- For other places with the same name, see Peru (disambiguation).
Peru is without a doubt one of the most captivating countries in South America. Famously home of the epic lost Inca citadel of Machu Picchu and the mindblowing Nazca Lines, this country's unique past awakens the adventurer in travellers of all sorts. Its awe-inspiring scenery varies from the wild Amazon jungles to vast coastal deserts and the icy peaks of the Andes. In it, Peru hosts a biodiversity rarely seen within the limits of a single country, with a list of spectacular wildlife far beyond the well-known llama's and circling condors. On top of all that, Peru's friendly, multi-ethnic people are a cultural treasure on their own. The enchanting mix of dozens of distinct indigenous groups and mestizo's, all with their own colourful traditions and food delicacies, is an encounter you won't easily forget.
In short, this is a country of unimaginable extremes where choosing your trip destinations may prove a true challenge. Whether you decide to go off the beaten track, follow in the footsteps of thousands of visitors before you who took the Gringo Trail along some of the best highlights, or go experience the jungle through a relaxing multiple day Amazon boat trip - Peru is likely to amaze you in everything you do.
Understand
Despite 36% of the population (mostly Amerindians in rural areas) living under the poverty line, most Peruvians are nationalists and will talk with love and pride about their country. For many of them government, police and political affairs may be distrusted and criticized, as corruption and scandals are all around. However, that is not what makes up their beloved state of Peru. It's the rich natural resources and strong history as the centre of the ancient Inca and later colonial Spanish empires that inspire their nationalist sentiments.
The general view of the U.S. government isn't very positive either, due to the Peruvian economic dependence on the U.S and foreign policy decisions of their North-American neighbours. That widely held aversion however does not extend to individual American travellers, who'll be welcomed as anyone else.
You'll often encounter the term gringo, which originally referred to all white people who don't speak Spanish. Now, many people use it for Americans or American look-alikes only, but it's typically not meant to offend. Peruvians will not hesitate to greet you with "¡Hola, gringo!", especially if you're blonde.
As in many South-American countries, efficiency or punctuality aren't among Peru's many qualities. Go with the flow and don't expect things to be exactly on time or precisely as planned. Take into account that outside of the main tourist spots people will often not speak English, and -trying to be helpful- might give wrong or inexact advice. For some general advice, have a look at our Tips for travel in developing countries.
Electricity

Electricity in Peru is 220 Volts and 60 Hertz. Exceptions are Talara, where a mixture of 110 V, 60 Hz and 220 V, 60 Hz is used, and Arequipa with 220 V, 50 Hz.
Two types of electrical outlets are used: one accepts two-pronged plugs with flat, parallel blades, the other one accepts plugs with two round prongs. Many, but not all outlets accept both. Grounded outlets exist but are uncommon. If you want to use a 110V device, make sure to check if it can take 220V, as you'll otherwise risk breaking your equipment. If not, bring a power adaptor. It's not recommended to adapt a three pin plug for use in a two pin outlet.
Time Zone
Peru Time (PET) is 5 hours behind Coordinated Universal Time (UTC/GMT). There's no daylight saving time.
History
Peru's oldest complex society called the Norte Chico civilization flourished in 3,000 B.C. Early developments were followed by cultures such as Cupisnique, Chavin, Paracas, Mochica, Nazca, Wari and Chimu. In the 15th century, the Inca Empire became the largest empire in the Americas.
Regions
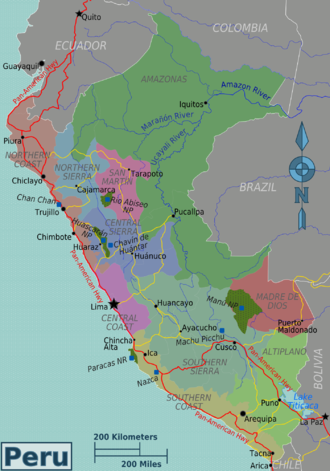
| Central Coast |
| Southern Coast |
| Northern Coast |
| Southern Sierra |
| Central Sierra |
| Northern Sierra |
| Altiplano |
| San Martín |
| Peruvian Amazon |
| Madre de Dios |
Cities
Other destinations
- Chan Chan — impressive set of ruins of an ancient Chimor mud city, and a UNESCO World Heritage site
- Chavín de Huántar — UNESCO World Heritage Site from the pre-Incan Chavin culture of around 900BC
- Huascarán National Park — high mountain park in Cordillera Blanca range
- Lake Titicaca — considered to be the highest commercially navigable body of water in the world
- Machu Picchu — this UNESCO World Heritage site is one of the most familiar symbols of the Incan Empire, and is one of the most famous and spectacular sets of ruins in the world
- Manú National Park — one of the most diverse areas in Peru
- Nazca lines — world famous for its geometrical figures and giant drawings in the desert sand
- Paracas National Reservation — a popular nature reserve on the Southern Coast
- Río Abiseo National Park
- Máncora — small beachtown with the best beaches and great surf, turns into a real partytown on weekends and holidays
Get in

Visas
Tourists from North America, Australia, Japan, Malaysia, Singapore and the European Union (and many others, check with the nearest Peruvian Embassy [1] or the Ministry of Foreign Affairs [2] for most updated information, although in Spanish) receive a visa upon arrival for up to 180 days.
When entering the country, you need to pass the immigration office (inmigración). There you get a stamp in your passport that states the number of days you are allowed to stay (usually 180 days). You can no longer get an extension, so make sure that you ask for the amount of time you think you'll need. When those 180 days are up and you would like to stay for longer, you can either cross the border to a neighbouring country (Ecuador, Colombia, Brazil, Bolivia or Chile) and return the next day and obtain another 180 days or simply overstay and pay the fine when you exit. The overstay fine is only US$1 per day overage, so if you stay 30 days longer it's US$30. Many people do this, since it's much cheaper than leaving the country and returning.
You will receive an extra official paper to be kept in the passport (make sure you don't lose it!). When leaving, you need to visit the emigration office (migración), where you get the exit stamp. Inmigración and migración are found on all border crossing-points. Traveling to and from neighboring countries by land is no problem.
By plane
The capital city of Lima has the Jorge Chávez International Airport with frequent flights all over the world. Main airlines are American Airlines, Delta, Lan, Lan Peru, Iberia, Copa, Taca, United and others. There are non-stop flights to Lima from Atlanta, Houston, Los Angeles, Miami, Newark, New York City, and San Francisco in the United States. There is also a non-stop flight to Toronto, Canada with Air Canada. There are five different airlines that offer non-stop service to Europe. In the future there may be non-stop flights from Oceania or Asia but for now travelers usually connect through Los Angeles (non-U.S.-citizen have to pass immigration even for transfer, consuming 1-2 hours - so ensure your stop-over is long enough!) or through Santiago de Chile.
The city of Iquitos has flights to Leticia, Colombia with AviaSelva. They have a US$10 departure tax.
For example, Iberia flies directly from Madrid to Lima, the trip lasting around 13 hours. However LAN and KLM flights are much better in quality. LAN and Iberia often fly in code share mode (1 plane, 2 flight codes) meaning if you've a LAN flight, you may have to check in at Iberia service desk or the opposite way, sometimes they send you from one to the next and back, so just queue at the shorter service desk. There is an internal flight tax, around US$6, same conditions as the international one.
When booking domestic flights, there are several Peruvian travel agencies that can get you your plane tickets for the "Peruvian price" for a fee of about US$20, you'll notice that the prices can vary by several hundred dollars for the SAME flights when looking at LANs Peruvian site (http://www.lan.com/index-es-pe.html) and the USA site (http://www.lan.com/index-en-us.html). You'll find that if you try to book the cheaper flights from the Peruvian site, they won't accept payment from American bank accounts (this is why you do it through a Peruvian travel agency).
Make sure to confirm your ticket 72 hours in advance, as you'll risk being bumped off your flight if you don't. Most travel agencies can do it for you, if you want.
From Ecuador
Although Ecuador neighbors Peru, it is hard to find cheap flights connecting anything but the capitals. In particular, flying from Ecuador to Iquitos is not possible directly, nor can you travel directly from other large towns across the border.
By boat
The city of Iquitos in the Amazonas region has connections by boat to Leticia in Colombia and Tabatinga in Brazil (about 10 hours).
Get around
Times and Distances
Yurimaguas-Iquitos(water): 2.5 days
Quito-Lima(bus): 25 hours
Lima-Cuzco(bus): 21 hours
Lima-Cuzco(plane): 1 hour
In cities and around
Inside the cities, there is usually no problem getting around on city buses or taxis. Buses cost between 0.70 and 1.50 Soles (US$0.20-0.40) inside a city, taxis between 7 and 8 soles (US$2-2.60) in Lima, normally less in other cities. "Taxi" does not necessarily mean a car; the term also refers to bicycles, motor rickshaws, and motor bikes for hire. Taxis are divided between "formal" taxis, painted and marked as such and have a sticker with SOAT, and informal ones, that are just cars with a windshield sticker that says "Taxi". The last ones are better left to the locals, especially if you don't speak Spanish. Apart from the more upscale radio taxi (also the more expensive ones), the fare is not fixed or metered, but it is negotiated with the driver before getting into the vehicle. Ask at your hotel or hostal about the rate you may expect to pay to ride to a specific location to have a point of reference. There is no tipping at taxis.
"Micros" (from microbus), are small minivans or Coaster buses, also known as "combis" and "custers". They do not have actual bus stops (they exist, although in practice the driver won't stop unless you ask), but fixed routes. The direction is shown by boards in the windscreen or painted on the side. If you want to catch a bus, just give the driver a sign (raise your hand similar to hitch-hiking) to stop. If the bus is not completely overfilled (and sometimes when it is, too), it will stop to pick you up. During the ride, the ticket collector will ask you for the fee or, if there is not a ticket collector, you pay the driver when you get off (this is more common when taking longer trips where most people are going to the last stop, for example from Ollantaytambo to Urubamba). If you want to exit, just say loudly "Bajo!" (BAH-ho) or "Esquina baja!" (s-KEE-nah BAH-ha), and the driver will stop at the next possibility. They are cramped and dirty, and not helpful unless in small towns or during off peak hours. They also stop in the middle of the road, so be careful when getting down.
Please note: Micros are very common but known for being quite dangerous, different government programs are trying to reduce the amount of micros, it is advised to not take a micro.
By bus
Some main roads, especially along the coastal strip, are paved, but there are still a lot of dirt roads in very poor condition. In the rainy season, landslides may block even major roads.
Inter-city travel is mostly by bus, and some cities have train connections. In contrast to colectivos, buses, and of course trains, start from fixed points, either the central bus terminal or the court of the appropriate bus company. It is a good idea to buy your ticket one day in advance so that you can be relatively sure of finding a seat. If you come directly before the bus leaves, you risk finding that there are no more seats available. In most bus terminals you need to buy a separate departure tax of 1 or 1,5 soles.
If you are so unlucky as to be taller than 1.80m/5'11", you will most likely be uncomfortable on the ride since the seats are much tighter than in Europe or some parts of North America. In this case, you can try to get the middle seat in the rear, but on dirt roads the rear swings heavily. In older buses, the seats in the first row are the best, but many buses have a driver cabin separated from the rest of the bus so that you look an a dark screen or a curtain rather than out the front windshield. In older buses, you can get one or two seats beside the driver, which gives you a good view of the passing landscape. In this case, don't be too surprised when the driver is chewing his coca leaves.
First-class express buses, complete with video, checked luggage and even meal service, travel between major cities, but remember to bring ear plugs as the video on these buses may be played extra-loud for the majority of the trip. You may need to present a passport to purchase a ticket.
Make sure that your luggage is rainproof since it is often transported on the roof of the bus when travelling in the Andes.
Avoid bus companies that allow travellers to get into the bus outside the official stations. They are normally badly managed and can be dangerous, due both to unsafe practices or to highway robberies, which are unfortunately not uncommon. This should be heeded especially by female travellers going on their own. There are many shoddy bus services in Peru, and it's best to go with one of the major companies such as Cruz del Sur, Oltursa or Ormeño. Get information at the hotel, hostal or tourist information booth before catching a ride.
By train
Even when going by train, it's best to buy the ticket in advance. Buy 1st class or buffet class (still higher), or you risk getting completely covered by luggage. People will put their luggage under your seat, in front of your feet, beside you and everywhere where some little place is left. This makes the journey quite uncomfortable, since you can't move any more and the view of the landscape is bad.
There are five rail lines in Peru:
- Cuzco - Machu Picchu
- Cuzco - Juliaca - Puno
- Arequipa - Juliaca
- Lima - Huancayo
- Huancayo - Huancavelica
Service between Arequipa and Juliaca has been suspended as of early 2007.
For more information on [trains to Machu Picchu], go to PeruRail's web site [3].
The Ferrocarril Central Andino the line joining Lima to Huancayo is the second highest railway in the world and the Highest in South America. The Journey on board of the Train of the Andes, through the heart of Peru is simply breathtaking. It is an 11 hour experience where the train reaches an altitude of 4781m.a.s.l (15,681 ft) and goes through 69 tunnels, 58 bridges and makes 6 zigzags. In 1999, the company was privatized, in 2005, Ferrocarril Central Andino renovated their passenger wagons in a Luxurious and comfortable way which puts the railway in the list of the most famous trains along with the Orient Express and the Transsiberien.
By foot
Beside the famous Inca trail to Machu Picchu, you can do a lot of more hikes all along the Sierra, preferably in the dry season. The hiker's Mecca is Huaraz, where you can find a lot of agencies that offer guided tours and/or equipment to borrow. The thin vegetation in the higher Sierra makes off-trail hiking easy. Good maps are hard to find inside Peru. It is better to bring them from home. Make sure you have enough iodine to purify your drinking water. When hiking in higher altitude, good acclimatisation is absolutely necessary. Take a good sleeping bag with you, since nights in the Sierra may become bitterly cold (-10°C in 4,500 m altitude are normal, sometimes still colder). Beware of thunderstorms that may rise up very suddenly. Rapid falling temperature and hard rain falls are a serious danger in higher altitudes. Don't forget that the night lasts for 12 hours year-round, so a flashlight is a good idea. When hiking on higher, but not snow covered mountains, water may be rare. Getting alcohol for stoves is easy: Either buy the blue colored alcohol de quemar or, better, simply buy pure drinking alcohol. You can get this in every town for about 3 Soles (US$0.85) per liter. (Don't even think about drinking it). It won't be so easy to find special fuel for gasoline stoves. Gasoline for cars can also be found in many hardware stores (ferreterias) sold by liters, but you can actually buy it directly on gas stations, provided you bring your own bottle.
By car
It is also possible to tour the interior of the country by car. This gives you a chance to get "off the beaten track" and explore some of the areas that haven't been transformed by tourism. An international driver's license is needed for driving in Peru.
Peru has three main roads which run from north to south: the fully paved Panamericana (RN 1) which passes through the whole country; more to the east there are the partially paved Carretera de la Sierra (RN 3) as well as the Carretera Marginal de la Selva (RN 5). Most parts of these roads are toll roads in the direction from north to south. The main roads are connected by 20 streets from west to east.
Beware that, aside from a few major roads which are in good condition, most roads are unpaved and your speed on them will be severely restricted. For these roads a 4WD is necessary. This is especially true during the rainy season from November to April. You should travel very well informed about your route. Take a good road map with you (e.g. Waterproof Peru Map by ITMB). On the web, cochera andina provides useful information about road conditions, travel times and distances for more than 130 routes in Peru.
Be sure to bring plenty of gas, as gas stations in unpopulated areas are very rare and will oftentimes be closed. Purchasing gas late at night can be an adventure all its own, as even in more populated areas gas stations tend to close early and the pumps are locked. The owner of the station sometimes sleeps inside and, if you can rouse him, he will come out and let you fill up. Be aware of the higher gasoline consumption in the mountains which often increases to more than 20 l/100 km (12 MPG) (5 gal/62 mi).
The traffic regulations are almost the same as in Europe and the U.S. But locals tend to interpret them freely. You better honk in unclear situations, e.g. in curves and at crossings to indicate the right of way. Also note that traffic checkpoints tend to be scattered throughout the country and the police may try to extract bribes from foreigners for passage. It would be wise to travel with a native speaker who can navigate the roads and deal with law enforcement.
Touting
Like in most countries, also in Peru there is a vast crowd of touts hanging around the airports and bus stations or bus terminals. It is any travellers' wise decision not to do business with the people that are trying to sell you their stuff on the street/bus station/airport. First of all, if they would have a decent place, they wouldn’t have to sell it to non suspecting tourists trying to drag them off from wherever they can find them. More important, it really is not a good idea to hand out money to the first person you meet upon arriving somewhere.
TIP: When you arrive in any town, be sure to have already decided what hotel you will be going to. Don't mention this or any other information to the touts awaiting you. They will use whatever you tell them to construe lies to make you change your mind and go with them. If you’ve already picked a reasonable hotel chances are that you will be OK there and they will have any (extra) information you’d be looking for, like bookings for tours or tickets.
Talk

- See also: Spanish phrasebook
The official language of Peru is Spanish, as in many South-American countries. It's worth getting familiar with some basic Spanish words, as you'll need them to make your way around outside the main tourist centres. Although English is spoken by an increasing number of young people in Lima and to a limited extent in the most popular tourist spots, you'll find English far less commonly understood than you might expect in a country where tourism is such a big industry.
Like in other Latin American countries, Peruvian Spanish replaces vosotros (and its 2nd-person plural conjugations) with ustedes (3rd-person plural). As an example: ¿Cómo estáis? becomes ¿Cómo están?. Also, South American Spanish likes diminutives (gringuito is more affectionate than gringo).
Especially when you're making your own way around, learning some Quechua or Aymara may open doors, as indigenous people will highly appreciate your effort. Quecha is the language of the Incas and the first language for many indigenous in the countryside of the Sierra. Aymara was the language of the Tihuanacu culture. Though not recognized as an official language, it's widely spoken on the Altiplatano. In both cases however, people will generally speak English too.
See


Forgotten temples in dense Amazon jungles, lost Inca cities, fabulous wildlife and extra-ordinary folklore. Peru holds all the stuff adventure movies are made of.
Many of the best Inca sites are around the beautiful city of Cusco, once the capital of the Inca Empire and now a World Heritage Site itself, as well as a bustling city. Book at least half a year in advance if you want to walk the famous 3 day hike Inca Trail, which commonly starts at the 15th century Inca dwellings of Ollantaytambo. Your imagination must be on its A-game to see past the large crowds at the end destination, Machu Picchu, but it's worth your trouble. Wait for the biggest crowds to leave, find a quiet spot away from the tourist hassle and contemplate your view of one of the most famous and spectacular archaeological sites in the world. The list of great Peruvian ruins from Pre-Columbian times is long, and not all of them are of Inca origin. A World Heritage Site, the ancient adobe capital Chan Chan, built by the Chimú culture, was conquered in the 15th century. Other popular sites are the tombs of Sipán, the ruined fortress of Kuelap, the pre-Incan burial grounds of Sillustani, and Caral, the most ancient city in the Americas. Particularly well-known are the spectacular Nazca lines, which you should see from the air, even if it'll take some haggling to get your ticket for the right price.
Natural attractions
Home to 84 out of the 104 recognized ecological zones in the world, Peru is incredibly rich in biological diversity. Benefiting from a broad array of landscapes and ecosystems, this country is a Valhalla for anyone who loves wildlife. It's condors, llama's and jaguars that Peru is famous for, but almost a third of the bird species in the world and no less than 4000 butterflies live here too.
One of the best places to see all of this natural beauty is Manú National Park. This World Heritage Site boasts over 15000 plant species, a 1000 different birds and some 220 mammals, including pumas, Giant anteaters and many monkeys. Disputably called the "world's deepest canyon", the stunning Colca Canyon is Peru's third most-visited destination, just a stones-throw out of the beautiful city of Arequipa. Get close to the celebrated Andean Condors as they fly along the high canyon walls or buy a colourful handmade souvenir from one of the indigenous people that populate the picturesque Colca Valley. Of all the peaks in the Peruvian Andes, the 6768m Huascarán in Huascarán National Park is the highest of all. This 3000 km² World Heritage Site holds 663 glaciers, 296 lakes and 41 tributaries of three major rivers. The large city of Iquitos is a popular starting point to discover the mystic Amazon River, one of the seven natural wonders of the world. It's also the capital city of the Charapa culture. Just a few other great picks out of the long list of protected areas in Peru are Pacaya-Samiria National Reserve, Rio Abiseo National Park and Cutervo National Park (with many caves).
Folklore
The diversity of Peru's people and cultures is reflected in a rich tradition of festivals, dance and music. In the Andes, the plaintive wail of the flute and beat of the drum accompany songs depicting indigenous life while dancers masked as devils and spirits are a marriage of pagan and Christian beliefs. In the jungle, ceremonial music and dance are a window into tribal life. And along the coast, a blend of elegant Spanish sounds and vibrant African rhythms reflect the Conquest and later slave labor of the New World.
Other highlights
Make your way to the blue waters of Lake Titicaca for an enchanting, high altitude encounter with local peasant women wearing bowler hats and join in the celebrations of their ancient communities. Puno is a good place to start, also for a laid-back boat ride to the various islands and Altiplano towns on and around the lake, all with their own character and historic remains. If you're craving perfect beaches and a sunburn, head to the crowded sands and resorts of Máncora. Spend a day in one of the many excellent museums in Lima and dance until the morning in one of the cities popular clubs. Buy shamanistic herbs at the market of Chiclayo and see the dozens of tombs around it.
Do
Trekking is a great way to see the country. The most widely known route is the classic Inca Trail to Machu Picchu. Other popular routes include Cordillera Blanca, Colca Canyon, Ausangate Trek and Salcantay (also spelt Salkantay) Trek.
Trek prices can vary considerably between companies, as can their respective porters' working conditions (no pack animals are allowed, hence equipment is carried by human porters). Although there is a minimum porter wage (42 Soles/day, about US$15) and maximum load porters can carry (25 kg/55 lb), not all companies keep to their claims!
Buy
The currency of Peru is the nuevo sol. As of 26 November 2013, US$1 = S/.2.80 and 1€ = S/.3.80 (S/. is the symbol for "nuevo sol"). Coins are available in five, two and one sol, and in 50, 20, 10, 5 and 1 centimo. 5 and 1 centimo coins are not normally accepted outside of big supermarkets or banks, so avoid them (or bring them home for a collection or to give to friends). Notes are available at 10, 20, 50, 100 and 200 soles denominations; 200 soles notes are uncommon and - just like large bills in other countries - will not be accepted in many places.
ATMs are available in big cities, upmarket hotels, and touristic areas. With a Cirrus or Maestro sign on it, you can withdraw cash easily. The exchange rate is the same as credit cards but fees are much lower. Some banks charge a fee for getting cash from their ATM's, with BBVA Banco Continental reportedly charging excessive fees without telling you in advance. Make sure to carry sufficient cash when visiting smaller towns, as your credit card or traveler checks might not be accepted there.
Credit cards and travelers checks are common. Although cash has a ca. 2% better change rate, you are strongly advised not to carry large amounts of cash on your journey. The Banco de Credito (BCP) gives good rates on traveler checks. Rates in change offices are often somewhat worse. It's always worth comparing them before changing your money. When changing your money in change offices, check their calculations. Most of them make calculations on the fly for the amount you want using an electronic calculator in plain view, even showing you the process step by step (unless they are brutally obvious, like changing tens or hundreds). If they don't show, keep the money in your pocket and find someone that does.
Always keep in mind that counterfeiting is a big problem in Peru: make sure to get familiar with the money and do not hesitate to reject any note or coin (especially the 5 sol coins) that look suspicious, just like any Peruvian would do. In other words, if you want to look like a savvy foreigner, take 10 seconds to check any paper note you get, even at a bank. All bills have a watermark and security stripe, and the large number on the extreme right denoting the denomination of the bill will change from purple to green when viewed at an angle. Don't take any note that is ripped; you won't be able to use it anywhere else but a bank.
If you are stuck with a counterfeit coin or note, if you try to use it at big stores they may want to confiscate it. Don't accept damaged/ripped bills, since you will have to take them to a bank in order to change them into new ones before you can spend them. Be especially careful when exchanging money with money-changers on the street (a common way for counterfeit money to enter the money supply) or at the border (notably the one with Ecuador).
Typically, small bills are very helpful to carry around. Change large bills into small ones as often as possible. If you only have 50 and 100 Soles notes on you, consider changing them at a bank. Local merchants and taxistas often claim to not have any change on them, forcing you to wait in public while they search for some (potentially dangerous) and sometimes with the hope that you'll grow impatient and let them keep the change.
In Peru, it's not as common for US$ to be accepted in transactions as in other countries (such as Ecuador), but some nice, new 10 or 20 US$ bills can be helpful in some situations. Often in small towns, local shops will change money for you. If so, it will be clearly marked.
Costs
If you're on a budget, you can get around well for US$50 a day. Basic hotels or hostels (hospedajes) are available everywhere, with dorm beds in youth hostels typically costing US$8-15. You'll find plenty of very cheap restaurants (US$0.50-1.50) but for slightly more (US$2 -3) you'll get an often much better lunch or dinner at better restaurants. Fancy restaurants are available in every city, with menus starting from US$20.
Buses are a fairly cheap way to get around. A 10 hour bus ride in a normal bus (not "Royal Class" or something like that) will set you back about US$6. If you can afford it, the more luxurious seats go for about double the price but will make a great difference in terms of comfort. Avoid bus companies that allow travellers to get into the bus outside the official stations. They are often badly managed and can be dangerous, due both to unsafe practices or to highway robberies, which are unfortunately not uncommon. This should be heeded especially by female travellers on their own. Your hotel, hostel or a local tourist information booth can point you to the better options.
Trains (except the ones for Machu Picchu, which are relatively expensive) run for similar fees.
Don't forget to retain your exit fee of US$30.25 They do accept USD or Soles for the fee and be sure to pay the exit fee before you get in line for security checks or you'll get to wait again.
Handicrafts
Peru is famous for a lot of different, really nice and relatively cheap handicrafts. Keep in mind that buying handicrafts support traditional skills and helps many families to gain their modest income. Look for:
- Pullovers, and a lot of other (alpaca-)woolen products in all the Sierra. Puno is maybe the cheapest place.
- Wall carpets (tejidos).
- Carvings on stone, wood and dried pumpkins.
- Silver and gold jewellery.
- typical music instruments like pan flutes (zampoñas), skin drums.
- many other
Do not accept any handicrafts that look like (or actually are) precolumbian pottery or jewelry. It is illegal to trade them and there is the possibility not only of them being confiscated, but of being prosecuted for illegal trading, even if the actual artifacts are copies or fakes. Dealing with the police from the criminal side is messy and really unpleasant.
Buyer beware: Watch out for fake (Bamba)Alpaca wool products many items sold to the unsuspecting gringo are actually synthetic or ordinary wool! That nice soft jumper in the market for US$8 or so is most certain to be acrylic. Even in places such as Puno there is no easy way to tell if it is made from Alpaca, sometimes it might have a small percentage of Alpaca mixed in with other fibres. Baby Alpaca is not from baby animals but the first shearing and the fibre is very soft and fine. Generally Alpaca fibre has a low lustre and a slightly greasy hand to it and is slow to recover from being stretched. Shop and compare; real Alpaca is expensive.
Bargaining
Bargaining is very common. If you are not used to it, respect some rules. If you intend to buy something, first ask the price, even if you already know what it actually should cost. Then check whether everything is all right. (Does the pullover fit you? Do you really want to buy it? Is the expiration date on the cheese exceeded? etc.) If the price is OK, pay it. If not, it's your turn to say a lower price, but stay realistic. First get an idea about how much you would expect to pay. Then say a price about 20-30% lower. It's always good if you can give some reason for that. Once you have said a price, you cannot give a lower one later. This would be regarded as a very impolite behavior. If you feel that you can't get your price, just say "No, gracias." and begin to walk away. This is your last chance. If you are lucky, the seller will give you a last offer, if not, say "No, gracias." again and go on walking. Realize that most of the products in touristy markets (i.e. the market in Pisac) will be sold in nearly every other market throughout your travels in Peru and South America, so try not to worry about never again finding that particular alpaca scarf.
You have a way for bargaining without saying an exact price, and it's saying "¿Nada menos?", then you will be asking just if they can lower a bit the price.
Keep in mind: Never begin to bargain if you don't really want to buy.
General Notes
Supermarkets can only be found in cities and are somewhat expensive. In every town, there is at least one market place or hall, except Lima that has a dense concentration of supermarkets, malls and department stores. In cities, there are different markets (or sections of one big market) for different articles.
Stores with similar articles tend to be grouped in the same street. So, if you once know the appropriate street when looking for something special, it shouldn't be no more problem to find it quite soon.
Giving tips in restaurants (at least when basic or middle-range) is not very common but 10% for good service is polite. In the cities, you will always find some beggars, either sitting on the streets, or doing a musical number on the buses. Many of them really need help, especially the elderly and handicapped. Usual givings are about 0.10 - 0.20 Soles (US$0.03-0.06). This is not much, but some unskilled workers don't get much more than 10 Soles for a hard working day. Whether you want to give money to child beggars or not is your decision. But consider that doing so may make it more attractive for parents to send their children begging in the street instead of sending them to school. Buy them food instead, they do need it.
Eat


Peruvian cuisine is among the most varied in the world. Not only does the country grow a variety of fruits and vegetables, but it does so throughout the year. Peruvian geography offers at least 8 different climates (desert along the coast, steep and high mountains, the Amazon basin). In Lima, due to its history as an important Spanish colonial port, the dishes are a mixture of amerindian, Spaniard, African, Asian and even Italian influences that contribute to the ever changing platos criollos (creole dishes). Rice is the staple foodstuff, and expect many dishes to include rice, in the Siera it's corn and potatoes, and in the Jungle yuca. Meat is traditionally included in most Peruvian dishes. Chicken (pollo), pork, sheep and beef are common. Alpacas are actually kept for wool, not for meat. Mostly, you will find that alpaca meat is rather tough. An Andean delicacy is guinea pig (cuy). Peruvian cuisine includes dishes which use various organs, including anticuchos, a kebab made from very marinated and spicy beef heart, and cau-cau (sounds like cow-cow), made from cow stomach served in a yellow sauce with potatoes. Anticuchos are a standard street stall food, but be careful with it.
Fish can be found along the coast (of course), but also in the jungle area since the rivers supply fresh fish (but beware of contamination in the area known as high jungle or selva alta, where most of the cocaine is made and strong chemicals get dumped into rivers; mining is a minor source of pollution in this area). In the Sierra, trout (truchas) are bred in several places. A very common fish dish is ceviche, raw fish prepared by marination in lime juice. Popular variations of the dish can include shellfish, and even sea urchin. The exact recipe and mode of preparation of ceviche will vary from region to region. Definitely worth a try, especially in summer, but cleanliness and sanitation make all the difference. Use care when buying from street vendors and remember that it is often served spicy.
Throughout Peru there is a wide variety of potato dishes (papas, not patatas as in Spain), the traditional Andean vegetable. Papa a la Huancaina is a tasty dish of potato slices and diced boiled egg topped with a thin, creamy yellow sauce, and usually includes a lettuce leaf and an olive or two. (A similar green sauce, called Ocopa, can be served over potatoes or yuca.) Papa rellena is mashed potato reformed into a potato-like shape, but with meat, vegetables, and other spicy filling in the middle. Aji de gallina is shredded chicken in a thick, spicy, cheese-based sauce over sliced potatoes, often with an olive and slice of hard-boiled egg. Causa is mashed potato layered with mayonnaise-based tuna or chicken salad mixed with hot peppers.
Many Peruvian dishes can contain strong condiments and be heavy, so if you have a weak stomach, proceed with caution.
Nowadays, the transport routes from the flat jungle areas are good enough to supply all the country with vegetables and fruits. Nevertheless, vegetables still have the status of a garnish for the meat. Vegetarian restaurants exist in all cities, but are relatively rare. In most areas, there is a rich offering of tropical fruits and fresh squeezed juices.
The natives typically eat in small restaurants or Chinese eateries ("chifas"); a menu there costs 5-8 Soles and includes a soup, a choice of main dish, and a drink.
If you count on international fast food chains, you will be disappointed. You find them almost nowhere except in the largest cities, and the prices are uniformly astronomical.
Peruvians are quite proud of their desserts, especially in Lima. Try them with care, since they tend to be extremely sweet and loaded with sugars, eggs yolks and similar ingredients. Try mazamorra morada, or purple custard, made from the same purple corn used for chicha morada drink; together with arroz con leche (rice with sweetened condensed milk) is called a combinado (combination). Picarones are a sort of donut, made from fried yams dough and served with chancaca, a very sweet sugarcane syrup. And the sweetest dessert suspiro Limeño is perfect if you are in sore need of a high-calorie glucose shock.
Drink
The Pisco-Nasca area is famous for wine cultivating. Their more expensive vintages compare favorably against Chilean imports. Beer is nice, stronger than American brands but less full bodied than European ones. Most of Peruvian beers are made by Backus, currently owned by SAB Miller.
When drinking at bars and/or restaurants, be aware that Peruvian "Happy Hour" is a little different than in most countries. Prices for drinks will usually be posted on the walls and be a little cheaper than normal. The real differences is that you will be served 2 drinks, instead of one, for the listed price -- giving a new meaning to the term "half price." This can be a great way to save money (if you are traveling with a group) or to meet locals (if you are traveling alone). It can also lead you to get completely falling-down-drunk by accident, so be careful.
- Caliente is a hot alcoholic drink served during celebrations in Andean towns such as Tarma. Its basically a herbal tea with white rum for that added kick.
- Chicha de Jora, A cheap traditional alcoholic drink made from corn that is fermented and rather high in alcohol content for a non-distilled beverage. Not normally available at formal restaurants and quite uncommon in Lima outside of residential areas. Places that sell chicha have a long stick with a brightly-colored plastic bag on it propped up outside their door.
- Chicha morada, not to be confused with the previous one, is a soft drink made from boiled purple corn, with sugar and spices added (not a soda). Quite refreshing, it is widely available and very recommendable. Normally Peruvian cuisine restaurants will have their freshly made supply as part of the menu; it is also available from street vendors or diners, but take care with the water. Bottled or canned chicha morada is made from concentrates and not as pleasant as freshly-boiled chicha.
- Coca Tea or Mate de Coca, a tea made from the leaves of the coca plant. It is legal to drink this tea in Peru. It is great for adjusting to the altitude or after a heavy meal. It may be found cold but normally is served hot.
- You can find many places that serve fresh fruit drinks. Peru has a wide variety of fruits since its natural variety, so if you get a good "jugueria" you will have lots of options to choose from.
- The Peruvian amazon cities offer some typical drinks too as: masato, chuchuhuasi, hidromiel and others.
- Coffee. Peru is the world's largest producer of organic coffee. Ask for 'cafe pasado', the essence produced by pouring boiling hot water over fresh ground coffee from places like Chanchamayo.
- All of Peru's wines are inexpensive. Tacama, Ocucaje and Santiago Queirolo branded wines are the most reliable.
- Emoliente. Another popular drink in Peru, often sold in the streets by vendors for 50 centimos. Served hot, its flavor is best described as a thick, viscous tea, but surprisingly refreshing - depending on what herb and fruit extracts you choose to put into it, of course. Normally the vendor's mix will be good enough if you choose not to say anything, but you're free to select the mix yourself. Normally sold hot, is the usual after-party drink, as a "reconstituyente", but it can be drunk cold too.
- Inca Kola. The Peruvian equivalent of Coca Cola in the rest of the world, which was recently purchased by Coca Cola yet retains its unique taste. It is bright yellow and has its own unique flavor. Some say it tastes like bubblegum.
- Pisco Sour. An alcoholic drink with an interesting ingredients list, such as egg whites, that is the main drink in Peru and is available in most places. It is made from Pisco, a Peruvian kind of brandy that is worth a try; it is a strong drink as pisco is over 40° (around 70-80 proof) spirit, and the sweet taste can be deceiving. Since Chile registered the brand Chilean Pisco for commercial purposes in some countries, Peruvian producers decided to defend the denomination of origin(Pisco is a very old city in Peru) by being very strict about the quality standards. Be sure that you will find a very high quality product in any brand of Pisco made in Peru.
Beer
Some large towns have their own brand of beer which is hard to get elsewhere in the country. Cusqueña is one of the most popular beers while Cristal is known as the beer of Peru, both can be found nation wide.
- Arequipeña
- Barena
- Brahma
- Cristal
- Cusqueña
- Franca
- Pilsen Callao
- Pilsen Trujillo
Sleep
Hotels in Peru are very common and fairly cheap. They range from 1 - 5 stars. 5 star hotels are normally for package tourism or business travel, and very uncommon outside of Lima. 4 star hotels are usually a bit on the expensive side (>US$60 per night) and not common, but in large cities. 3 star hotels are a good compromise between price and quality and usually US$30-50. 2 and 1 star hotels are very cheap (<US$30), but don't expect hot water or a particularly safe neighborhood.
In many cities there are hotels in residential areas, but they are not tourist hotels but "couples" rooms for lovers. They are usually signed as "Hostel", which can confuse the unaware traveller thinking it was for backpackers.
Learn
Peruvian Spanish, particularly in the Sierra and jungle, is pronounced much less clearly than European Spanish and Spanish from other Latin American countries, especially Mexico, Colombia and Chile. People don't tend to speak too fast, although in coastal areas, especially Lima, people speak considerably faster than in other areas, and they also use slang quite liberally. On the whole, Peru is a good and cheap place to embark on Spanish courses (once you are there).
Some slang terms:
chévere, bacán, cool.
chela (Cerveza), a beer.
Me da cólera, Me llega, it pisses me off.
Ya, right, sure (sometimes "ok" or "yup").
Loco, crazy person.Usually said in a friendly manner, also means "mate, friend, buddie"
Tombo, is cop (and cops don't like hearing it).
Chibolo(a), a kid.
Bamba fake, counterfeit goods & products
Money is often referred to as plata (as in silver). Mucha plata = too much money ("that's expensive!").
Some slang terms come from Quechua:
Que piña: means 'what bad luck' even though 'piña' in Quechua means 'coraje' or in English 'infuriating'.
Tengo una yaya: means 'I'm injured'. In quechua 'yaya' means injury. And 'yawar' means blood.
Arranca arranca no mas: means 'get the hell out'
Work
While there a very limited options for unskilled work and local wages are very low, teaching English or other language tutoring is an option.
Avoid paying for volunteering. Simply contact a bunch of NGOs and let them know you are interested in working for them. Sometimes you can also get a paid job after doing some volunteer work. Just be clear that you are able to stay a fixed amount of time for unpaid work, and that you would need some money to continue your work.
Stay safe
In Lima ring 105. In Lima and some of the larger cities there is a sort of local police called "Serenazgo": you may ask for help but they have no tourist oriented services.
- Be aware of your surroundings and try to avoid unlit or unpopulated areas especially at night. There is a lot of petty crime that can turn violent. Avoid groups of male youngsters since there are many small gangs trying to rob passers-by. If you witness a robbery. be very careful before intervening, since robbers may be armed and are quite prone to shooting if they feel threatened.
- Armed robberies of tourists are fairly common.
- A dirty old backpack with valuable contents is safer than a new one with old clothes in it. It's often good not to look too rich.
- Some travelers don't use wallets, but keep the bills and coins directly in their pocket. Let's say some little bills on the left side and the rest on the right side. Thus, the pickpocket's job gets much harder.
- Don't walk around with debit or credit cards in your pocket. Leave them in a safe place when you do not directly need them, because tourists have been kidnapped and forced to take out money each day for a period of a few days.
- If you want to take large amounts of cash out with you, a neck wallet is always a good idea - you can hide it under your shirt.
- Watch out for false bills. Every bank has posters that explain what to check when getting higher valued bills. The only security element that has not been falsified is the bichrome 10,20,50,100 or 200 now also used on US$ bills. Don't be shy about checking any bills you receive. Most Peruvians do so, too. You may get false bills even at upscale places or (quite unusually, but it's been known to happen) banks, so check there too.
- Ignore any requests to carry luggage or packages for strangers. There could be illegal items or drugs in there, and you are the one who'll be caught with them and have the problems afterwards.
- Small quantities of drugs for personal use or possession (up to 2 g for powdered cocaine or 8 g for marijuana) are permitted by law (Section 299 of the Penal Code of Peru) PROVIDED THAT the user is in possession of only ONE type of drug. However, if you purchase drugs, know your source. It may be inadvisable to buy from strangers or street dealers.
REGARDING MARIJUANA in Peru: Possession for personal consumption in the max amount of 8 g is legal according to the Peruvian Penal Code article 299. What is considered illegal is the trafficking part, that is: buying, selling or having more than 8 g. So be careful who you buy from and do not buy more than 8 g per person.
- When taking a taxi, take a quick look in the back seat and in the trunk, to make sure there is nobody hiding there. There've been reports of armed robberies/kidnappings taking place in taxis. Afterwards, tourists are blindfolded and driven outside the city and left behind by the highway.
- At the border crossing from Ecuador (Huaquillas) to Peru people have tried to steal passports by acting like plain clothed police officers. They give you another form to fill in which is fake. This has taken place although police and customs personnel have been next to them.
- When traveling on buses, it is recommended to keep your backpack under your seat with the strap hooked around your leg.
Police
- Tourist police are dressed in white shirts, instead of the usual green ones, and normally speak English and are quite helpful to tourists. The common police officer does not speak other language but Spanish but normally will try to help. DO NOT get in an argument with police, since they may forget about your needs and feel insulted.
Dealing with the police can take a lot of time. In order to get a copy of a police report you need to go to a Banco de la Nación and pay 3 soles. Without this the police won't give you a copy, and obviously you can only arrange this during working days.
Stay healthy
Vaccinations and Prophylaxis
Vaccine requirement The quantity and type of vaccines necessary to travel to Peru depend on several factors, like medical antecedents and locations included in the trip. The most habitual vaccines needed to travel to Peru are against tétanos, diphtheria, typhoid fever, hepatitis A and B, yellow fever (it is obligatory to present the certificate of vaccination against yellow fever to enter in some countries of Africa), rabies and meningitis. Some of these vaccines require more than a dose or a major time to be effective. For that reason, there is recommendable to inquire on necessary vaccines with an advance of 6 to 8 weeks before your trip.
Hepatitis A Recommended for all travelers.
Typhoid fever Recommended for all travelers.
[Yellow fever]Vaccination Center Perú [4] The government of Peru recommends the vaccine for all travelers who are going to visit forest areas (Amazonia) below 2,300 m (7,546 ft). Travelers that only visit Lima, Cusco and Machu Picchu do not need vaccine for yellow fever. Vaccine for yellow fever is also required for all travelers who arrive from other countries infected with yellow fever in Africa and America. In recent years, there has been reported yellow fever in Cusco (Concepcion 2007), San Martin, Loreto, Pasco, Amazonas, Ancash, Ayacucho, Huánuco, Junín, Madre de Dios, Puno and Ucayali.
Hepatitis B For Travelers who could have sexual relations with local people, especially if the visit is by more than 6 months. Rabies For travelers who could have near contact with animals and have not get access to medical services.
Measles, Parotiditis, Rubella (SPR) If they have not been vaccinated before, two doses for all travelers are recommended.
Tétanos - diphtheria Recommended re-vaccination every 10 years.
What should I take in the suitcase? It is recommendable to travel with a small medical kit (Traveler Kit) that includes some basic medicines like antacid, analgesic pills, NSAIDs and antihistamine drugs. Also it is necessary to take some dehydrated solutions for oral hydratation in case of severe diarrhea. Also, It must include first aid articles as sterile strips, antiseptics and bandages. Do not forget to put some antibiotic against severe diarrhea or dysentery and other infections, as well as sterilized needles (because they are difficult to find in some isolated zones). Finally, you must put into your luggage scissors, clamps, a thermometer, lip balm, a suntan lotion, purifying water tablets and cleanliness equipment. If you use contact lenses or glasses, take an extra pair. You must also carry a small flashlight and a Swiss Army knife. The Traveler Kit must be prepared by your physician according to your health and destination.
Malaria Malaria is a disease that can be fatal and is transmitted by mosquitoes. This mosquito specially pricks by night. If you are going to travel to Peru, it is very important to know what areas present a high prevalence of malaria.
The prevention of the disease is made through a medication against the malaria (prophylaxis) and the protection against the punctures of insects.
There are many antimalarial medicines. The optimal choice depends on the characteristics of the trip and the traveler. So, it is important to have some medical advice about the advantages and disadvantages of each medication. The more effective drugs are:
MEFLOQUINE (LARIAM): very extended use. Side effects include visions, and more serious neurological reactions. Those people with psychiatric and neurological problems must not take this medication.
DOXYCYCLINE: Side effects include cutaneous reactions by contact with the sun or the risk of fungal vaginitis in the women.
MALARONE: highly effective, few side effects, expensive and difficult to obtain in Peru, only in specialized Travel Medicine CenterTravel Medicine Peru [5]
CHLOROQUINE: low risk of side effects and the most useful until years ago. Nowadays, they only have 50/60% of effectiveness for malaria in Peru (specially for the south zone where malaria falciparum has not been reported).
Whatever your choice you need to take antimalarial medicine if you are going to travel to a zone affected by the disease, and continue with the medication beyond your return. The risk of malaria, or any other disease in Peru, is much greater for a tourist than for local people. Do not suspend your medication before the indicated period.
In Peru there is no risk of malaria in the big cities. No risk in Lima and surrounding areas or in areas above the 1500 m (4,921 ft). There is a risk: On the coast north of the country (Tumbes, Piura, Lambayeque). In the Amazon region: Loreto department (Iquitos) with 97% of cases of falciparum country, San Martin, Ucayali, Just as Amazon (chachapoyas), Cajamarca (Jaen).It was also reported cases of vivax malaria (falciparum not) in Cuzco Department (Province of Concepción away from the tourist area of Machu Picchu) and Madre de Dios.
It is recommended that: The precautions to protect themselves from being bitten by mosquitoes are essential especially in the evening and night (especially when visiting rural or peripheral). Use a repellent (on exposed skin) containing DEET (N, N-diethylmetatoluamide to 30% -50% are effective for several hours) or Picaridina (7-15%).
Basic cares about hygiene and food It is difficult to guarantee the security of food and drink, specially in developing countries. Nevertheless you may continue enjoying local meals, this is part of the pleasures of an international trip. Be selective. The diseases that you could get go from a small diarrhea or dysentery, to one more serious disease (e.g. Parasitic infection) that could ruin your trip. Therefore you should take certain precautions: Try to eat only cooked foods Avoid buffet or any other food that has been reheated and exposed to the contact with flies Avoid seafood in unknown places Crude fruits and vegetables are very difficult to sterilize: do not eat them unless you have the security that they have been washed in drinkable water or if they are possible to peel without touching the pulp. In the tropic the safest fruits are bananas and papayas. Be careful, you could reject any food you consider not safe, if it is necessary, ask for cooked food specially for you. Do not eat any food that offers few guarantees to you.
Tap water. Drink water only when you are certain it is safe. Don't drink tap water. If you are using tap water to brush your teeth or rinse your mouth, spit as much out as possible. Tap water can be made drinkable by boiling it (bringing it to boiling point in a kettle should be sufficient) or by purification methods such as iodine tablets or UV light. Bottled water is cheap and tastes better than boiled water. Check the bottle to make sure that it has not been opened and refilled. In restaurants, (if you don't trust them) you could request the bottle to be opened in your presence and never take ice in your drinks (ice cubes are often made with tap water). Remember, alcohol does not make tap water drinkable!
Insect bites Avoiding insect bites reduces the risk of contracting diseases transmitted by mosquitos such as yellow fever, dengue fever, leishmaniosis and malaria. Wearing long sleeves is a good idea. Use insect repellent that contains DEET. Directly apply it to your skin and clothes. Use a mosquito sleeping net impregnated with repellent, as well as other anti-mosquitos stuff in your room or tent (spirals or electrical mosquito repellents) at night.
Rabies In Peru there have been reported cases of rabies in animals even in small zoo parks, so you should avoid to touch or to play with any type of animal. Rabies is not only transmitted through biting, but also by scratches and licks. In case of wound, it is necessary to clean it with an antiseptic lotion. If the wound is deep it is recommendable to examine it by a doctor. Take some advice about antirabic vaccines before starting off, mainly if your trip is long.
Heat and sun Do not expect to become quickly aclimated to the heat (specially in Amazonia). It will take at least 3 weeks to obtain it. During this period, avoid physical fatigue, use fresh clothes, mainly during the warmest hours of the day. Avoid direct exhibition to the sun.Use a solar cream and a hat.
Thirst is a very poor indicator of the amount of water that human needs. It is very important to take a sufficient amount from liquid (not alcohol, coffee or tea, because they are diuretics and causes a greater loss of water). The best probe that you are well hydrated is when your body produces clear abundant urine.
AIDS and other diseases
As in any another country, please take the necessary precautions to avoid HIV infection and other sexual diseases.
Accidents and injuries Accidents and injuries produce more deaths of travellers than diseases. Please be in constant alert.
Do not drive in bad illuminated streets by night. Do not drive a bicycle or a motorcycle. Do not drive in a drunk condition and moderate your speed. If you take a taxi, ask the driver to go slowly. Use the security belt and, if you travel with children, use an adaptable chair Take a small medicinal kit: small wounds can become infected very easily. If the wound is deep it is recommendable to examine it by a doctor.
Back to home If you have contracted malaria or another tropical disease, it is possible that the symptoms do not become evident until much after your return to home and you may not even associate them to your trip. Visit your physician and remember to tell him about your trip to Peru.
Pharmacies
Common medicines, like antibiotics, can be bought in pharmacies (farmacias or boticas) quite cheaply and without restrictions. However, make sure the expiration date has not been reached. Pharmacists are mostly very helpful and can be consulted if needed. For less serious illnesses, they may replace a doctor.
Diarrhea
Electrolytic drinks help guard against dehydration. You can get powders to dissolve in water in almost every pharmacy. If not, just dissolve sugar and salt in water. Bacterial diarrhea can be treated with antibiotics, if it doesn't vanish during a week. Usually, pharmacies are quite helpful.
Food and drink
If you stay in good hotels you may be able to avoid catching diarrhea, otherwise you might. Just don't worry too much about. There are some rules that could avoid the worst:
- Avoid unboiled tap water, if possible. This can be difficult; If you eat a salad or drink some fruit juice, it will probably be prepared with tap water. Avoid ice in drinks if you can.
- If you must drink tap water, use some purification like mikropur.
- Don't eat food prepared in the street (if you can resist it).
- When going to cheap restaurants, first have a smell and listen to what your nose says.
- In some areas, refrigerators are rare. Just go to the meat section of a typical market hall and take a smell, you will understand. If you would rather eat vegetarian food, it can be hard to find. Chicken is worth a try, since they are mostly fresh.
- Don't eat unpasteurized milk products.
Altitude
If you do not have experience with higher altitudes above 3,500m (12,000 ft), don't underestimate it! Collapses of unacclimatized tourists are not unusual. If coming from sea level, stay at medium height ca. 3,000 m (10,000 ft) for at least one week. Then, altitudes of around 4,500 m (15,000 ft) should not be a risk, although you still will strongly feel the height.
See also: Altitude sickness
Sunburn
Since Peru is close to the equator, the sun can become dangerous for your skin and eyes. Especially in the Sierra, the strong UV radiation due to the height in combination with the rather cold air may burn your skin before you notice it. Sun-blockers are easy to get in drug stores (boticas). If your eyes are sensitive to light, better bring good sunglasses from home. Of course, you can buy sunglasses in Peru, too, but you should really be sure that they block the whole UV spectrum, otherwise, they might be worse than none.
Sanitary facilities
Outside of obviously well-set up restaurants and hotels in cities and towns, toilets are often quite primitive and sometimes really dirty. It's a good idea to bring your own paper with you,as Peruvian toilet paper maybe too rough as well as being one ply. It's usual. Toilet doors are marked with "baño", "S.H." or "SS.HH.". The latter two are abbreviations for servicio higienico, which is the rather formal expression. Expect to pay no more than 20 centimos at public restrooms for paper. You will find it handy to keep a roll of toilet paper and a small bottle of hand sanitizer in your backpack.
In hostels or budget hotels, you cannot rely on having water all the time. In the Andean region, it also can easily happen that showers have more or less hot water only in the afternoon since the water is heated by solar energy only. Electrically heated showers are widely spread, but the electric installation is sometimes really dangerous, since the water heater is mostly situated at the shower head. Have a look on it before turning on the shower, especially if you are tall enough that you could touch the cables or other metal during showering which can electrocute you. Don't be too paranoid though, an electric shock is mostly painful.
As woman, if you use tampons during your period, you should bring them with you from home, because they are not very popular in Peru. In Lima, you'll be able to find them in supermarket chains like Santa Isabel or Wong or at drug stores / chemists, known as farmacias and boticas. When you find them, buy enough for the rest of the trip, they are virtually unknown in the rest of the country. Alternatively you could pack a menstrual cup because they are reuseable and compact.
Respect
Don't use the word "indio", although it's Spanish. For natives, it's very much like the English "n-word" since it was used by Spanish conquerors. The politically correct way of speaking is "el indígena" or "la indígena" - although, like "n-word", very close people inside a circle of friends can get away with it. Another word to be careful with is chola/cholo or cholita, meaning indígena. This may be used affectionately among indigenous people (it'a very common appellation for a child, for instance) but is offensive coming from an outsider.
Even if you have about 20 "No drugs" T-shirts at home, accept that especially people from the country side chew coca leaves. See it as a part of the culture with social and ritual components. And keep in mind: Coca leaves are not cocaine and they are legal. You can try them to experience the culture. If you don't like to chew them, try a mate de hojas de coca. Also quite effective against altitude sickness. However, the use of coca leaf tea may lead to testing positive on North American drug tests within the next few weeks.
Officially, most of the Peruvians are Roman Catholic, but especially in the countryside, the ancient pre-Hispanic religiosity is still alive. Respect that when visiting temple ruins or other ritual places and behave as if you were in a church.
Connect
In all towns and villages that are not too small, it is no problem to find public telephones for national and international calls. Usually, you find them in bars or stores. Some of them accept coins, but watch out for stuck coins or dodgy-looking coin receivers as these might make you lose your money. Don't worry if your 1 Nuevo Sol coins don't get through at first, just keep trying and it will eventually work. Many public phones can be expensive, and an attractive alternative is a Locutorio, or "call-center". Typical rates include .2 Nuevo Sol/minute for calls in the country, and .5 Nuevo Sol/minute for most international calls.
You also can buy phone cards with a 12 digit secret number on it. Using a phone card, first dial 147. When done so, you will be told how much your card is still valid and be asked (in Spanish, of course) for your secret number. After having typed it, you are asked for the phone number you want to connect to. Type it in. Then you get told how much time you can talk. After that, the connection is tried.
For international calls, it is often a good idea to go to an Internet cafe that offers Internet based phone calls. You find them in the cities. Internet cafes, called in Peru cabinas públicas, grow like mushrooms in Peru and if you are not really on the countryside, it should not be a problem at all to find one. Even in a smaller town like Mancora or Chivay you can still find Internet cafes with 512kbit/s ADSL. The connection is quite reliable and they are cheap (1.50-3 Soles, US$0.60-1.20 per hour). Just don't expect most of them to actually sell coffee - or anything at all but computer time or services like printing. It is not uncommon to find cabinas that burn CDs directly from SD, CF or Memory sticks. Many internet cafes have headphones and microphones, for free or for an extra fee. See also Online telephone service for travel.
Tourist offices
- iperú, ☏ +51 1 574-8000, [email protected]. This government tourist office has a presence in most cities that are popular with tourists, and is helpful with information. They also keep tabs on businesses and log complaints, so you can check out tuor operators, etc. before you confirm. Their services are free.