-Pyrones." Advances in Cycloaddition. 1999, 5, 47-83.