Portal:Tropical cyclones
The Tropical Cyclones Portal

A tropical cyclone is a storm system characterized by a large low-pressure center, a closed low-level circulation and a spiral arrangement of numerous thunderstorms that produce strong winds and heavy rainfall. Tropical cyclones feed on the heat released when moist air rises, resulting in condensation of water vapor contained in the moist air. They are fueled by a different heat mechanism than other cyclonic windstorms such as Nor'easters, European windstorms and polar lows, leading to their classification as "warm core" storm systems. Most tropical cyclones originate in the doldrums, approximately ten degrees from the Equator.
The term "tropical" refers to both the geographic origin of these systems, which form almost exclusively in tropical regions of the globe, as well as to their formation in maritime tropical air masses. The term "cyclone" refers to such storms' cyclonic nature, with anticlockwise rotation in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise rotation in the Southern Hemisphere. Depending on its location and intensity, a tropical cyclone may be referred to by names such as "hurricane", "typhoon", "tropical storm", "cyclonic storm", "tropical depression" or simply "cyclone".
Types of cyclone: 1. A "Typhoon" is a tropical cyclone located in the North-west Pacific Ocean which has the most cyclonic activity and storms occur year-round. 2. A "Hurricane" is also a tropical cyclone located at the North Atlantic Ocean or North-east Pacific Ocean which have an average storm activity and storms typically form between May 15 and November 30. 3. A "Cyclone" is a tropical cyclone that occurs in the South Pacific and Indian Oceans.
Selected named cyclone -
Tropical Depression Greg was a Pacific tropical cyclone that formed at an unusually low latitude in the South China Sea, and became the worst tropical cyclone to affect Malaysia since reliable records began. The last storm of the 1996 Pacific typhoon season, Greg formed on December 24 on the same two monsoon troughs that also spawned Tropical Storm Fern in the basin and cyclones Ophelia, Phil and Fergus in the Southern Hemisphere. The storm headed an east-southeastward track and despite an unfavorable environment for intensification, Greg strengthened to a tropical storm on Christmas Day. It then reached its peak intensity shortly, with maximum sustained winds of 85 km/h (55 mph) and a minimum barometric pressure of 1002 hPa before making landfall along the northern portion of the Malaysian state of Sabah between 1700 and 1800 UTC (3:00 - 4:00 am MYT) on December 26. After crossing the state, it weakened to a tropical depression before passing through Tawi-Tawi in the Philippines on the next day. Wind shear further degraded the system until it dissipated on December 27 on the Celebes Sea, south of Mindanao.
Greg was the only two systems to made landfall in Malaysia, before Vamei in 2001 did so, nearly five years later. The storm brought extensive and catastrophic damages across Sabah, causing over $280 million in damage (1996 USD) and 238 deaths, which mainly are foreigners and tourists. Another 102 individuals were also rendered missing. Flash floods and widespread mudslides were also recorded throughout the state, destroying houses and overflowing rivers, respectively. (Full article...)Selected article -
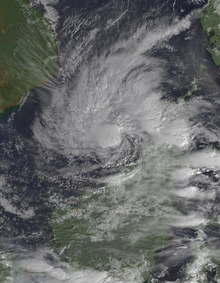
The 1943 Surprise Hurricane was the first hurricane to be entered by a reconnaissance aircraft. The first tracked tropical cyclone of the 1943 Atlantic hurricane season, this system developed as a tropical storm while situated over the northeastern Gulf of Mexico on July 25. The storm gradually strengthened while tracking westward and reached hurricane status late on July 26. Thereafter, the hurricane curved slightly west-northwestward and continued intensifying. Early on July 27, it became a Category 2 hurricane on the modern-day Saffir–Simpson hurricane wind scale and peaked with winds of 105 mph (165 km/h). The system maintained this intensity until landfall on the Bolivar Peninsula in Texas late on July 27. After moving inland, the storm initially weakened rapidly, but remained a tropical cyclone until dissipating over north-central Texas on July 29.
Because the storm occurred during World War II, information and reports were censored by the government of the United States and news media. Advisories also had to be cleared through the Weather Bureau office in New Orleans, resulting in late releases. This in turn delayed preparations ahead of the storm. In Louisiana, the storm produced gusty winds and heavy rains, though no damage occurred. The storm was considered the worst in Texas since the 1915 Galveston hurricane. Wind gusts up to 132 mph (212 km/h) were reported in the Galveston-Houston area. Numerous buildings and houses were damaged or destroyed. The storm caused 19 fatalities, 14 of which occurred after two separate ships sank. Overall, damage reached approximately $17 million (equivalent to $299 million in 2023). (Full article...)Selected image -

Selected season -

The 2007 Pacific hurricane season was a well below-average Pacific hurricane season, featuring only one major hurricane. The season officially started on May 15 in the eastern Pacific and on June 1 in the central Pacific, and ended on November 30; these dates conventionally delimit the period during which most tropical cyclones form in the region. The first tropical cyclone of the season, Alvin, developed on May 27, while the final system of the year, Kiko, dissipated on October 23. Due to unusually strong wind shear, activity fell short of the long-term average, with a total of 11 named storms, 4 hurricanes, and 1 major hurricane. At the time, 2007 featured the second-lowest value of the Accumulated cyclone energy (ACE) index since reliable records began in 1971. Two tropical cyclones – Cosme and Flossie – crossed into the central Pacific basin during the year, activity below the average of 4 to 5 systems.
Impact during the season was relatively minimal. In early June, Tropical Storm Barbara moved ashore just northwest of the Mexico–Guatemala border, causing $55 million (2007 USD) in damage and 4 deaths. In late July, Cosme passed south of the island of Hawaii as a weakening tropical depression; light rain and increased surf resulted. A few days later, Dalila passed offshore the coastline of southwestern Mexico, killing 11 and causing minimal damage. Hurricane Flossie followed a similar track to Cosme in mid-August, producing gusty winds and light precipitation in Hawaii. Hurricane Henriette in early September produced torrential rainfall in southwestern Mexico, killing 6 and causing $25 million in damage. Baja California received moderate rains from Hurricane Ivo in mid-September, though no damage nor fatalities were reported. In mid-October, Tropical Storm Kiko passed just offshore the coastline of southwestern Mexico. Though no deaths were reported on the Mexico mainland, the storm capsized a ship with 30 people on board, 15 of whom were recovered dead, and 9 of whom were reported missing. Overall, the season ended with $80 million in damage and 49 deaths. (Full article...)Related portals
Currently active tropical cyclones

Italicized basins are unofficial.
- North Atlantic (2024)
- No active systems
- East and Central Pacific (2024)
- No active systems
- West Pacific (2024)
- Severe Tropical Storm Gaemi
- Tropical Storm Prapiroon
- North Indian Ocean (2024)
- No active systems
- Mediterranean (2024–25)
- No active systems
- South-West Indian Ocean (2024–25)
- No active systems
- Australian region (2024–25)
- No active systems
- South Pacific (2024–25)
- No active systems
- South Atlantic (2024–25)
- No active systems
Last updated: 11:44, 21 July 2024 (UTC)
Tropical cyclone anniversaries

July 20,
- 1974 - Typhoon Ivy made landfall on eastern Luzon in the Philippines, killing 66 people.
- 1986 - Hurricane Estelle (pictured) attains Category 4 hurricane intensity while nearing Hawaii which caused only $2 million in damages including the deaths on two people.

July 21,
- 2006 - Tropical Storm Beryl briefly made landfall on Nantucket, Massachusetts. Beryl brought only minimal effects to the East Coast of the United States and Atlantic Canada.
- 2010 - Typhoon Chanthu (pictured) reached Category 1 typhoon intensity while nearing South China which caused about $324 million in damages and killing 13 people in total.

July 22,
- 2003 - Typhoon Imbudo (pictured) made landfall in the eastern Philippines. Imbudo killed a total of 41 people in the Philippines and China.
- 2015 - Typhoon Halola reaches its peak intensity as a Category 2 after originating in the Central Pacific.
Did you know…




- …that the Joint Typhoon Warning Center considers that Typhoon Vera (pictured) of 1986 is actually two distinct systems, formed from two separated low-level circulations?
- …that Hurricane Agatha (pictured) was the strongest Pacific hurricane to make landfall in Mexico in May since records began in 1949?
- …that Cyclone Raquel (track pictured) travelled between the Australian and South Pacific basins between the 2014–15 and 2015–16 seasons, spanning both seasons in both basins?
- …that Cyclone Amphan (pictured) in 2020 was the first storm to be classified as a Super Cyclonic Storm in the Bay of Bengal since 1999?
General images -

The list of Florida storms from 1950 to 1974 encompasses 85 Atlantic tropical or subtropical cyclones that affected the U.S. state of Florida. Collectively, tropical cyclones in Florida during the time period resulted in about $7.04 billion (2017 USD) in damage, primarily from Hurricanes Donna and Dora. Additionally, tropical cyclones in Florida were directly responsible for 93 fatalities during the period, as well as responsible for 23 indirect deaths. Several tropical cyclones produced over 20 inches (500 mm) of rainfall in the state, including Hurricane Easy which is the highest total during the time period. The 1969 season was the year with the most tropical cyclones affecting the state, with a total of 8 systems. The 1954 and 1967 seasons were the only years during the time period in which a storm did not affect the state.
The strongest hurricane to hit the state during the time period was Donna in 1960, which was the 8th strongest hurricane on record to strike the United States. Additionally, Hurricanes Easy, King, Isbell, and Betsy hit the state as major hurricanes.
(Full article...)Topics
Subcategories
Related WikiProjects
WikiProject Tropical cyclones is the central point of coordination for Wikipedia's coverage of tropical cyclones. Feel free to help!
WikiProject Weather is the main center point of coordination for Wikipedia's coverage of meteorology in general, and the parent project of WikiProject Tropical cyclones. Three other branches of WikiProject Weather in particular share significant overlaps with WikiProject Tropical cyclones:
- The Non-tropical storms task force coordinates most of Wikipedia's coverage on extratropical cyclones, which tropical cyclones often transition into near the end of their lifespan.
- The Floods task force takes on the scope of flooding events all over the world, with rainfall from tropical cyclones a significant factor in many of them.
- WikiProject Severe weather documents the effects of extreme weather such as tornadoes, which landfalling tropical cyclones can produce.
Things you can do
 |
Here are some tasks awaiting attention:
|
Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus