Boger pyridine synthesis
The Boger pyridine synthesis is a cycloaddition approach to the formation of pyridines named after its inventor Dale L. Boger, who first reported it in 1981.[1] The reaction is a form of inverse-electron demand Diels-Alder reaction in which an enamine reacts with a 1,2,4-triazine to form the pyridine nucleus.[2][3] The reaction is especially useful for accessing pyridines that would be difficult or impossible to access via other methods and has been used in the total synthesis of several complicated natural products.[4]
Mechanism
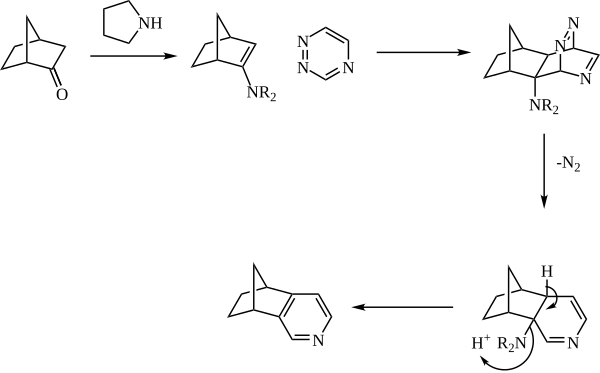
The enamine is generally generated in situ from catalytic amine (such as pyrrolidine) and a ketone. The enamine then reacts as the dienophile with a 1,2,4-triazine. The initial adduct then expels nitrogen, and the pyridine is rearomatized with loss of the amine.
References
- ^ Boger, Dale L.; Panek, James S. (May 1981). "Diels-Alder reaction of heterocyclic azadienes. I. Thermal cycloaddition of 1,2,4-triazine with enamines: simple preparation of substituted pyridines". The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 46 (10): 2179–2182. doi:10.1021/jo00323a044.
- ^ Boger, Dale L. (October 1986). "Diels-Alder reactions of heterocyclic aza dienes. Scope and applications". Chemical Reviews. 86 (5): 781–793. doi:10.1021/cr00075a004.
- ^ Li, Jie Jack (2002). Name Reactions A Collection of Detailed Reaction Mechanisms. Berlin: Springer-Verlag. p. 40. ISBN 3-540-43024-5.
- ^ . doi:10.1021/ja982078.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help); Missing or empty|title=(help)
