ਭਾਰਤ: ਰੀਵਿਜ਼ਨਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਫ਼ਰਕ
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (21 ਵਰਤੋਂਕਾਰ ਦੁਆਰਾ 47 ਵਿਚਕਾਰਲੀਆਂ ਸੋਧਾਂ ਨਹੀਂ ਦਿਖਾਈ ਗਈ) | |||
| ਲਕੀਰ 1: | ਲਕੀਰ 1: | ||
{{Infobox |
{{Infobox country |
||
| native_name = भारत गणराज्य |
|||
| conventional_long_name = ਭਾਰਤ ਗਣਰਾਜ |
| conventional_long_name = ਭਾਰਤ ਗਣਰਾਜ |
||
| common_name = ਭਾਰਤ |
| common_name = ਭਾਰਤ |
||
| native_name = <!--ਇਸ ਨੂੰ ਜਾਣਕਾਰੀਡੱਬੇ ਤੋਂ ਨਾ ਹਟਾਓ ਕਿਉਂਕਿ ਜਾਣਕਾਰੀਡੱਬੇ ਦੇ ਅਨੁਵਾਦ ਅਤੇ ਲਿਪੀਅੰਤਰਨ ਇਸ ਦੇ ਅਧੀਨ ਨਹੀਂ ਆਉਂਦੇ ਹਨ [[WP:Manual of Style/India-related articles#Indic scripts in leads and infoboxes]].--> {{transliteration|hi|ISO|Bhārat Gaṇarājya}}<br />{{smaller|(see [[ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀਆਂ ਸਰਕਾਰੀ ਬੋਲੀਆਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਨਾਮ|ਹੋਰ ਸਥਾਨਕ ਨਾਮ]])}} |
|||
| image_flag = Flag of India.svg |
|||
| |
| image_flag = Flag of India.svg |
||
| alt_flag = ਲੇਟਵੇਂ ਤਿਰੰਗੇ ਝੰਡੇ ਵਾਲੇ, ਉੱਪਰ ਤੋਂ ਹੇਠਾਂ ਤੱਕ, ਡੂੰਘੇ ਭਗਵੇਂ, ਚਿੱਟੇ ਅਤੇ ਹਰੇ ਹਰੀਜੱਟਲ ਬੈਂਡ। ਚਿੱਟੇ ਬੈਂਡ ਦੇ ਕੇਂਦਰ ਵਿੱਚ 24 ਸਪੋਕਸ ਵਾਲਾ ਇੱਕ ਨੇਵੀ-ਨੀਲਾ ਪਹੀਆ ਹੈ। |
|||
| symbol_type = National Emblem |
|||
| image_coat = Emblem of India.svg |
|||
| national_motto = ''"[[ਸਤ੍ਯਮੇਵ ਜਯਤੇ]]" '' |
|||
| symbol_width = 60px |
|||
| image_map = Map_of_India.webp |
|||
| alt_coat = ਤਿੰਨ ਸ਼ੇਰ ਖੱਬੇ, ਸੱਜੇ ਅਤੇ ਦਰਸ਼ਕ ਵੱਲ ਮੂੰਹ ਕਰਦੇ ਹੋਏ, ਇੱਕ ਫ੍ਰੀਜ਼ ਦੇ ਉੱਪਰ, ਜਿਸ ਵਿੱਚ ਇੱਕ ਸਰਪਟ ਘੋੜਾ, ਇੱਕ 24-ਸਪੋਕ ਵ੍ਹੀਲ, ਅਤੇ ਇੱਕ ਹਾਥੀ ਹੈ। ਹੇਠਾਂ ਇੱਕ ਮਨੋਰਥ ਹੈ: "सत्यमेव जयते". |
|||
| map_width = 220px |
|||
| symbol_type = [[ਭਾਰਤ ਦਾ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਚਿੰਨ੍ਹ|ਮੋਹਰ]] |
|||
| national_anthem = ''[[ਜਨ ਗਣ ਮਨ]]''<ref>{{cite web|title=''National Anthem'' - Know India portal|url=http://india.gov.in/knowindia/national_anthem.php|accessdate=2007-08-31|publisher=[[National Informatics Centre|National Informatics Centre(NIC)]]|year=2007}}</ref> |
|||
| other_symbol = {{native phrase|sa|"[[ਵੰਦੇ ਮਾਤਰਮ]]"|italics=off}}<br />"I Bow to Thee, Mother"{{lower|0.2em|{{efn|"[...] ''ਜਨ ਗਣ ਮਨ'' ਭਾਰਤ ਦਾ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਗੀਤ ਹੈ, ਜੋ ਕਿ ਮੌਕੇ ਦੇ ਆਉਣ 'ਤੇ ਸਰਕਾਰ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਅਧਿਕਾਰਤ ਸ਼ਬਦਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਅਜਿਹੇ ਬਦਲਾਅ ਦੇ ਅਧੀਨ ਹੈ; ਅਤੇ ਗੀਤ ''ਵੰਦੇ ਮਾਤਰਮ'', ਜਿਸ ਨੇ ਭਾਰਤੀ ਆਜ਼ਾਦੀ ਦੇ ਸੰਘਰਸ਼ ਵਿਚ ਇਤਿਹਾਸਕ ਭੂਮਿਕਾ ਨਿਭਾਈ ਹੈ, ਨੂੰ ''ਜਨ ਗਣ ਮਨ'' ਨਾਲ ਬਰਾਬਰ ਸਨਮਾਨ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਜਾਵੇਗਾ ਅਤੇ ਇਸ ਦੇ ਬਰਾਬਰ ਦਰਜਾ ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤ ਹੋਵੇਗਾ।{{sfn|Constituent Assembly of India|1950}}<!--end efn:-->}}{{sfn|National Informatics Centre|2005}}<!--end lower:--><ref name="india.gov.in" />}} |
|||
| other_symbol_type = <span class="plainlinks">[[National anthem|National Song]]<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://parliamentofindia.nic.in/ls/debates/vol12p1.htm|title=Constituent Assembly of India — Volume XII|publisher=[[National Informatics Centre|National Informatics Centre(NIC)]]|accessdate=2007-06-29|date=1950-01-24|work=Constituent Assembly of India: Debates|publisher=parliamentofindia.nic.in, National Informatics Centre|quote=The composition consisting of the words and music known as Jana Gana Mana is the National Anthem of India, subject to such alterations in the words as the Government may authorise as occasion arises; and the song Vande Mataram, which has played a historic part in the struggle for Indian freedom, shall be honoured equally with Jana Gana Mana and shall have equal status with it.}}</ref> |
|||
| other_symbol_type = ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਗੀਤ |
|||
| other_symbol = ''[[ਵੰਦੇ ਮਾਤਰਮ]]''<ref>{{cite web|title=''National Song'' - Know India portal |url=http://india.gov.in/knowindia/national_song.php|accessdate=2007-08-30|publisher=[[National Informatics Centre|National Informatics Centre(NIC)]]|year=2007}}</ref> |
|||
| national_motto = {{native phrase|sa|"[[ਸਤਿਅਮੇਵ ਜਯਤੇ]]"|italics=off}} |
|||
| official_languages = [[ਹਿੰਦੀ]], [[ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ]] |
|||
| national_anthem = {{native phrase|bn|"[[ਜਨ ਗਣ ਮਨ]]"|italics=off|paren=omit}}<ref name="india.gov.in">{{cite web |url=https://india.gov.in/india-glance/national-symbols |title=National Symbols | National Portal of India |publisher=[[India.gov.in]] |quote=ਭਾਰਤ ਦਾ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਗੀਤ ਜਨ ਗਣ ਮਨ, ਮੂਲ ਰੂਪ ਵਿੱਚ ਰਾਬਿੰਦਰਨਾਥ ਟੈਗੋਰ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਬੰਗਾਲੀ ਵਿੱਚ ਰਚਿਆ ਗਿਆ ਸੀ, ਨੂੰ ਸੰਵਿਧਾਨ ਸਭਾ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਇਸਦੇ ਹਿੰਦੀ ਸੰਸਕਰਣ ਵਿੱਚ 24 ਜਨਵਰੀ 1950 ਨੂੰ ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਗੀਤ ਵਜੋਂ ਅਪਣਾਇਆ ਗਿਆ ਸੀ। |access-date=1 March 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170204121208/https://india.gov.in/india-glance/national-symbols |archive-date=4 February 2017 }}</ref><ref name="tatsama">{{cite news |title=National anthem of India: a brief on 'Jana Gana Mana' |url=https://www.news18.com/news/india/national-anthem-of-india-a-brief-on-jana-gana-mana-498576.html |date=14 August 2012 |access-date=7 June 2019 |publisher=[[News18 India|News18]] |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190417194530/https://www.news18.com/news/india/national-anthem-of-india-a-brief-on-jana-gana-mana-498576.html |archive-date=17 April 2019}}</ref><br />"Thou Art the Ruler of the Minds of All People"{{lower|0.2em|{{sfn|Wolpert|2003|p=1}}<ref name="india.gov.in" />}}<br /> |
|||
| languages_type = ਭਾਰਤੀ ਮਾਨਤਾ ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤ ਭਾਸ਼ਾਵਾ |
|||
<div style="display:inline-block;margin-top:0.4em;">[[File:Jana Gana Mana instrumental.ogg]]</div> |
|||
| languages = {{collapsible list|title=[[ਅਸਾਮੀ ਭਾਸ਼ਾ|ਅਸਾਮੀ]]|[[ਬੰਗਾਲੀ ਭਾਸ਼ਾ|ਬੰਗਾਲੀ]]|[[ਬੋਡੋ ਭਾਸ਼ਾ|ਬੋਡੋ]]|[[ਡੋਗਰੀ ਭਾਸ਼ਾ|ਡੋਗਰੀ]]|[[ਗੁਜਰਾਤੀ ਭਾਸ਼ਾ|ਗੁਜਰਾਤੀ]]|[[ਹਿੰਦੀ]]|[[ਕੰਨੜ ਭਾਸ਼ਾ|ਕੰਨੜ]]|[[ਕਸ਼ਮੀਰੀ ਭਾਸ਼ਾ|ਕਸ਼ਮੀਰੀ]]|[[ਕੌਕਣੀ ਭਾਸ਼ਾ|ਕੌਕਣੀ]]|[[ਮੈਥਲੀ ਭਾਸ਼ਾ|ਮਿਥਾਲੀ]] |[[ਮਲਿਆਲਮ ਭਾਸ਼ਾ|ਮਲਿਆਲਮ]] |[[ਮੇਇਤੀ ਭਾਸ਼ਾ|ਮਨੀਪੁੜੀ]] |[[ਮਰਾਠੀ ਭਾਸ਼ਾ|ਮਰਾਠੀ]] |[[ਨੇਪਾਲੀ ਭਾਸ਼ਾ|ਨੇਪਾਲੀ]] |[[ਉਡੀਆ ਭਾਸ਼ਾ|ਉਡੀਆ]] |[[ਪੰਜਾਬੀ ਭਾਸ਼ਾ|ਪੰਜਾਬੀ]]|[[ਸੰਸਕ੍ਰਿਤ]] |[[ਸੰਤਾਲੀ ਭਾਸ਼ਾ|ਸੰਤਾਲੀ]] |[[ਸਿੰਧੀ ਭਾਸ਼ਾ|ਸਿੰਧੀ]]|[[ਤਾਮਿਲ ਭਾਸ਼ਾ|ਤਾਮਿਲ]]|[[ਤੇਲਗੂ ਭਾਸ਼ਾ|ਤੇਲਗੂ]] |[[ਉਰਦੂ]]<ref>Official Languages Resolution, 1968, [http://www.rajbhasha.gov.in/dolresolutioneng.htm para. 2].</ref>}} |
|||
| national_languages = ਕੋਈ ਨਹੀਂ<ref name="Times News Network" /><ref name="NoneNtl" /><ref name="Press Trust of India" /> |
|||
| capital = [[ਨਵੀਂ ਦਿੱਲੀ]] |
|||
| image_map = India (orthographic projection).svg |
|||
| latd = 28 |
|||
| map_width = 250px |
|||
| latm = 34 |
|||
| alt_map = ਭਾਰਤ 'ਤੇ ਕੇਂਦਰਿਤ ਇੱਕ ਗਲੋਬ ਦਾ ਚਿੱਤਰ, ਜਿਸ ਵਿੱਚ ਭਾਰਤ ਨੂੰ ਉਜਾਗਰ ਕੀਤਾ ਗਿਆ ਹੈ। |
|||
| latNS = N |
|||
| map_caption = ਗੂੜ੍ਹੇ ਹਰੇ ਰੰਗ ਵਿੱਚ ਦਿਖਾਇਆ ਗਿਆ ਭਾਰਤ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਨਿਯੰਤਰਿਤ ਖੇਤਰ; ਹਲਕੇ ਹਰੇ ਵਿੱਚ ਦਿਖਾਇਆ ਗਿਆ ਖੇਤਰ ਦਾਅਵਾ ਕੀਤਾ ਗਿਆ ਪਰ ਨਿਯੰਤਰਿਤ ਨਹੀਂ ਕੀਤਾ ਗਿਆ |
|||
| longd = 77 |
|||
| capital = [[ਨਵੀਂ ਦਿੱਲੀ]] |
|||
| longm = 12 |
|||
| coordinates = {{Coord|28|36|50|N|77|12|30|E|type:city_region:IN}} |
|||
| longEW = E |
|||
| largest_city = |
| largest_city = {{plainlist| |
||
* [[ਮੁੰਬਈ]] (ਸ਼ਹਿਰ ਉਚਿਤ) |
|||
| demonym = ਭਾਰਤੀ |
|||
* [[ਦਿੱਲੀ]] (ਮਹਾਨਗਰ ਖੇਤਰ) |
|||
| government_type = [[ਫੈਡਰਲ ਗਣਰਾਜ]]<br />[[ਸੰਸਦੀ ਸੰਗਠਨ|ਸੰਸਦੀ ਲੋਕਰਾਜ]]<ref name="IndiaGlance">{{cite web|title=India at a Glance|work=Know India Portal|publisher=[[National Informatics Centre|National Informatics Centre(NIC)]]|url=http://india.gov.in/knowindia/india_at_a_glance.php|accessdate=2007-12-07}}</ref> |
|||
| leader_title1 = [[ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰਪਤੀ|ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰਪਤੀ]] |
|||
| leader_name1 = [[ਰਾਮ ਨਾਥ ਕੋਵਿੰਦ]] |
|||
| leader_title2 = [[ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਉਪ-ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰਪਤੀ|ਉਪ-ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰਪਤੀ]] |
|||
| leader_name2 = [[ਵੈਂਕਈਆ ਨਾਇਡੂ]] |
|||
| leader_title3 = [[ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਪ੍ਰਧਾਨ ਮੰਤਰੀ|ਪ੍ਰਧਾਨ ਮੰਤਰੀ]] |
|||
| leader_name3 = [[ਨਰਿੰਦਰ ਮੋਦੀ]] |
|||
| legislature = [[ਭਾਰਤ ਦਾ ਸੰਸਦ|ਸੰਸਦ]] |
|||
| upper_house = [[ਰਾਜ ਸਭਾ]] |
|||
| lower_house = [[ਲੋਕ ਸਭਾ]] |
|||
| area_km2 = 3287240 |
|||
| area_sq_mi = 1269210<!--Do not remove per [[WP:MOSNUM]]--> |
|||
| area_rank = 7ਵਾਂ |
|||
| area_magnitude = 1 E12 |
|||
| percent_water = 9.56 |
|||
| population_estimate = 1,210,193,422<ref name="CIA"/> |
|||
| population_estimate_year = 2011 |
|||
| population_estimate_rank = 2(ਦੂਜਾ) |
|||
| population_census = 1,147,995,904<ref>{{cite web|url=http://censusindia.gov.in/Census_Data_2001/India_at_glance/popu1.aspx|title=India at a glance: Population|work=Census of India, 2001|publisher=Government of India|accessdate=2009-04-25}}</ref> |
|||
| population_census_year = 2008 |
|||
| population_density_km2 = 349 |
|||
| population_density_sq_mi = 904<!--Do not remove per [[WP:MOSNUM]]--> |
|||
| population_density_rank = 32ਵਾਂ |
|||
| GDP_PPP_year = 2008 |
|||
| GDP_PPP = $3,288 trillion<ref name=imf2>{{cite web|url=http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2009/01/weodata/weorept.aspx?pr.x=49&pr.y=11&sy=2006&ey=2009&scsm=1&ssd=1&sort=country&ds=.&br=1&c=534&s=NGDPD,NGDPDPC,PPPGDP,PPPPC,LP&grp=0&a= |title=India|publisher=International Monetary Fund|accessdate=2009-04-22}}</ref> <!-- Do not use CIA as source! IMF is more reliable source than CIA! --> |
|||
| GDP_PPP_rank = |
|||
| GDP_PPP_per_capita = $2,762<ref name=imf2/> <!-- Do not use CIA as source! IMF is more reliable source than CIA! --> |
|||
| GDP_PPP_per_capita_rank = |
|||
| GDP_nominal = $1,209 trillion<ref name=imf2/> <!-- Do not use CIA as source! IMF is more reliable source than CIA! --> |
|||
| GDP_nominal_rank = |
|||
| GDP_nominal_year = 2008 |
|||
| GDP_nominal_per_capita = $1,016<ref name=imf2/> <!-- Do not use CIA as source! IMF is more reliable source than CIA! --> |
|||
| GDP_nominal_per_capita_rank = |
|||
| HDI_year = 2008 |
|||
| HDI = 0.609 |
|||
| HDI_rank = 132 |
|||
| HDI_category = <span style="color:#fc0;">medium</span> |
|||
| Gini = 36.8<ref name="CIA_GINI">{{cite web|url=https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/fields/2172.html|title=Field Listing - Distribution of family income - Gini index|date=15 May 2008|work=[[The World Factbook]]|publisher=[[CIA]]|accessdate=2008-06-06}}</ref> |
|||
| Gini_year = 2004 |
|||
| sovereignty_type = ਆਜਾਦੀ |
|||
| sovereignty_note = [[ਯੂਨਾਈਟਡ ਕਿੰਗਡਮ]] ਤੋਂ |
|||
| established_event1 = ਮਿਲੀ |
|||
| established_date1 = 15 ਅਗਸਤ 1947 |
|||
| established_event2 = [[ਗਣਰਾਜ]] |
|||
| established_date2 = 26 ਜਨਵਰੀ 1950 |
|||
| currency = [[ਭਾਰਤੀ ਰੁਪਏ]] (₨) |
|||
| currency_code = INR |
|||
| time_zone = [[ਭਾਰਤੀ ਮਿਆਰੀ ਸਮਾਂ]] |
|||
| utc_offset = +5:30 |
|||
| time_zone_DST = not observed |
|||
| utc_offset_DST = +5:30 |
|||
| cctld = [[.in]] |
|||
| calling_code = 91 |
|||
| drives_on = ਖੱਬੇ |
|||
| footnotes = {{Collapsible list|state=uncollapsed|title='''ਬਿਨਾਂ ਨੰਬਰਾਂ ਤੋਂ ਫੁੱਟਨੋਟ:'''|'''‡''' ਇਹ ਨੰਬਰ [[ਯੂਨਾਈਟਡ ਨੈਸ਼ਨਜ਼]] ਦੇ ਅਨੁਸਾਰ ਹੈ, ਪਰ ਭਾਰਤੀ ਸਰਕਾਰ ਇਸ ਨੂੰ 3,287,260 ਸਕੂਏਅਰ ਕਿਲੋਮੀਟਰ ਲਿਖਦੀ ਹੈ।<ref>{{cite web|title=Total Area of India|url=http://lcweb2.loc.gov/frd/cs/profiles/India.pdf|accessdate=2007-09-03|format=PDF|work=[[Country Studies]], India|publisher=[[Library of Congress]]{{ndash}} [[Federal Research Division]]|date=December 2004|quote=The country’s exact size is subject to debate because some borders are disputed. The Indian government lists the total area as 3,287,260 square kilometers and the total land area as 3,060,500 square kilometers; the United Nations lists the total area as 3,287,263 square kilometers and total land area as 2,973,190 square kilometers.|archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20050226190554/http://lcweb2.loc.gov/frd/cs/profiles/India.pdf|archivedate=2005-02-26|dead-url=no}}</ref>}} |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
| official_languages = {{hlist |[[ਹਿੰਦੀ]]|[[ਭਾਰਤੀ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ|ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ]]{{efn|[[ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਸੰਵਿਧਾਨ ਦੇ ਭਾਗ XVII]] ਦੇ ਅਨੁਸਾਰ, [[ਦੇਵਨਾਗਰੀ]] ਲਿਪੀ ਵਿੱਚ [[ਮਿਆਰੀ ਹਿੰਦੀ|ਹਿੰਦੀ]] ਦੇ ਨਾਲ [[ਭਾਰਤੀ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ|ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ]] ਇੱਕ ਵਾਧੂ ਭਾਸ਼ਾ ਵਜੋਂ ਸੰਘ ਦੀ ਸਰਕਾਰੀ ਭਾਸ਼ਾ ਹੈ। ।{{sfn|National Informatics Centre|2005}}{{sfn|Ministry of Home Affairs 1960}}<ref name="india.gov.in2">{{cite web |url=https://india.gov.in/india-glance/profile |title=Profile | National Portal of India |publisher=[[India.gov.in]] |access-date=23 August 2013 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130830064815/https://india.gov.in/india-glance/profile |archive-date=30 August 2013 }}</ref> [[ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਰਾਜ ਅਤੇ ਕੇਂਦਰ ਸ਼ਾਸਿਤ ਪ੍ਰਦੇਸ਼|ਰਾਜ ਅਤੇ ਕੇਂਦਰ ਸ਼ਾਸਿਤ ਪ੍ਰਦੇਸ਼]] ਦੀ ਹਿੰਦੀ ਜਾਂ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਤੋਂ ਇਲਾਵਾ ਆਪਣੀ ਵੱਖਰੀ ਸਰਕਾਰੀ ਭਾਸ਼ਾ ਹੋ ਸਕਦੀ ਹੈ।}}<ref>{{cite web |url=https://rajbhasha.gov.in/en/constitutional-provisions |title=Constitutional Provisions – Official Language Related Part-17 of the Constitution of India |website=[[Department of Official Language]] via [[Government of India]] |access-date=18 April 2021 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210418112326/https://rajbhasha.gov.in/en/constitutional-provisions |archive-date=18 April 2021}}</ref>}} |
|||
. |
|||
| regional_languages = {{collapsible list |
|||
|titlestyle = background:transparent;text-align:left; |
|||
|title = [[ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਅਧਿਕਾਰਤ ਦਰਜੇ ਵਾਲੀਆਂ ਭਾਸ਼ਾਵਾਂ|ਰਾਜ ਪੱਧਰ]] ਅਤੇ [[ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਸੰਵਿਧਾਨ ਦੀ ਅੱਠਵੀਂ ਅਨੁਸੂਚੀ|{{nowrap|ਅੱਠਵੀਂ ਅਨੁਸੂਚੀ}}]]<ref name="langoff">{{cite web |url=https://nclm.nic.in/shared/linkimages/NCLM50thReport.pdf |title=50th Report of the Commissioner for Linguistic Minorities in India (July 2012 to June 2013) |publisher=Commissioner for Linguistic Minorities, [[Ministry of Minority Affairs]], [[Government of India]] |access-date=26 December 2014 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160708012438/https://nclm.nic.in/shared/linkimages/NCLM50thReport.pdf |archive-date=8 July 2016}}</ref> |
|||
|{{hlist |
|||
| [[ਅਸਾਮੀ ਭਾਸ਼ਾ|ਅਸਾਮੀ]] |
|||
| [[ਬੰਗਾਲੀ ਭਾਸ਼ਾ|ਬੰਗਾਲੀ]] |
|||
| [[ਬੋਡੋ ਭਾਸ਼ਾ (ਭਾਰਤ)|ਬੋਡੋ]] |
|||
| [[ਡੋਗਰੀ ਭਾਸ਼ਾ|ਡੋਗਰੀ]] |
|||
| [[ਗੁਜਰਾਤੀ ਭਾਸ਼ਾ|ਗੁਜਰਾਤੀ]] |
|||
| [[ਹਿੰਦੀ]] |
|||
| [[ਕੰਨੜ]] |
|||
| [[ਕਸ਼ਮੀਰੀ ਭਾਸ਼ਾ|ਕਸ਼ਮੀਰੀ]] |
|||
| [[ਕਕਬਰਕ]] |
|||
| [[ਕੋਂਕਣੀ ਭਾਸ਼ਾ|ਕੋਂਕਣੀ]] |
|||
| [[ਮੈਥਲੀ ਭਾਸ਼ਾ|ਮੈਥਲੀ]] |
|||
| [[ਮਲਿਆਲਮ]] |
|||
| [[ਮੇਤੇ ਭਾਸ਼ਾ|ਮਨੀਪੁਰੀ]] |
|||
| [[ਮਰਾਠੀ ਭਾਸ਼ਾ|ਮਰਾਠੀ]] |
|||
| [[ਮਿਜ਼ੋ ਭਾਸ਼ਾ|ਮਿਜ਼ੋ]] |
|||
| [[ਨੇਪਾਲੀ ਭਾਸ਼ਾ|ਨੇਪਾਲੀ]] |
|||
| [[ਓਡੀਆ ਭਾਸ਼ਾ|ਓਡੀਆ]] |
|||
| [[ਪੰਜਾਬੀ ਭਾਸ਼ਾ|ਪੰਜਾਬੀ]] |
|||
| [[ਸੰਸਕ੍ਰਿਤ]] |
|||
| [[ਸੰਥਾਲੀ ਭਾਸ਼ਾ|ਸੰਥਾਲੀ]] |
|||
| [[ਤਮਿਲ਼ ਭਾਸ਼ਾ|ਤਮਿਲ਼]] |
|||
| [[ਤੇਲੁਗੂ ਭਾਸ਼ਾ|ਤੇਲੁਗੂ]] |
|||
| [[ਉਰਦੂ]] |
|||
}} |
|||
}} |
|||
| languages_type = ਮੂਲ ਭਾਸ਼ਾਵਾਂ |
|||
| languages = [[ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਮੂਲ ਬੋਲਣ ਵਾਲਿਆਂ ਦੀ ਸੰਖਿਆ ਅਨੁਸਾਰ ਭਾਸ਼ਾਵਾਂ ਦੀ ਸੂਚੀ|447 ਭਾਸ਼ਾਵਾਂ]]{{efn|Different sources give widely differing figures, primarily based on how the terms "language" and "dialect" are defined and grouped. [[Ethnologue]] lists 461 tongues for India (out of 6,912 worldwide), 447 of which are living, while 14 are extinct.<ref name="Ethnologue">{{cite web|editor=Lewis, M. Paul |editor2=Simons, Gary F. |editor3=Fennig, Charles D.|year=2014|title=Ethnologue: Languages of the World (Seventeenth edition) : India|publisher=[[Ethnologue]] by SIL International|location= Dallas, Texas|url= https://www.ethnologue.com/country/IN|access-date=15 December 2014}}</ref><ref name="Ethnologue2">{{cite web|url=https://archive.ethnologue.com/15/ethno_docs/distribution.asp?by=area|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141217151950/https://archive.ethnologue.com/15/ethno_docs/distribution.asp?by=area|title=Ethnologue : Languages of the World (Seventeenth edition) : Statistical Summaries |publisher=[[Ethnologue]] by SIL International |archive-date=17 December 2014|access-date=17 December 2014}}</ref>}} |
|||
| demonym = [[ਭਾਰਤੀ ਲੋਕ|ਭਾਰਤੀ]] |
|||
| government_type = [[ਸੰਘਵਾਦ|ਸੰਘੀ]] [[ਸੰਸਦੀ ਪ੍ਰਣਾਲੀ|ਸੰਸਦੀ]] [[ਭਾਰਤ ਦਾ ਸੰਵਿਧਾਨ|ਸੰਵਿਧਾਨਕ]] [[ਗਣਰਾਜ]] |
|||
| leader_title1 = [[ਭਾਰਤ ਦਾ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰਪਤੀ|ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰਪਤੀ]] |
|||
| leader_name1 = [[ਦ੍ਰੋਪਦੀ ਮੁਰਮੂ]] |
|||
| leader_title2 = [[ਭਾਰਤ ਦਾ ਉਪ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰਪਤੀ|ਉਪ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰਪਤੀ]] |
|||
| leader_name2 = [[ਜਗਦੀਪ ਧਨਖੜ]] |
|||
| leader_title3 = [[ਭਾਰਤ ਦਾ ਪ੍ਰਧਾਨ ਮੰਤਰੀ|ਪ੍ਰਧਾਨ ਮੰਤਰੀ]] |
|||
| leader_name3 = [[ਨਰਿੰਦਰ ਮੋਦੀ]] |
|||
| leader_title4 = [[ਸੁਪਰੀਮ ਕੋਰਟ ਦੇ ਚੀਫ ਜਸਟਿਸ|ਮੁੱਖ ਜੱਜ]] |
|||
| leader_name4 = [[ਧਨੰਜਯ ਯਸ਼ਵੰਤ ਚੰਦਰਚੂੜ]] |
|||
| leader_title5 = [[ਲੋਕ ਸਭਾ ਦਾ ਸਪੀਕਰ|ਲੋਕ ਸਭਾ ਸਪੀਕਰ]] |
|||
| leader_name5 = [[ਓਮ ਬਿਰਲਾ]] |
|||
| legislature = [[ਭਾਰਤੀ ਸੰਸਦ|ਸੰਸਦ]] |
|||
| upper_house = [[ਰਾਜ ਸਭਾ]] |
|||
| lower_house = [[ਲੋਕ ਸਭਾ]] |
|||
| sovereignty_type = [[ਭਾਰਤ ਦਾ ਆਜ਼ਾਦੀ ਸੰਗਰਾਮ|ਆਜ਼ਾਦੀ]] |
|||
| sovereignty_note = [[ਯੂਨਾਈਟਡ ਕਿੰਗਡਮ]] ਤੋਂ |
|||
| established_event1 = [[ਭਾਰਤ ਦਾ ਰਾਜ|ਰਾਜ]] |
|||
| established_date1 = [[ਸੁਤੰਤਰਤਾ ਦਿਵਸ (ਭਾਰਤ)|15 ਅਗਸਤ 1947]] |
|||
| established_event2 = [[ਗਣਰਾਜ]] |
|||
| established_date2 = [[ਗਣਤੰਤਰ ਦਿਵਸ (ਭਾਰਤ)|26 ਜਨਵਰੀ 1950]] |
|||
| area_km2 = 3,287,263<ref name="india.gov.in" /> |
|||
| area_footnote = {{efn|"ਦੇਸ਼ ਦਾ ਸਹੀ ਆਕਾਰ ਬਹਿਸ ਦਾ ਵਿਸ਼ਾ ਹੈ ਕਿਉਂਕਿ ਕੁਝ ਸਰਹੱਦਾਂ ਵਿਵਾਦਿਤ ਹਨ। ਭਾਰਤ ਸਰਕਾਰ ਕੁੱਲ ਖੇਤਰ ਨੂੰ ਇਸ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਸੂਚੀਬੱਧ ਕਰਦੀ ਹੈ |
|||
{{convert|3287260|km2|sqmi|abbr=on}} ਅਤੇ ਕੁੱਲ ਜ਼ਮੀਨੀ ਖੇਤਰ |
|||
{{convert|3060500|km2|sqmi|abbr=on}}; ਸੰਯੁਕਤ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰ ਕੁੱਲ ਖੇਤਰ ਨੂੰ ਇਸ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਸੂਚੀਬੱਧ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ |
|||
{{convert|3287263|km2|sqmi|abbr=on}} ਅਤੇ ਕੁੱਲ ਜ਼ਮੀਨੀ ਖੇਤਰ {{convert|2973190|km2|sqmi|abbr=on}}."{{sfn|Library of Congress|2004}} }} |
|||
| area_rank = 7ਵਾਂ |
|||
| area_sq_mi = 1,269,346 |
|||
| percent_water = 9.6 |
|||
| population_estimate = 1,375,586,000<ref>{{Cite book |url=https://ruralindiaonline.org/en/library/resource/population-projections-for-india-and-states-2011-2036/ |title=Population Projections for India and States, 2011-2036 |date=2020-07-01 |language=en}}</ref> |
|||
| population_estimate_year = 2022 |
|||
| population_estimate_rank = ਦੂਜਾ |
|||
| population_census = 1,210,854,977<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.censusindia.gov.in/2011census/population_enumeration.html|title=Population Enumeration Data (Final Population)|work=2011 Census Data|publisher=[[Registrar General and Census Commissioner of India|Office of the Registrar General & Census Commissioner, India]]|access-date=17 June 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160522213913/https://www.censusindia.gov.in/2011census/population_enumeration.html|archive-date=22 May 2016}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.censusindia.gov.in/2011census/PCA/A-2_Data_Tables/00%20A%202-India.pdf|title=A – 2 Decadal Variation in Population Since 1901|work=2011 Census Data|publisher=[[Registrar General and Census Commissioner of India|Office of the Registrar General & Census Commissioner, India]]|access-date=17 June 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160430213141/https://www.censusindia.gov.in/2011census/PCA/A-2_Data_Tables/00%20A%202-India.pdf|archive-date=30 April 2016}}</ref> |
|||
| population_census_year = 2011 |
|||
| population_census_rank = ਦੂਜਾ |
|||
| population_density_km2 = {{Pop density|{{Indian population clock}}|3287263|km2|disp=num|prec=1}} |
|||
| population_density_sq_mi = {{Pop density|{{Indian population clock}}|1269219|sqmi|disp=num|prec=1}} |
|||
| population_density_rank = 19ਵਾਂ |
|||
| GDP_PPP = {{increase}} {{nowrap|$11.665 trillion}}<ref name=imf>{{cite news |url=https://www.imf.org/en/Publications/WEO/weo-database/2022/October/weo-report?c=534,&s=NGDP_RPCH,NGDPD,PPPGDP,NGDPDPC,PPPPC,PPPSH,&sy=2020&ey=2027&ssm=0&scsm=1&scc=0&ssd=1&ssc=0&sic=0&sort=country&ds=.&br=1 |title=World Economic Outlook Database: October 2022 |newspaper=Imf |publisher=[[International Monetary Fund]] |date=October 2022 |access-date=11 October 2022}}</ref> |
|||
| GDP_PPP_year = 2022 |
|||
| GDP_PPP_rank = ਤੀਜਾ |
|||
| GDP_PPP_per_capita = {{increase}} $8,293<ref name=imf /> |
|||
| GDP_PPP_per_capita_rank = 127ਵਾਂ |
|||
| GDP_nominal = {{increase}} {{nowrap|$3.469 trillion}}<ref name=imf /> |
|||
| GDP_nominal_year = 2022 |
|||
| GDP_nominal_rank = 5ਵਾਂ |
|||
| GDP_nominal_per_capita = {{increase}} $2,466<ref name=imf /> |
|||
| GDP_nominal_per_capita_rank = 139ਵਾਂ |
|||
| Gini = 35.7 <!--number only--> |
|||
| Gini_year = 2011 |
|||
| Gini_change = |
|||
| Gini_ref = <ref>{{cite web|title=Gini Index coefficient|url=https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/field/gini-index-coefficient-distribution-of-family-income/country-comparison|website=[[The World Factbook]]|publisher=[[Central Intelligence Agency]]|access-date=10 July 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210707032440/https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/field/gini-index-coefficient-distribution-of-family-income/country-comparison|archive-date=7 July 2021}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|title=Gini index (World Bank estimate) – India |url=https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SI.POV.GINI?locations=IN|publisher=[[World bank]]}}</ref> |
|||
| HDI = 0.633 <!--number only--> |
|||
| HDI_year = 2021 <!--Please use the year to which the HDI [[Human Development Index]] data refers, not the publication year--> |
|||
| HDI_change = decrease <!--increase/decrease/steady--> |
|||
| HDI_ref = <ref name="UNHDR">{{cite web|url=https://hdr.undp.org/system/files/documents/global-report-document/hdr2021-22pdf_1.pdf|title=Human Development Report 2021/2022|language=en|publisher=[[United Nations Development Programme]]|date=8 September 2022|access-date=8 September 2022}}</ref> |
|||
| HDI_rank = 132ਵਾਂ |
|||
| currency = [[ਭਾਰਤੀ ਰੁਪਈਆ]] (₹) |
|||
| currency_code = INR |
|||
| time_zone = [[ਭਾਰਤੀ ਮਿਆਰੀ ਸਮਾਂ|IST]] |
|||
| utc_offset = +05:30 |
|||
| utc_offset_DST = |
|||
| DST_note = ''[[ਚਾਨਣ ਬਚਾਊ ਸਮਾਂ|DST]] ਨਹੀਂ ਦੇਖਿਆ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ'' |
|||
| time_zone_DST = |
|||
| date_format = {{ubl |
|||
| {{nowrap|{{abbr|dd|day}}-{{abbr|mm|month}}-{{abbr|yyyy|year}}}}{{efn|ਦੇਖੋ [[ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਮਿਤੀ ਅਤੇ ਸਮਾਂ ਸੰਕੇਤ]]}} |
|||
}} |
|||
| drives_on = left<ref>{{Cite web |title=List of all left- & right-driving countries around the world |url=https://www.worldstandards.eu/cars/list-of-left-driving-countries/ |date=13 May 2020 |access-date=10 June 2020 |website=worldstandards.eu}}</ref> |
|||
| calling_code = [[ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਟੈਲੀਫੋਨ ਨੰਬਰ|+91]] |
|||
| cctld = [[.in]] |
|||
| englishmotto = "Truth Alone Triumphs"{{lower|0.2em|{{sfn|National Informatics Centre|2005}}}} |
|||
| religion_year = 2011 |
|||
| religion = {{ubl |
|||
| 79.8% [[ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿਚ ਹਿੰਦੂ ਧਰਮ|ਹਿੰਦੂ]] |
|||
| 14.2% [[ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਇਸਲਾਮ ਧਰਮ|ਇਸਲਾਮ]] |
|||
| 2.3% [[ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਇਸਾਈ ਧਰਮ|ਇਸਾਈ]] |
|||
| 1.7% [[ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਸਿੱਖ ਧਰਮ|ਸਿੱਖ]] |
|||
| 0.7% [[ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਬੁੱਧ ਧਰਮ ਦਾ ਇਤਿਹਾਸ|ਬੁੱਧ]] |
|||
| 0.4% [[ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਜੈਨ ਧਰਮ|ਜੈਨ]] |
|||
| 0.23% [[ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਨਾਸਤਿਕਤਾ|ਗੈਰ-ਸੰਬੰਧਿਤ]] |
|||
| 0.65% [[ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਧਰਮ|ਹੋਰ]]<ref name="Census2011religion" /> |
|||
}} |
|||
| official_website = <!-- do not add www.gov.in – The article is about the country, not the government – from Template:Infobox country, do not use government website (e.g. usa.gov) for countries (e.g. United States) --> |
|||
| today = |
|||
| iso3166code = IN |
|||
}} |
|||
'''ਭਾਰਤ'''<!--Do not add pronunciation as per [[Wikipedia:Manual of Style/Lead section]].-->, ਅਧਿਕਾਰਤ ਤੌਰ 'ਤੇ '''ਭਾਰਤ ਗਣਰਾਜ''' (ਆਈਐੱਸਓ: {{transliteration|hi|ISO|Bhārat Gaṇarājya}}<!--Do not add pronunciation as per [[Wikipedia:Manual of Style/Lead section]].-->),<ref>–{{citation|title=The Essential Desk Reference |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=yjcOAQAAMAAJ&pg=PA76|year=2002|publisher=[[Oxford University Press]] |isbn=978-0-19-512873-4|page=76}} "Official name: Republic of India.";<br />–{{citation|author=John Da Graça|title=Heads of State and Government|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=M0YfDgAAQBAJ&pg=PA421 |year=2017|publisher=[[Macmillan Publishers|Macmillan]] |location=London |isbn=978-1-349-65771-1|page=421}} "Official name: Republic of India; Bharat Ganarajya (Hindi)";<br />–{{citation|author=Graham Rhind |title=Global Sourcebook of Address Data Management: A Guide to Address Formats and Data in 194 Countries |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=iGdQDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA302|year=2017|publisher=[[Taylor & Francis]] |isbn=978-1-351-93326-1|page=302}} "Official name: Republic of India; Bharat.";<br />–{{citation|last=Bradnock|first=Robert W.|title=The Routledge Atlas of South Asian Affairs |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=zzjbCgAAQBAJ&pg=PA108|year=2015|publisher=[[Routledge]]|isbn=978-1-317-40511-5|page=108}} "Official name: English: Republic of India; Hindi:Bharat Ganarajya";<br />–{{citation|title=Penguin Compact Atlas of the World|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=pLw-ReHIgvQC&pg=PA140|year=2012|publisher=[[Penguin Group|Penguin]] |isbn=978-0-7566-9859-1|page=140}} "Official name: Republic of India";<br />–{{citation|title=Merriam-Webster's Geographical Dictionary |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Co_VIPIJerIC&pg=PA515|year=1997|isbn=978-0-87779-546-9 |edition=3rd |publisher=[[Merriam-Webster]]|pages=515–516}} "Officially, Republic of India";<br />–{{citation|title=Complete Atlas of the World: The Definitive View of the Earth |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=O5moCwAAQBAJ&pg=PA54-IA10 |edition=3rd|year=2016|publisher=[[DK Publishing]] |isbn=978-1-4654-5528-4|page=54}} "Official name: Republic of India";<br />–{{citation|title=Worldwide Government Directory with Intergovernmental Organizations 2013|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=CQWhAQAAQBAJ&pg=PA726|year= 2013|publisher=[[CQ Press]]|isbn=978-1-4522-9937-2|page=726}} "India (Republic of India; Bharat Ganarajya)"</ref> [[ਦੱਖਣੀ ਏਸ਼ੀਆ]] ਵਿੱਚ ਇੱਕ ਦੇਸ਼ ਹੈ। <!--PLEASE DO NOT change the lead sentence: it is the result of a talk page consensus.--> ਇਹ ਖੇਤਰ ਦੇ ਹਿਸਾਬ ਨਾਲ ਸੱਤਵਾਂ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਵੱਡਾ ਦੇਸ਼; ਜੂਨ 2023 ਤੱਕ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਵੱਧ ਆਬਾਦੀ ਵਾਲਾ ਦੇਸ਼;<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.bbc.com/news/world-asia-india-65322706|title=Most populous nation: Should India rejoice or panic?|date=2023-05-01|accessdate=2023-05-03|website=[[BBC News]]|publisher=[[British Broadcasting Corporation]]|first=Soutik|last=Biswas}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |url=https://www.un.org/development/desa/pd/sites/www.un.org.development.desa.pd/files/wpp2022_summary_of_results.pdf |title=World Population Prospects 2022: Summary of Results |publisher=United Nations Department of Social and Economic Affairs |year=2022 |location=New York |pages=i}}</ref> ਅਤੇ 1947 ਵਿੱਚ ਆਪਣੀ ਆਜ਼ਾਦੀ ਦੇ ਸਮੇਂ ਤੋਂ, ਦੁਨੀਆ ਦਾ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਵੱਧ ਆਬਾਦੀ ਵਾਲਾ ਲੋਕਤੰਤਰ ਹੈ।{{sfn|Metcalf|Metcalf|2012|p=327|ps=: "Even though much remains to be done, especially in regard to eradicating poverty and securing effective structures of governance, India's achievements since independence in sustaining freedom and democracy have been singular among the world's new nations."}}<ref name=stein-arnold>{{citation|last=Stein|first=Burton|author-link=Burton Stein|editor-last=Arnold|editor-first=David|editor-link=David Arnold (historian)|title=A History of India|edition=2|publisher=Wiley-Blackwell|year = 2012|series=The Blackwell History of the World Series|quote=One of these is the idea of India as 'the world's largest democracy', but a democracy forged less by the creation of representative institutions and expanding electorate under British rule than by the endeavours of India's founding fathers – Gandhi, Nehru, Patel and Ambedkar – and the labours of the Constituent Assembly between 1946 and 1949, embodied in the Indian constitution of 1950. This democratic order, reinforced by the regular holding of nationwide elections and polling for the state assemblies, has, it can be argued, consistently underpinned a fundamentally democratic state structure – despite the anomaly of the Emergency and the apparent durability of the Gandhi-Nehru dynasty.}}</ref>{{sfn|Fisher|2018|pp=184–185|ps=: "Since 1947, India's internal disputes over its national identity, while periodically bitter and occasionally punctuated by violence, have been largely managed with remarkable and sustained commitment to national unity and democracy."}} ਦੱਖਣ ਵੱਲ [[ਹਿੰਦ ਮਹਾਂਸਾਗਰ|ਹਿੰਦ ਮਹਾਸਾਗਰ]], ਦੱਖਣ-ਪੱਛਮ ਵੱਲ [[ਅਰਬ ਸਾਗਰ]] ਅਤੇ ਦੱਖਣ-ਪੂਰਬ ਵੱਲ [[ਬੰਗਾਲ ਦੀ ਖਾੜੀ]] ਨਾਲ ਘਿਰਿਆ ਹੋਇਆ, ਇਹ ਪੱਛਮ ਵੱਲ [[ਪਾਕਿਸਤਾਨ]] ਨਾਲ ਜ਼ਮੀਨੀ ਸਰਹੱਦਾਂ ਸਾਂਝੀਆਂ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ।;{{efn|1 = The [[Government of India]] also regards [[Afghanistan]] as a bordering country, as it considers all of [[Kashmir]] to be part of India. However, this is [[Kashmir conflict|disputed]], and the region bordering Afghanistan is administered by Pakistan. Source: {{cite web |title=Ministry of Home Affairs (Department of Border Management) |url=https://mha.nic.in/sites/upload_files/mha/files/BMIntro-1011.pdf|access-date=1 September 2008|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150317182910/https://mha.nic.in/sites/upload_files/mha/files/BMIntro-1011.pdf|archive-date=17 March 2015|url-status=dead}} }} ਉੱਤਰ ਵੱਲ [[ਚੀਨ]], [[ਨੇਪਾਲ]] ਅਤੇ [[ਭੂਟਾਨ]]; ਅਤੇ ਪੂਰਬ ਵੱਲ [[ਬੰਗਲਾਦੇਸ਼]] ਅਤੇ [[ਮਿਆਂਮਾਰ]]। ਹਿੰਦ ਮਹਾਸਾਗਰ ਵਿੱਚ, ਭਾਰਤ [[ਸ੍ਰੀਲੰਕਾ|ਸ਼੍ਰੀਲੰਕਾ]] ਅਤੇ [[ਮਾਲਦੀਵ]] ਦੇ ਨੇੜੇ ਹੈ; ਇਸ ਦੇ [[ਅੰਡੇਮਾਨ ਅਤੇ ਨਿਕੋਬਾਰ ਟਾਪੂ]] [[ਥਾਈਲੈਂਡ]], ਮਿਆਂਮਾਰ ਅਤੇ [[ਇੰਡੋਨੇਸ਼ੀਆ]] ਨਾਲ ਸਮੁੰਦਰੀ ਸਰਹੱਦ ਸਾਂਝੇ ਕਰਦੇ ਹਨ। |
|||
ਆਧੁਨਿਕ ਮਨੁੱਖ 55,000 ਸਾਲ ਪਹਿਲਾਂ ਅਫ਼ਰੀਕਾ ਤੋਂ [[ਭਾਰਤੀ ਉਪਮਹਾਂਦੀਪ|ਭਾਰਤੀ ਉਪ-ਮਹਾਂਦੀਪ]] 'ਤੇ ਆਏ ਸਨ।<ref name="PetragliaAllchin">{{harvnb|Petraglia|Allchin|2007|p=[https://books.google.com/books?id=Qm9GfjNlnRwC&pg=PA10 10]}}, "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by modern humans originating in Africa. ... Coalescence dates for most non-European populations average to between 73–55 ka."</ref><ref name="Dyson2018p1">{{harvnb|Dyson|2018|p=[https://books.google.com/books?id=3TRtDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA1 1]}}, "Modern human beings—''Homo sapiens''—originated in Africa. Then, intermittently, sometime between 60,000 and 80,000 years ago, tiny groups of them began to enter the north-west of the Indian subcontinent. It seems likely that initially they came by way of the coast. ... it is virtually certain that there were ''Homo sapiens'' in the subcontinent 55,000 years ago, even though the earliest fossils that have been found of them date to only about 30,000 years before the present."</ref><ref name="Fisher2018p23">{{harvnb|Fisher|2018|p=[https://books.google.com/books?id=kZVuDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA23 23]}}, "Scholars estimate that the first successful expansion of the ''Homo sapiens'' range beyond Africa and across the Arabian Peninsula occurred from as early as 80,000 years ago to as late as 40,000 years ago, although there may have been prior unsuccessful emigrations. Some of their descendants extended the human range ever further in each generation, spreading into each habitable land they encountered. One human channel was along the warm and productive coastal lands of the Persian Gulf and northern Indian Ocean. Eventually, various bands entered India between 75,000 years ago and 35,000 years ago."</ref> |
|||
{| class="infobox borderless" |
|||
|+ ਭਾਰਤ ਗਣਰਾਜ ਦੇ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਚਿੰਨ੍ਹ (Official) |
|||
ਉਹਨਾਂ ਦੇ ਲੰਬੇ ਕਿੱਤੇ, ਸ਼ੁਰੂ ਵਿੱਚ ਵੱਖੋ-ਵੱਖਰੇ ਰੂਪਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਸ਼ਿਕਾਰੀ-ਇਕੱਠੇ ਕਰਨ ਵਾਲਿਆਂ ਦੇ ਰੂਪ ਵਿੱਚ, ਨੇ ਖੇਤਰ ਨੂੰ ਬਹੁਤ ਹੀ ਵਿਭਿੰਨਤਾ ਬਣਾ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਹੈ, ਮਨੁੱਖੀ ਜੈਨੇਟਿਕ ਵਿਭਿੰਨਤਾ ਵਿੱਚ ਅਫਰੀਕਾ ਤੋਂ ਬਾਅਦ ਦੂਜੇ ਸਥਾਨ 'ਤੇ ਹੈ।<ref name="Dyson2018-28a">{{harvnb|Dyson|2018|p=[https://books.google.com/books?id=3TRtDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA28 28]}}</ref> 9,000 ਸਾਲ ਪਹਿਲਾਂ [[ਸਿੰਧ ਦਰਿਆ|ਸਿੰਧ ਨਦੀ]] ਬੇਸਿਨ ਦੇ ਪੱਛਮੀ ਹਾਸ਼ੀਏ ਵਿੱਚ ਉਪ-ਮਹਾਂਦੀਪ ਵਿੱਚ ਸੈਟਲਡ ਜੀਵਨ ਉਭਰਿਆ ਸੀ, ਹੌਲੀ ਹੌਲੀ ਤੀਜੀ ਹਜ਼ਾਰ ਸਾਲ ਬੀਸੀਈ ਦੀ [[ਸਿੰਧੂ ਘਾਟੀ ਸੱਭਿਅਤਾ|ਸਿੰਧੂ ਘਾਟੀ ਸਭਿਅਤਾ]] ਵਿੱਚ ਵਿਕਸਤ ਹੋਇਆ।<ref name="Combined-2">(a) {{harvnb|Dyson|2018|pp=[https://books.google.com/books?id=3TRtDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA4 4–5]}};<br />(b) {{harvnb|Fisher|2018|p=[https://books.google.com/books?id=kZVuDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA23 33]}}</ref> |
|||
|- |
|||
! '''ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਵਿਰਾਸਤ ਜਾਨਵਰ''' |
|||
12000 ਈਸਾ ਪੂਰਵ ਤੱਕ, [[ਸੰਸਕ੍ਰਿਤ ਭਾਸ਼ਾ|ਸੰਸਕ੍ਰਿਤ]] ਦਾ ਇੱਕ ਪੁਰਾਤਨ ਰੂਪ, ਇੱਕ ਇੰਡੋ-ਯੂਰਪੀਅਨ ਭਾਸ਼ਾ, ਉੱਤਰ ਪੱਛਮ ਤੋਂ ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਫੈਲ ਗਈ ਸੀ।<ref name="Lowe2015">{{cite book |last=Lowe |first=John J. |title=Participles in Rigvedic Sanskrit: The syntax and semantics of adjectival verb forms |year=2015|publisher=[[Oxford University Press]] |isbn=978-0-19-100505-3 |pages=1–2 |quote=(The Rigveda) consists of 1,028 hymns (suktas), highly crafted poetic compositions originally intended for recital during rituals and for the invocation of and communication with the Indo-Aryan gods. Modern scholarly opinion largely agrees that these hymns were composed between around 1500 BCE and 1200 BCE, during the eastward migration of the Indo-Aryan tribes from the mountains of what is today northern Afghanistan across the Punjab into north India. |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=L07CBwAAQBAJ&pg=PA2}}</ref><ref name="Combined-4-Rigveda">(a) {{cite book|title=The Blackwell Companion to Hinduism|last=Witzel|first=Michael|publisher=[[John Wiley & Sons]]|year=2008|isbn=978-0-470-99868-7|editor=Gavin Flood|pages=68–70|chapter=Vedas and Upanisads|quote=It is known from internal evidence that the Vedic texts were orally composed in northern India, at first in the Greater Punjab and later on also in more eastern areas, including northern Bihar, between ca. 1500 BCE and ca. 500–400 BCE. The oldest text, the Rgveda, must have been more or less contemporary with the Mitanni texts of northern Syria/Iraq (1450–1350 BCE); ... The Vedic texts were orally composed and transmitted, without the use of script, in an unbroken line of transmission from teacher to student that was formalized early on. This ensured an impeccable textual transmission superior to the classical texts of other cultures; it is in fact something of a ''tape-recording'' of ca. 1500–500 BCE. Not just the actual words, but even the long-lost musical (tonal) accent (as in old Greek or in Japanese) has been preserved up to the present. (pp. 68–69) ... The RV text was composed before the introduction and massive use of iron, that is before ca. 1200–1000 BCE. (p. 70)|author-link=Michael Witzel|chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=SKBxa-MNqA8C&pg=PA68}}<br />(b) {{citation |last=Doniger |first=Wendy |title=On Hinduism |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=fUnaAgAAQBAJ&pg=PR18 |pages=xviii, 10 |year=2014 |publisher=[[Oxford University Press]] |isbn=978-0-19-936009-3 |quote=A Chronology of Hinduism: ca. 1500–1000 BCE Rig Veda; ca. 1200–900 BCE Yajur Veda, Sama Veda and Atharva Veda (p. xviii); Hindu texts began with the ''Rig Veda'' ('Knowledge of Verses'), composed in northwest India around 1500 BCE (p. 10) |author-link=Wendy Doniger}}<br />(c) {{harvnb|Ludden|2014|p=[https://books.google.com/books?id=pBq9DwAAQBAJ&pg=PA19 19]}}, "In Punjab, a dry region with grasslands watered by five rivers (hence 'panch' and 'ab') draining the western Himalayas, one prehistoric culture left no material remains, but some of its ritual texts were preserved orally over the millennia. The culture is called Aryan, and evidence in its texts indicates that it spread slowly south-east, following the course of the Yamuna and Ganga Rivers. Its elite called itself Arya (pure) and distinguished themselves sharply from others. Aryans led kin groups organized as nomadic horse-herding tribes. Their ritual texts are called Vedas, composed in Sanskrit. [[Vedic Sanskrit]] is recorded only in hymns that were part of Vedic rituals to Aryan gods. To be Aryan apparently meant to belong to the elite among pastoral tribes. Texts that record Aryan culture are not precisely datable, but they seem to begin around 1200 BCE with four collections of Vedic hymns (Rg, Sama, Yajur, and Artharva)." |
|||
| |
|||
<br />(d) {{harvnb|Dyson|2018|pp=[https://books.google.com/books?id=3TRtDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA14 14–15]}}, "Although the collapse of the Indus valley civilization is no longer believed to have been due to an 'Aryan invasion' it is widely thought that, at roughly the same time, or perhaps a few centuries later, new Indo-Aryan-speaking people and influences began to enter the subcontinent from the north-west. Detailed evidence is lacking. Nevertheless, a predecessor of the language that would eventually be called Sanskrit was probably introduced into the north-west sometime between 3,900 and 3,000 years ago. This language was related to one then spoken in eastern Iran; and both of these languages belonged to the Indo-European language family. ... It seems likely that various small-scale migrations were involved in the gradual introduction of the predecessor language and associated cultural characteristics. However, there may not have been a tight relationship between movements of people on the one hand, and changes in language and culture on the other. Moreover, the process whereby a dynamic new force gradually arose—a people with a distinct ideology who eventually seem to have referred to themselves as 'Arya'—was certainly two-way. That is, it involved a blending of new features which came from outside with other features—probably including some surviving Harappan influences—that were already present. Anyhow, it would be quite a few centuries before Sanskrit was written down. And the hymns and stories of the Arya people—especially the Vedas and the later Mahabharata and Ramayana epics—are poor guides as to historical events. Of course, the emerging Arya were to have a huge impact on the history of the subcontinent. Nevertheless, little is known about their early presence."; <br /> (e) {{harvnb|Robb|2011|pp=[https://books.google.com/books?id=GQ-2VH1LO_EC&pg=PA46 46–]}}, "The expansion of Aryan culture is supposed to have begun around 1500 BCE. It should not be thought that this Aryan emergence (though it implies some migration) necessarily meant either a sudden invasion of new peoples, or a complete break with earlier traditions. It comprises a set of cultural ideas and practices, upheld by a Sanskrit-speaking elite, or Aryans. The features of this society are recorded in the Vedas."</ref> ਇਸ ਦਾ ਪ੍ਰਮਾਣ ਅੱਜ ''[[ਰਿਗਵੇਦ]]'' ਦੇ ਭਜਨਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਮਿਲਦਾ ਹੈ। ਇੱਕ ਮੌਖਿਕ ਪਰੰਪਰਾ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਸੁਰੱਖਿਅਤ ਰੱਖਿਆ ਗਿਆ ਸੀ ਜੋ ਪੂਰੀ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਚੌਕਸ ਸੀ, ਰਿਗਵੇਦ ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ [[ਹਿੰਦੂ ਧਰਮ]] ਦੀ ਸ਼ੁਰੂਆਤ ਨੂੰ ਰਿਕਾਰਡ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ।<ref name="Combined-3">(a) {{citation|last1=Jamison|first1=Stephanie|author-link1=Stephanie W. Jamison|last2=Brereton|first2=Joel |title=The Rigveda|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=1LTRDwAAQBAJ|year=2020|publisher=[[Oxford University Press]] |isbn=978-0-19-063339-4|pages=2, 4|quote=The RgVeda is one of the four Vedas, which together constitute the oldest texts in Sanskrit and the earliest evidence for what will become Hinduism. (p. 2) Although Vedic religion is very different in many regards from what is known as Classical Hinduism, the seeds are there. Gods like Visnu and Siva (under the name Rudra), who will become so dominant later, are already present in the Rgveda, though in roles both lesser than and different from those they will later play, and the principal Rgvedic gods like Indra remain in later Hinduism, though in diminished capacity (p. 4).}};<br />(b) {{citation|last=Flood|first=Gavin|author-link=Gavin Flood|editor=Gavin Flood|title=The Oxford History of Hinduism: Hindu Practice: Hindu Practice|chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=4yT3DwAAQBAJ&pg=PA4|year= 2020|publisher=[[Oxford University Press]]|isbn=978-0-19-105322-1|pages=4–|chapter=Introduction|quote=I take the term 'Hinduism to meaningfully denote a range and history of practice characterized by a number of features, particularly reference to Vedic textual and sacrificial origins, belonging to endogamous social units (jati/varna), participating in practices that involve making an offering to a deity and receiving a blessing (puja), and a first-level cultural polytheism (although many Hindus adhere to a second-level monotheism in which many gods are regarded as emanations or manifestations of the one, supreme being).}};<br />(c) {{cite book|last=Michaels|first=Axel|author-link=Axel Michaels|editor=Patrick Olivelle, Donald R. Davis|title=The Oxford History of Hinduism: Hindu Law: A New History of Dharmaśāstra|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=QAJCDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA86|year=2017|publisher=[[Oxford University Press]]|location=Oxford |isbn=978-0-19-100709-5|pages=86–97|quote=Almost all traditional Hindu families observe until today at least three ''samskaras'' (initiation, marriage, and death ritual). Most other rituals have lost their popularity, are combined with other rites of passage, or are drastically shortened. Although ''samskaras'' vary from region to region, from class (''varna'') to class, and from caste to caste, their core elements remain the same owing to the common source, the Veda, and a common priestly tradition preserved by the ''Brahmin'' priests. (p 86)}}<br />(d) {{cite book|last=Flood|first=Gavin D.|title=An Introduction to Hinduism|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=KpIWhKnYmF0C&pg=PA35|year=1996|publisher=[[Cambridge University Press]]|isbn=978-0-521-43878-0|page=35|quote=It is this Sansrit, vedic, tradition which has maintained a continuity into modern times and which has provided the most important resource and inspiration for Hindu traditions and individuals. The Veda is the foundation for most later developments in what is known as Hinduism.}}</ref> ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀਆਂ [[ਦਰਾਵੜੀ ਭਾਸ਼ਾਵਾਂ|ਦ੍ਰਾਵਿੜ ਭਾਸ਼ਾਵਾਂ]] ਨੂੰ ਉੱਤਰੀ ਅਤੇ ਪੱਛਮੀ ਖੇਤਰਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਬਦਲ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਗਿਆ ਸੀ।<ref name="Combined-4">{{harvnb|Dyson|2018|pp=[https://books.google.com/books?id=3TRtDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA16 16], [https://books.google.com/books?id=3TRtDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA25 25]}}</ref> |
|||
| [[Image:2005-bandipur-tusker.jpg|50px]] |
|||
|- |
|||
400 ਈਸਾ ਪੂਰਵ ਤੱਕ, ਹਿੰਦੂ ਧਰਮ ਦੇ ਅੰਦਰ ਜਾਤ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਪੱਧਰੀਕਰਨ ਅਤੇ ਬੇਦਖਲੀ ਉਭਰ ਕੇ ਸਾਹਮਣੇ ਆਈ ਸੀ, ਅਤੇ [[ਬੁੱਧ ਧਰਮ|ਬੌਧ]] ਅਤੇ [[ਜੈਨ ਧਰਮ]] ਪੈਦਾ ਹੋ ਗਏ ਸਨ, ਸਮਾਜਿਕ ਵਿਵਸਥਾਵਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਖ਼ਾਨਦਾਨੀ ਨਾਲ ਜੋੜਿਆ ਨਹੀਂ ਗਿਆ ਸੀ।<ref name="Dyson2018-16a">{{harvnb|Dyson|2018|p=[https://books.google.com/books?id=3TRtDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA16 16]}}</ref><ref name="Fisher2018-59">{{harvnb|Fisher|2018|p=[https://books.google.com/books?id=kZVuDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA59 59]}}</ref> |
|||
! '''ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਪੰਛੀ''' |
|||
| |
|||
ਸ਼ੁਰੂਆਤੀ ਸਿਆਸੀ ਮਜ਼ਬੂਤੀ ਨੇ [[ਗੰਗਾ ਦਰਿਆ|ਗੰਗਾ]] ਬੇਸਿਨ ਵਿੱਚ ਸਥਿਤ [[ਮੌਰੀਆ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ|ਮੌਰੀਆ]] ਅਤੇ [[ਗੁਪਤ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ]] ਨੂੰ ਜਨਮ ਦਿੱਤਾ।<ref name="Combined-5">(a) {{harvnb|Dyson|2018|pp=[https://books.google.com/books?id=3TRtDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA16 16–17]}};<br />(b) {{harvnb|Fisher|2018|p=[https://books.google.com/books?id=kZVuDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA67 67]}};<br />(c) {{harvnb|Robb|2011|pp=[https://books.google.com/books?id=GQ-2VH1LO_EC&pg=PA56 56–57]}};<br />(d) {{harvnb|Ludden|2014|pp=[https://books.google.com/books?id=pBq9DwAAQBAJ&pg=PA29 29–30]}}.</ref> |
|||
| [[Image:Pavo muticus (Tierpark Berlin) - 1017-899-(118).jpg|50px]] |
|||
|- |
|||
ਉਹਨਾਂ ਦਾ ਸਮੂਹਿਕ ਯੁੱਗ ਵਿਆਪਕ ਰਚਨਾਤਮਕਤਾ ਨਾਲ ਭਰਿਆ ਹੋਇਆ ਸੀ, ਪਰ ਔਰਤਾਂ ਦੀ ਡਿੱਗਦੀ ਸਥਿਤੀ, ਅਤੇ ਵਿਸ਼ਵਾਸ ਦੀ ਇੱਕ ਸੰਗਠਿਤ ਪ੍ਰਣਾਲੀ ਵਿੱਚ ਛੂਤ-ਛਾਤ ਨੂੰ ਸ਼ਾਮਲ ਕਰਨ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਵੀ ਚਿੰਨ੍ਹਿਤ ਕੀਤਾ ਗਿਆ ਸੀ।<ref name="Combined-6">(a) {{harvnb|Ludden|2014|pp=[https://books.google.com/books?id=pBq9DwAAQBAJ&pg=PA28 28–29]}}; |
|||
! '''ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਰੁੱਖ''' |
|||
<br />(b) {{citation|author=Glenn Van Brummelen |editor=Thomas F. Glick |editor2=Steven Livesey |editor3=Faith Wallis |title=Medieval Science, Technology, and Medicine: An Encyclopedia|chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=77y2AgAAQBAJ&pg=PA46|year=2014|publisher=[[Routledge]]|isbn=978-1-135-45932-1|pages=46–48|chapter=Arithmetic}}</ref><ref name="Combined-7">(a) {{harvnb|Dyson|2018|p=[https://books.google.com/books?id=3TRtDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA20 20]}};<br />(b) {{harvnb|Stein|2010|p=90}};<br />(c) {{citation |last=Ramusack|first=Barbara N.|editor1=Barbara N. Ramusack |editor2=Sharon L. Sievers |title=Women in Asia: Restoring Women to History|chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=CNi9Jc22OHsC&pg=PA27|year=1999 |publisher=[[Indiana University Press]]|isbn=0-253-21267-7|pages=27–29|chapter=Women in South Asia}}</ref>{{efn|"A Chinese pilgrim also recorded evidence of the caste system as he could observe it. According to this evidence the treatment meted out to untouchables such as the Chandalas was very similar to that which they experienced in later periods. This would contradict assertions that this rigid form of the caste system emerged in India only as a reaction to the Islamic conquest."{{sfn|Kulke|Rothermund|2004|p = 93}}}}{{sfn|Kulke|Rothermund|2004|p = 93}} [[ਦੱਖਣੀ ਭਾਰਤ]] ਵਿੱਚ, ਮੱਧ ਰਾਜਾਂ ਨੇ [[ਦੱਖਣ-ਪੂਰਬੀ ਏਸ਼ੀਆ]] ਦੇ ਰਾਜਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਦ੍ਰਾਵਿੜ-ਭਾਸ਼ਾ ਦੀਆਂ ਲਿਪੀਆਂ ਅਤੇ ਧਾਰਮਿਕ ਸਭਿਆਚਾਰਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਨਿਰਯਾਤ ਕੀਤਾ।<ref name="AsherAsher2006-17">{{harvnb|Asher|Talbot|2006|p=[https://books.google.com/books?id=ZvaGuaJIJgoC&pg=PA17 17]}}</ref> |
|||
| |
|||
| [[Image:Banyan tree on the banks of Khadakwasla Dam.jpg|50px]] |
|||
ਸ਼ੁਰੂਆਤੀ ਮੱਧਕਾਲੀ ਯੁੱਗ ਵਿੱਚ, [[ਇਸਾਈ ਧਰਮ|ਈਸਾਈ ਧਰਮ]], [[ਇਸਲਾਮ]], [[ਯਹੂਦੀ ਧਰਮ]], ਅਤੇ ਜੋਰਾਸਟ੍ਰੀਅਨ ਧਰਮ ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਦੱਖਣੀ ਅਤੇ ਪੱਛਮੀ ਤੱਟਾਂ ਉੱਤੇ ਸਥਾਪਿਤ ਹੋ ਗਏ ਸਨ।<ref name="Combined-8">(a) {{harvnb|Ludden|2014|p=[https://books.google.com/books?id=pBq9DwAAQBAJ&pg=PA54 54]}}; |
|||
|- |
|||
<br />(b) {{harvnb|Asher|Talbot|2006|pp=[https://books.google.com/books?id=ZvaGuaJIJgoC&pg=PA78 78–79]}}; |
|||
! '''ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਫੁੱਲ ''' |
|||
<br />(c) {{harvnb|Fisher|2018|p=[https://books.google.com/books?id=kZVuDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA76 76]}}</ref> |
|||
| |
|||
[[ਮੱਧ ਏਸ਼ੀਆ]] ਦੀਆਂ ਮੁਸਲਿਮ ਫੌਜਾਂ ਨੇ ਰੁਕ-ਰੁਕ ਕੇ ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਉੱਤਰੀ ਮੈਦਾਨਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਆਪਣੇ ਕਬਜ਼ੇ ਵਿੱਚ ਕਰ ਲਿਆ, ਅੰਤ ਵਿੱਚ [[ਦਿੱਲੀ ਸਲਤਨਤ]] ਦੀ ਸਥਾਪਨਾ ਕੀਤੀ, ਅਤੇ ਉੱਤਰੀ ਭਾਰਤ ਨੂੰ ਮੱਧਕਾਲੀ ਇਸਲਾਮ ਦੇ ਬ੍ਰਹਿਮੰਡੀ ਨੈਟਵਰਕ ਵਿੱਚ ਖਿੱਚ ਲਿਆ।<ref name="Combined-13">(a) {{harvnb|Ludden|2014|pp=[https://books.google.com/books?id=pBq9DwAAQBAJ&pg=PA68 68–70]}};<br />(b) {{harvnb|Asher|Talbot|2006|pp=[https://books.google.com/books?id=ZvaGuaJIJgoC&pg=PA19 19], 24}}</ref><ref name="Combined-10">(a) {{harvnb|Dyson|2018|p=[https://books.google.com/books?id=3TRtDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA48 48]}}; |
|||
| [[Image:Sacred lotus Nelumbo nucifera.jpg|50px]] |
|||
<br />(b) {{harvnb|Asher|Talbot|2006|p=[https://books.google.com/books?id=ZvaGuaJIJgoC&pg=PA53 52]}}</ref> |
|||
|- |
|||
! '''ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਜਾਨਵਰ''' |
|||
15ਵੀਂ ਸਦੀ ਵਿੱਚ, [[ਵਿਜੈਨਗਰ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ]] ਨੇ ਦੱਖਣ ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਇੱਕ ਲੰਬੇ ਸਮੇਂ ਤੱਕ ਚੱਲਣ ਵਾਲੇ ਸੰਯੁਕਤ ਹਿੰਦੂ ਸੱਭਿਆਚਾਰ ਦੀ ਸਿਰਜਣਾ ਕੀਤੀ।<ref name="AsherAsher2006-74">{{harvnb|Asher|Talbot|2006|p=[https://books.google.com/books?id=ZvaGuaJIJgoC&pg=PA74 74]}}</ref> |
|||
| |
|||
| [[Image:Panthera tigris.jpg|50px]] |
|||
[[ਪੰਜਾਬ]] ਵਿੱਚ, [[ਸਿੱਖੀ|ਸਿੱਖ ਧਰਮ]] ਦਾ ਉਭਾਰ ਹੋਇਆ, ਸੰਸਥਾਗਤ ਧਰਮ ਨੂੰ ਰੱਦ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੋਇਆ।<ref name="AsherAsher2006-267">{{harvnb|Asher|Talbot|2006|p=[https://books.google.com/books?id=ZvaGuaJIJgoC&pg=PA267 267]}}</ref> |
|||
|- |
|||
[[ਮੁਗ਼ਲ ਸਲਤਨਤ|ਮੁਗਲ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ]], 1526 ਵਿੱਚ, ਦੋ ਸਦੀਆਂ ਦੀ ਸਾਪੇਖਿਕ ਸ਼ਾਂਤੀ ਦੀ ਸ਼ੁਰੂਆਤ ਕੀਤੀ, ਚਮਕਦਾਰ ਆਰਕੀਟੈਕਚਰ ਦੀ ਵਿਰਾਸਤ ਛੱਡ ਕੇ।<ref name="AsherAsher2006-152">{{harvnb|Asher|Talbot|2006|p=[https://books.google.com/books?id=ZvaGuaJIJgoC&pg=PA152 152]}}</ref>{{efn|"Shah Jahan eventually sent her body 800 km (500 mi) to Agra for burial in the Rauza-i Munauwara ("Illuminated Tomb") – a personal tribute and a stone manifestation of his imperial power. This tomb has been celebrated globally as the Taj Mahal."<ref name="Fisher2018-106" />}}<ref name="Fisher2018-106">{{harvnb|Fisher|2018|p=[https://books.google.com/books?id=kZVuDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA106 106]}}</ref> |
|||
! '''ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਜਲੀ ਸਮੁੰਦਰੀ ਥਣਧਾਰੀ''' |
|||
| |
|||
ਹੌਲੀ-ਹੌਲੀ [[ਬ੍ਰਿਟਿਸ਼ ਈਸਟ ਇੰਡੀਆ ਕੰਪਨੀ]] ਦੇ ਸ਼ਾਸਨ ਦਾ ਵਿਸਤਾਰ ਹੋਇਆ, ਜਿਸ ਨੇ ਭਾਰਤ ਨੂੰ ਇੱਕ ਬਸਤੀਵਾਦੀ ਆਰਥਿਕਤਾ ਵਿੱਚ ਬਦਲ ਦਿੱਤਾ, ਪਰ ਇਸਦੀ [[ਪ੍ਰਭੂਸੱਤਾ]] ਨੂੰ ਵੀ ਮਜ਼ਬੂਤ ਕੀਤਾ।<ref name="Combined-11">(a) {{harvnb|Asher|Talbot|2006|p=[https://books.google.com/books?id=ZvaGuaJIJgoC&pg=PA289 289]}} |
|||
| [[Image:PlatanistaHardwicke.jpg|50px]] |
|||
<br />(b) {{harvnb|Fisher|2018|p=[https://books.google.com/books?id=kZVuDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA120 120]}}</ref> [[ਬ੍ਰਿਟਿਸ਼ ਰਾਜ|ਬ੍ਰਿਟਿਸ਼ ਕ੍ਰਾਊਨ ਸ਼ਾਸਨ]] 1858 ਵਿੱਚ ਸ਼ੁਰੂ ਹੋਇਆ। ਭਾਰਤੀਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਦਿੱਤੇ ਗਏ ਅਧਿਕਾਰ ਹੌਲੀ-ਹੌਲੀ ਦਿੱਤੇ ਗਏ,<ref name="Combined-12">{{citation|last=Taylor|first=Miles|editor=Aldrish, Robert |editor2=McCreery, Cindy |title=Crowns and Colonies: European Monarchies and Overseas Empires|chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=iR3GDQAAQBAJ&pg=PA39|year=2016|publisher=[[Manchester University Press]]|isbn=978-1-5261-0088-7|pages=38–39|chapter=The British royal family and the colonial empire from the Georgians to Prince George}}</ref>{{sfn|Peers|2013|p=[https://books.google.com/books?id=dyQuAgAAQBAJ&pg=PA76 76]}} ਪਰ ਤਕਨੀਕੀ ਤਬਦੀਲੀਆਂ ਪੇਸ਼ ਕੀਤੀਆਂ ਗਈਆਂ, ਅਤੇ ਸਿੱਖਿਆ ਅਤੇ ਜਨਤਕ ਜੀਵਨ ਦੇ ਆਧੁਨਿਕ ਵਿਚਾਰਾਂ ਨੇ ਜੜ੍ਹ ਫੜ ਲਈ।<ref name="EmbreeHay1988">{{citation |
|||
|- |
|||
|last1=Embree|first1=Ainslie Thomas|last2=Hay|first2=Stephen N.|last3=Bary|first3=William Theodore De|title=Sources of Indian Tradition: Modern India and Pakistan|chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=XoMRuiSpBp4C&pg=PA85|year=1988|publisher=[[Columbia University Press]]|isbn=978-0-231-06414-9|page=85|chapter=Nationalism Takes Root: The Moderates}}</ref> ਇੱਕ ਮੋਹਰੀ ਅਤੇ ਪ੍ਰਭਾਵਸ਼ਾਲੀ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰਵਾਦੀ ਲਹਿਰ ਉਭਰੀ, ਜੋ ਅਹਿੰਸਕ ਵਿਰੋਧ ਲਈ ਮਸ਼ਹੂਰ ਸੀ ਅਤੇ ਬ੍ਰਿਟਿਸ਼ ਸ਼ਾਸਨ ਨੂੰ ਖਤਮ ਕਰਨ ਦਾ ਮੁੱਖ ਕਾਰਕ ਬਣ ਗਈ।<ref name="Marshall2001">{{citation|last=Marshall|first=P. J.|title=The Cambridge Illustrated History of the British Empire|url={{Google books|S2EXN8JTwAEC|page=PA179|keywords=|text=|plainurl=yes}}|year=2001|publisher=Cambridge University Press|isbn=978-0-521-00254-7|page=179|quote=The first modern nationalist movement to arise in the non-European empire, and one that became an inspiration for many others, was the Indian Congress.}}</ref><ref name="Chiriyankandath2016">{{citation|last=Chiriyankandath|first=James |title=Parties and Political Change in South Asia|url={{Google books|c4n7CwAAQBAJ|page=PA2|keywords=|text=|plainurl=yes}}|year=2016|publisher=Routledge|isbn=978-1-317-58620-3|page=2|quote=South Asian parties include several of the oldest in the post-colonial world, foremost among them the 129-year-old Indian National Congress that led India to independence in 1947}}</ref> 1947 ਵਿੱਚ ਬ੍ਰਿਟਿਸ਼ ਭਾਰਤੀ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਨੂੰ ਦੋ [[ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀ ਵੰਡ|ਆਜ਼ਾਦ ਰਾਜਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਵੰਡਿਆ]] ਗਿਆ ਸੀ,<ref name="fisher-partition">{{harvnb|Fisher|2018|pp=173–174}}: "The partition of South Asia that produced India and West and East Pakistan resulted from years of bitter negotiations and recriminations ... The departing British also decreed that the hundreds of princes, who ruled one-third of the subcontinent and a quarter of its population, became legally independent, their status to be settled later. Geographical location, personal and popular sentiment, and substantial pressure and incentives from the new governments led almost all princes eventually to merge their domains into either Pakistan or India. ... Each new government asserted its exclusive sovereignty within its borders, realigning all territories, animals, plants, minerals, and all other natural and human-made resources as either Pakistani or Indian property, to be used for its national development... Simultaneously, the central civil and military services and judiciary split roughly along religious 'communal' lines, even as they divided movable government assets according to a negotiated formula: 22.7 percent for Pakistan and 77.3 percent for India."</ref><ref name="chatterji-partition">{{citation|last1=Chatterji|first1=Joya|last2=Washbrook|first2=David|chapter=Introduction: Concepts and Questions|title=Routledge Handbook of the South Asian Diaspora|editor1-last=Chatterji|editor1-first=Joya|editor2-last=Washbrook|editor2-first=David|location=London and New York|publisher=Routledge|isbn=978-0-415-48010-9|year=2013|quote=[[Joya Chatterji]] describes how the partition of the British Indian empire into the new nation states of India and Pakistan produced new diaspora on a vast, and hitherto unprecedented, scale, but hints that the sheer magnitude of refugee movements in South Asia after 1947 must be understood in the context of pre-existing migratory flows within the partitioned regions (see also Chatterji 2013). She also demonstrates that the new national states of India and Pakistan were quickly drawn into trying to stem this migration. As they put into place laws designed to restrict the return of partition emigrants, this produced new dilemmas for both new nations in their treatment of 'overseas Indians'; and many of them lost their right to return to their places of origin in the subcontinent, and also their claims to full citizenship in host countries.}}</ref><ref name="talbot-sing">{{citation |last1=Talbot |first1=Ian |last2=Singh |first2=Gurharpal |title=The Partition of India |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=utKmPQAACAAJ |year=2009 |publisher=Cambridge University Press |isbn=978-0-521-85661-4 |access-date=15 November 2015 |archive-date=13 December 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161213073754/https://books.google.com/books?id=utKmPQAACAAJ |url-status=live|quote=When the British divided and quit India in August 1947, they not only partitioned the subcontinent with the emergence of the two nations of India and Pakistan but also the provinces of Punjab and Bengal. ... Indeed for many the Indian subcontinent's division in August 1947 is seen as a unique event which defies comparative historical and conceptual analysis}}</ref><ref name="khan-great-partition">{{citation|last=Khan|first=Yasmin|author-link=Yasmin Khan|title=The Great Partition: The Making of India and Pakistan|edition=2nd|location=New Haven and London|publisher=Yale University Press|isbn=978-0-300-23032-1|year=2017|orig-year=2007|page=1|quote=South Asians learned that the British Indian empire would be partitioned on 3 June 1947. They heard about it on the radio, from relations and friends, by reading newspapers and, later, through government pamphlets. Among a population of almost four hundred million, where the vast majority live in the countryside, ploughing the land as landless peasants or sharecroppers, it is hardly surprising that many thousands, perhaps hundreds of thousands, did not hear the new for many weeks afterwards. For some, the butchery and forced relocation of the summer months of 1947 may hve been the first that they knew about the creation of the two new states rising from the fragmentary and terminally weakened British empire in India}}</ref> ਹਿੰਦੂ-ਬਹੁਗਿਣਤੀ [[ਭਾਰਤ ਦਾ ਡੋਮੀਨੀਅਨ]] ਅਤੇ ਇੱਕ ਮੁਸਲਿਮ-ਬਹੁਗਿਣਤੀ [[ਪਾਕਿਸਤਾਨ ਦਾ ਡੋਮੀਨੀਅਨ]], ਵੱਡੇ ਪੱਧਰ 'ਤੇ ਜਾਨੀ ਨੁਕਸਾਨ ਅਤੇ ਇੱਕ ਬੇਮਿਸਾਲ ਪਰਵਾਸ ਦੇ ਵਿਚਕਾਰ।<ref>(a) {{harvnb|Copland|2001|pp=71–78}};<br />(b) {{harvnb|Metcalf|Metcalf|2006|p=222}}.</ref> |
|||
! '''ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਰੀਂਗਣਾ ਜੀਵ''' |
|||
| |
|||
ਭਾਰਤ 1950 ਤੋਂ ਇੱਕ [[ਸੰਘੀ ਗਣਰਾਜ]] ਰਿਹਾ ਹੈ, ਇੱਕ ਲੋਕਤੰਤਰੀ [[ਸੰਸਦੀ ਪ੍ਰਣਾਲੀ]] ਦੁਆਰਾ ਸ਼ਾਸਨ ਕੀਤਾ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ। ਇਹ ਬਹੁਲਵਾਦੀ, [[ਬਹੁਭਾਸ਼ਾਵਾਦ|ਬਹੁ-ਭਾਸ਼ੀ]] ਅਤੇ ਬਹੁ-ਜਾਤੀ ਸਮਾਜ ਹੈ। ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀ ਆਬਾਦੀ 1951 ਵਿੱਚ 361 ਮਿਲੀਅਨ ਤੋਂ ਵਧ ਕੇ 2022 ਵਿੱਚ ਲਗਭਗ 1.4 ਬਿਲੀਅਨ ਹੋ ਗਈ।<ref name="Dyson2018-219">{{harvnb|Dyson|2018|pp=[https://books.google.com/books?id=3TRtDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA219 219], 262}}</ref> |
|||
| [[Image:King-Cobra.jpg|50px]] |
|||
|- |
|||
ਉਸੇ ਸਮੇਂ ਦੌਰਾਨ, ਇਸਦੀ ਨਾਮਾਤਰ [[ਪ੍ਰਤੀ ਵਿਅਕਤੀ ਆਮਦਨ]] US$64 ਸਾਲਾਨਾ ਤੋਂ US$2,601 ਤੱਕ ਵਧ ਗਈ, ਅਤੇ ਇਸਦੀ ਸਾਖਰਤਾ ਦਰ 16.6% ਤੋਂ 74% ਹੋ ਗਈ। 1951 ਵਿੱਚ ਮੁਕਾਬਲਤਨ ਬੇਸਹਾਰਾ ਦੇਸ਼ ਹੋਣ ਤੋਂ<ref name="Fisher2018-8">{{harvnb|Fisher|2018|p=[https://books.google.com/books?id=kZVuDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA8 8]}}</ref> ਭਾਰਤ ਇੱਕ ਤੇਜ਼ੀ ਨਾਲ ਵਧ ਰਹੀ ਮੁੱਖ ਅਰਥਵਿਵਸਥਾ ਅਤੇ ਸੂਚਨਾ ਤਕਨਾਲੋਜੀ ਸੇਵਾਵਾਂ ਦਾ ਇੱਕ ਕੇਂਦਰ ਬਣ ਗਿਆ ਹੈ, ਇੱਕ ਵਿਸਤ੍ਰਿਤ ਮੱਧ ਵਰਗ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ।<ref name="MetcalfMetcalf2012-265">{{harvnb|Metcalf|Metcalf|2012|pp=[https://books.google.com/books?id=mjIfqyY7jlsC&pg=PA265 265–266]}}</ref> ਇਸਦਾ ਇੱਕ [[ਭਾਰਤੀ ਪੁਲਾੜ ਖੋਜ ਸੰਸਥਾ|ਸਪੇਸ ਪ੍ਰੋਗਰਾਮ]] ਹੈ। ਭਾਰਤੀ ਫਿਲਮਾਂ, ਸੰਗੀਤ ਅਤੇ ਅਧਿਆਤਮਿਕ ਸਿੱਖਿਆਵਾਂ ਗਲੋਬਲ ਸੱਭਿਆਚਾਰ ਵਿੱਚ ਵਧਦੀ ਭੂਮਿਕਾ ਨਿਭਾਉਂਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ।<ref name="MetcalfMetcalf2012-266">{{harvnb|Metcalf|Metcalf|2012|p=[https://books.google.com/books?id=mjIfqyY7jlsC&pg=PA266 266]}}</ref> ਭਾਰਤ ਨੇ ਆਪਣੀ ਗਰੀਬੀ ਦੀ ਦਰ ਨੂੰ ਕਾਫ਼ੀ ਹੱਦ ਤੱਕ ਘਟਾ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਹੈ, ਹਾਲਾਂਕਿ ਆਰਥਿਕ ਅਸਮਾਨਤਾ ਵਧਣ ਦੀ ਕੀਮਤ 'ਤੇ।<ref name="Dyson2018-216-a">{{harvnb|Dyson|2018|p=[https://books.google.com/books?id=3TRtDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA216 216]}}</ref> ਭਾਰਤ ਇੱਕ ਪਰਮਾਣੂ-ਹਥਿਆਰ ਵਾਲਾ ਦੇਸ਼ ਹੈ, ਜੋ ਫੌਜੀ ਖਰਚਿਆਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਉੱਚ ਦਰਜੇ 'ਤੇ ਹੈ। ਇਸ ਦੇ ਆਪਣੇ ਗੁਆਂਢੀ ਦੇਸ਼ਾਂ ਪਾਕਿਸਤਾਨ ਅਤੇ ਚੀਨ ਨਾਲ [[ਕਸ਼ਮੀਰ]] ਨੂੰ ਲੈ ਕੇ ਵਿਵਾਦ ਹਨ, ਜੋ 20ਵੀਂ ਸਦੀ ਦੇ ਅੱਧ ਤੋਂ ਅਣਸੁਲਝੇ ਹੋਏ ਹਨ।<ref name="kashmir-disputes">(a) {{citation |title=Kashmir, region Indian subcontinent |encyclopedia=[[Encyclopaedia Britannica]] |url=https://www.britannica.com/place/Kashmir-region-Indian-subcontinent |access-date=15 August 2019 |url-access=subscription |quote=Kashmir, region of the northwestern Indian subcontinent{{nbsp}}... has been the subject of dispute between India and Pakistan since the partition of the Indian subcontinent in 1947. |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190813203817/https://www.britannica.com/place/Kashmir-region-Indian-subcontinent |archive-date=13 August 2019 |url-status=live}};<br />(b) {{citation |last1=Pletcher |first1=Kenneth |title=Aksai Chin, Plateau Region, Asia |encyclopedia=[[Encyclopaedia Britannica]] |url=https://www.britannica.com/place/Aksai-Chin |access-date=16 August 2019 |url-access=subscription |quote=Aksai Chin, Chinese (Pinyin) Aksayqin, portion of the Kashmir region, ... constitutes nearly all the territory of the Chinese-administered sector of Kashmir that is claimed by India |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190402090308/https://www.britannica.com/place/Aksai-Chin |archive-date=2 April 2019}};<br />(c) {{cite encyclopedia|title=Kashmir|encyclopedia=[[Encyclopedia Americana]]: Jefferson to Latin |publisher=[[Scholastic Library Publishing]] |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=l_cWAQAAMAAJ&pg=PA328 |year=2006 |isbn=978-0-7172-0139-6 |page=328 |first=C. E |last=Bosworth |quote=KASHMIR, kash'mer, the northernmost region of the Indian subcontinent, administered partly by India, partly by Pakistan, and partly by China. The region has been the subject of a bitter dispute between India and Pakistan since they became independent in 1947}}</ref> ਭਾਰਤ ਨੂੰ ਜਿਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਸਮਾਜਿਕ-ਆਰਥਿਕ ਚੁਣੌਤੀਆਂ ਦਾ ਸਾਹਮਣਾ ਕਰਨਾ ਪੈਂਦਾ ਹੈ, ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਲਿੰਗ ਅਸਮਾਨਤਾ, ਬਾਲ ਕੁਪੋਸ਼ਣ,<ref name="NarayanJohn2018-lead">{{cite journal|last1=Narayan |first1=Jitendra |last2=John|first2=Denny|last3=Ramadas|first3=Nirupama|title=Malnutrition in India: status and government initiatives|journal=[[Journal of Public Health Policy]]|volume=40|issue=1|year=2018 |pages=126–141|issn=0197-5897 |doi=10.1057/s41271-018-0149-5|pmid=30353132|s2cid=53032234}}</ref> ਅਤੇ [[ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਹਵਾ ਪ੍ਰਦੂਸ਼ਣ|ਹਵਾ ਪ੍ਰਦੂਸ਼ਣ]] ਦੇ ਵਧਦੇ ਪੱਧਰ।<ref name="BalakrishnanDey2019-lead">{{cite journal|last1=Balakrishnan|first1=Kalpana|last2=Dey|first2=Sagnik|title=The impact of air pollution on deaths, disease burden, and life expectancy across the states of India: the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017|journal=[[The Lancet Planetary Health]]|volume=3|issue=1|year=2019|pages=e26–e39|display-authors=etal |issn=2542-5196 |doi=10.1016/S2542-5196(18)30261-4|pmid=30528905|pmc=6358127}}</ref> ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀ ਧਰਤੀ ਮੈਗਾਡਾਇਵਰਸ ਹੈ, ਚਾਰ ਜੈਵ ਵਿਭਿੰਨਤਾ ਦੇ ਹੌਟਸਪੌਟਸ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ।<ref name="IUCN-India">{{citation|title=India|publisher=[[International Union for Conservation of Nature]] (IUCN)|url=https://www.iucn.org/asia/countries/india|year=2019|access-date=21 May 2019|archive-date=1 November 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201101033802/https://www.iucn.org/asia/countries/india|url-status=dead}}</ref> ਇਸਦੇ ਜੰਗਲਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਇਸਦੇ ਖੇਤਰ ਦਾ 21.7% ਸ਼ਾਮਲ ਹੈ।<ref name="ISFR" /> ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਜੰਗਲੀ ਜੀਵ, ਜਿਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੂੰ [[ਭਾਰਤ ਦਾ ਸੱਭਿਆਚਾਰ|ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀ ਸੰਸਕ੍ਰਿਤੀ]] ਵਿੱਚ ਪਰੰਪਰਾਗਤ ਤੌਰ 'ਤੇ ਸਹਿਣਸ਼ੀਲਤਾ ਨਾਲ ਦੇਖਿਆ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ, ਨੂੰ ਇਹਨਾਂ ਜੰਗਲਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ, ਅਤੇ ਕਿਤੇ ਹੋਰ, ਸੁਰੱਖਿਅਤ ਨਿਵਾਸ ਸਥਾਨਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਸਮਰਥਨ ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤ ਹੈ।.{{sfn|Karanth|Gopal|2005|p=374}} |
|||
! '''ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਵਿਰਾਸਤ ਜਾਨਵਰ''' |
|||
| |
|||
| [[Image:Hanuman Langur.jpg|50px]] |
|||
|- |
|||
! '''ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਫਲ''' |
|||
| |
|||
| [[Image:An Unripe Mango Of Ratnagiri (India).JPG|50px]] |
|||
|- |
|||
! '''ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਮੰਦਰ''' |
|||
| |
|||
| [[Image:New Delhi Temple.jpg|50px]] |
|||
|- |
|||
! '''ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਨਦੀ ''' |
|||
| |
|||
| [[Image:River Ganges.JPG|50px]] |
|||
|- |
|||
! '''ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਪਰਬਤ''' |
|||
| |
|||
| [[Image:Nanda Devi 2006.JPG|50px]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| |
|||
|} |
|||
==ਨਾਂ ਦੀ ਉਤਪੱਤੀ== |
==ਨਾਂ ਦੀ ਉਤਪੱਤੀ== |
||
ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਦੋ ਅਧਿਕਾਰਤ ਨਾਂ ਹਨ - ਹਿੰਦੀ ਵਿੱਚ '''ਭਾਰਤ''' (भारत) ਅਤੇ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਵਿੱਚ '''ਇੰਡੀਆ''' (India)। ਇਸ |
ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਦੋ ਅਧਿਕਾਰਤ ਨਾਂ ਹਨ - ਹਿੰਦੀ ਵਿੱਚ '''ਭਾਰਤ''' (भारत) ਅਤੇ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਵਿੱਚ '''ਇੰਡੀਆ''' (''India'')। ਇਸ ਨੂੰ ਹਿੰਦੁਸਤਾਨ ਵੀ ਆਖਦੇ ਹਨ। ਇੰਡੀਆ ਨਾਂ ਦੀ ਉਤਪਤੀ [[ਸਿੰਧੂ ਨਦੀ]] ਦੇ ਅੰਗਰੇਜੀ ਨਾਂ "ਇੰਡਸ" ਤੋਂ ਹੋਈ ਹੈ। ਭਾਰਤ ਨਾਂ, ਇੱਕ ਪ੍ਰਾਚੀਨ ਹਿੰਦੂ ਸਮਰਾਟ [[ਭਰਤ]] ਜੋ ਕਿ [[ਮਨੂੰ]] ਦੇ ਵੰਸ਼ਜ ਰਿਸ਼ਭਦੇਵ ਦੇ ਜੇਠੇ ਪੁੱਤ ਸਨ ਅਤੇ ਜਿਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੀ ਕਥਾ ਸ੍ਰੀਮਦ ਭਾਗਵਤ ਪੁਰਾਣ ਵਿੱਚ ਹੈ, ਦੇ ਨਾਮ ਤੋਂ ਲਿਆ ਗਿਆ ਹੈ। ਭਾਰਤ (ਭਾ+ਰਤ) ਸ਼ਬਦ ਦਾ ਮਤਲਬ ਹੈ ਆਂਤਰਿਕ ਪ੍ਰਕਾਸ਼ ਜਾਂ ਵਿਵੇਕ-ਰੂਪੀ ਪ੍ਰਕਾਸ਼ ਵਿੱਚ ਲੀਨ। ਇੱਕ ਤੀਜਾ ਨਾਮ '''ਹਿੰਦੁਸਤਾਨ''' (ہندوستان) ਵੀ ਹੈ ਜਿਸਦਾ ਮਤਲਬ "ਹਿੰਦ ਦੀ ਭੂਮੀ" ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ਜੋ ਕਿ ਪ੍ਰਾਚੀਨ ਕਾਲ ਰਿਸ਼ੀਆਂ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਗਿਆ ਸੀ। ਪ੍ਰਾਚੀਨ ਕਾਲ ਵਿੱਚ ਇਹ ਘੱਟ ਪ੍ਰਚੱਲਤ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਸੀ ਅਤੇ ਬਾਅਦ ਵਿੱਚ ਜ਼ਿਆਦਾ ਪ੍ਰਚੱਲਤ ਹੋਇਆ ਖਾਸ ਤੌਰ ਉੱਤੇ ਅਰਬ/ਈਰਾਨ ਵਿੱਚ। ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਇਹ ਨਾਮ ਮੁਗਲ ਕਾਲ ਵਿੱਚ ਜ਼ਿਆਦਾ ਪ੍ਰਚੱਲਤ ਹੋਇਆ ਹਾਲਾਂਕਿ ਇਸਦੀ ਸਮਕਾਲੀ ਵਰਤੋਂ ਘੱਟ ਅਤੇ ਅਕਸਰ ਉੱਤਰੀ ਭਾਰਤ ਲਈ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ। ਇਸ ਤੋਂ ਇਲਾਵਾ ਹਿੰਦੁਸਤਾਨ ਨੂੰ ਵੇਦ-ਕਾਲ ਵਿੱਚ [[ਆਰਿਆਵਰਤ]] [[ਜੰਬੂਦੀਪ]] ਅਤੇ [[ਅਜਨਾਭ-ਦੇਸ]] ਦੇ ਨਾਮ ਵਜੋਂ ਵੀ ਜਾਣਿਆ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਰਿਹਾ ਹੈ। ਬਹੁਤ ਪਹਿਲਾਂ ਇਹ ਦੇਸ਼ [[ਸੋਨੇ ਦੀ ਚਿੜੀ]] ਦੇ ਰੂਪ ਵਿੱਚ ਜਾਣਿਆ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਸੀ।<ref>{{cite web |
||
|title = Hindustan |
|title = Hindustan |
||
|url = http://www.britannica.com/eb/article-9040520/Hindustan |
|url = http://www.britannica.com/eb/article-9040520/Hindustan |
||
| ਲਕੀਰ 147: | ਲਕੀਰ 189: | ||
{{main|ਭਾਰਤ ਦਾ ਇਤਿਹਾਸ}} |
{{main|ਭਾਰਤ ਦਾ ਇਤਿਹਾਸ}} |
||
[[ਤਸਵੀਰ:Sanchi2.jpg|thumb|ਤੀਜੀ ਸ਼ਤਾਬਦੀ ਵਿੱਚ ਸਮਰਾਟ [[ਅਸ਼ੋਕ]] ਦੁਆਰਾ ਬਣਾਇਆ ਗਿਆ ਵਿਚਕਾਰ ਪ੍ਰਦੇਸ਼ ਵਿੱਚ [[ਸਾਂਚੀ ਦਾ ਸਤੂਪ]]]] |
[[ਤਸਵੀਰ:Sanchi2.jpg|thumb|ਤੀਜੀ ਸ਼ਤਾਬਦੀ ਵਿੱਚ ਸਮਰਾਟ [[ਅਸ਼ੋਕ]] ਦੁਆਰਾ ਬਣਾਇਆ ਗਿਆ ਵਿਚਕਾਰ ਪ੍ਰਦੇਸ਼ ਵਿੱਚ [[ਸਾਂਚੀ ਦਾ ਸਤੂਪ]]]] |
||
[[ਪੱਥਰ ਯੁੱਗ]] ਭੀਮਬੇਟਕਾ [[ਮੱਧ ਪ੍ਰਦੇਸ਼]] ਦੀ ਗੁਫਾਵਾਂ ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਮਨੁੱਖੀ ਜੀਵਨ ਦਾ ਪ੍ਰਾਚੀਨਤਮ ਪ੍ਰਮਾਣ ਹਨ। ਪਹਿਲੀਆਂ ਸਥਾਈ ਬਸਤੀਆਂ ਨੇ 9000 ਸਾਲ ਪੂਰਵ ਵਿੱਚ ਰੂਪ ਧਾਰਿਆ। ਇਹੀ ਅੱਗੇ ਚੱਲ ਕੇ [[ |
[[ਪੱਥਰ ਯੁੱਗ]] ਭੀਮਬੇਟਕਾ [[ਮੱਧ ਪ੍ਰਦੇਸ਼]] ਦੀ ਗੁਫਾਵਾਂ ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਮਨੁੱਖੀ ਜੀਵਨ ਦਾ ਪ੍ਰਾਚੀਨਤਮ ਪ੍ਰਮਾਣ ਹਨ। ਪਹਿਲੀਆਂ ਸਥਾਈ ਬਸਤੀਆਂ ਨੇ 9000 ਸਾਲ ਪੂਰਵ ਵਿੱਚ ਰੂਪ ਧਾਰਿਆ। ਇਹੀ ਅੱਗੇ ਚੱਲ ਕੇ [[ਸਿੰਧੂ ਘਾਟੀ ਸੱਭਿਅਤਾ]] ਵਿੱਚ ਵਿਕਸਿਤ ਹੋਈਆਂ, ਜੋ 2600 ਈਸਾ ਪੂਰਵ ਅਤੇ 1900 ਈਸਾ ਪੂਰਵ ਦੇ ਵਿਚਕਾਰ ਆਪਣੇ ਸਿਖਰ ਉੱਤੇ ਸੀ। ਲਗਭਗ 1600 ਈਸਾ ਪੂਰਵ ਵਿੱਚ ਆਰਿਆ ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਆਏ ਅਤੇ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੇ ਉੱਤਰ-ਭਾਰਤੀ ਖੇਤਰਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ [[ਵੈਦਿਕ ਸੱਭਿਅਤਾ]] ਦਾ ਸੂਤਰਪਾਤ ਕੀਤਾ। ਇਸ ਸੱਭਿਅਤਾ ਦੇ ਸਰੋਤ [[ਵੇਦ]] ਅਤੇ [[ਪੁਰਾਣ]] ਹਨ। ਪਰ [[ਆਰਿਆ-ਹਮਲਾ-ਸਿੱਧਾਂਤ]] ਅਜੇ ਤੱਕ ਵਿਵਾਦਤ ਹੈ। ਬਾਲ ਗੰਗਾਧਰ ਸਹਿਤ ਸਹਿਤ ਕੁਝ ਵਿਦਵਾਨਾਂ ਦੀ ਮਾਨਤਾ ਇਹ ਹੈ ਕਿ ਆਰਿਆ ਹਿੰਦੁਸਤਾਨ ਦੇ ਹੀ ਸਥਾਈ ਨਿਵਾਸੀ ਰਹੇ ਹਨ ਅਤੇ ਵੈਦਿਕ ਇਤਹਾਸ ਕਰੀਬ 75000 ਸਾਲ ਪ੍ਰਾਚੀਨ ਹੈ ਜੋ ਕਿ ਗਲਤ ਸਾਬਤ ਹੋਇਆ ਹੈ। ਇਸ ਸਮੇਂ ਦੱਖਣ ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ [[ਦ੍ਰਵਿੜ ਸੱਭਿਅਤਾ]] ਦਾ ਵਿਕਾਸ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਰਿਹਾ। ਦੋਨਾਂ ਜਾਤੀਆਂ ਨੇ ਇੱਕ ਦੂਜੇ ਦੀਆਂ ਖੂਬੀਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਅਪਣਾਉਂਦੇ ਹੋਏ ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਇੱਕ ਮਿਸ਼ਰਤ-ਸੰਸਕ੍ਰਿਤੀ ਦੀ ਉਸਾਰੀ ਕੀਤੀ। |
||
500 ਈਸਵੀ ਪੂਰਵ ਤੋਂ ਬਾਅਦ ਕਈ ਅਜ਼ਾਦ ਰਾਜ ਬਣ ਗਏ। ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਸ਼ੁਰੂਆਤੀ ਰਾਜ-ਵੰਸ਼ਾਂ ਵਿੱਚੋਂ ਉੱਤਰ-ਭਾਰਤ ਦਾ [[ਮੌਰਿਆ ਰਾਜਵੰਸ਼]] ਜ਼ਿਕਰਯੋਗ ਹੈ ਜਿਸਦੇ ਸਮਰਾਟ [[ਅਸ਼ੋਕ]] ਦਾ ਵਿਸ਼ਵ ਇਤਹਾਸ ਵਿੱਚ ਵਿਸ਼ੇਸ਼ ਸਥਾਨ ਹੈ। 180 ਈਸਵੀ ਦੀ ਸ਼ੁਰੂਆਤ ਤੋਂ ਮੱਧ-ਏਸ਼ਿਆ ਵੱਲੋਂ ਕਈ ਹਮਲੇ ਹੋਏ, ਜਿਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੇ ਨਤੀਜੇ ਵਜੋਂ ਉੱਤਰ-ਭਾਰਤੀ ਉਪ-ਮਹਾਦੀਪ ਵਿੱਚ [[ਯੂਨਾਨੀ]], [[ਸ਼ੱਕ]], [[ਪਾਰਥੀ]] ਅਤੇ [[ਓੜਕ ਕੁਸ਼ਾਣ ਰਾਜ-ਵੰਸ਼]] ਸਥਾਪਤ ਹੋਏ। |
500 ਈਸਵੀ ਪੂਰਵ ਤੋਂ ਬਾਅਦ ਕਈ ਅਜ਼ਾਦ ਰਾਜ ਬਣ ਗਏ। ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਸ਼ੁਰੂਆਤੀ ਰਾਜ-ਵੰਸ਼ਾਂ ਵਿੱਚੋਂ ਉੱਤਰ-ਭਾਰਤ ਦਾ [[ਮੌਰਿਆ ਰਾਜਵੰਸ਼]] ਜ਼ਿਕਰਯੋਗ ਹੈ ਜਿਸਦੇ ਸਮਰਾਟ [[ਅਸ਼ੋਕ]] ਦਾ ਵਿਸ਼ਵ ਇਤਹਾਸ ਵਿੱਚ ਵਿਸ਼ੇਸ਼ ਸਥਾਨ ਹੈ। 180 ਈਸਵੀ ਦੀ ਸ਼ੁਰੂਆਤ ਤੋਂ ਮੱਧ-ਏਸ਼ਿਆ ਵੱਲੋਂ ਕਈ ਹਮਲੇ ਹੋਏ, ਜਿਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੇ ਨਤੀਜੇ ਵਜੋਂ ਉੱਤਰ-ਭਾਰਤੀ ਉਪ-ਮਹਾਦੀਪ ਵਿੱਚ [[ਯੂਨਾਨੀ]], [[ਸ਼ੱਕ]], [[ਪਾਰਥੀ]] ਅਤੇ [[ਓੜਕ ਕੁਸ਼ਾਣ ਰਾਜ-ਵੰਸ਼]] ਸਥਾਪਤ ਹੋਏ। |
||
| ਲਕੀਰ 154: | ਲਕੀਰ 197: | ||
12ਵੀਂ ਸ਼ਤਾਬਦੀ ਦੇ ਅਰੰਭ ਵਿੱਚ, ਭਾਰਤ ਉੱਤੇ ਇਸਲਾਮੀ ਹਮਲਿਆਂ ਦੇ ਬਾਅਦ, ਉੱਤਰੀ ਅਤੇ ਕੇਂਦਰੀ ਭਾਰਤ ਦਾ ਸਾਰਾ ਹਿੱਸਾ [[ਦਿੱਲੀ]] ਸਲਤਨਤ ਦੇ ਸ਼ਾਸਨ ਅਧੀਨ ਹੋ ਗਿਆ; ਅਤੇ ਬਾਅਦ ਵਿੱਚ, ਸਾਰਾ [[ਉੱਪ-ਮਹਾਂਦੀਪ]] [[ਮੁਗਲ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ]] ਦੇ ਅਧੀਨ। ਦੱਖਣ ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ [[ਵਿਜੇਨਗਰ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ]] ਸ਼ਕਤੀਸ਼ਾਲੀ ਨਿਕਲਿਆ। ਹਾਲਾਂਕਿ ਖਾਸ ਕਰਕੇ ਮੁਕਾਬਲਤਨ ਰੂਪ ਵਲੋਂ, ਦੱਖਣ ਵਿੱਚ ਅਨੇਕਾਂ ਰਾਜ ਬਾਕੀ ਰਹੇ, ਅਤੇ ਹੋਂਦ ਵਿੱਚ ਆਏ। ਮੁਗਲਾਂ ਦੇ ਸੰਖੇਪ ਅਧਿਕਾਰ ਦੇ ਬਾਅਦ ਸਤਾਰਵੀਂ ਸਦੀ ਵਿੱਚ ਦੱਖਣ ਅਤੇ ਮੱਧ ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ [[ਮਰਾਠਿਆਂ]] ਦਾ ਜੋਰ ਹੋਇਆ। ਉੱਤਰ ਪੱਛਮ ਵਿੱਚ ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਦਾ ਸ਼ਕਤੀਸ਼ਾਲੀ ਰਾਜ ਹੋਂਦ ਵਿੱਚ ਆਇਆ। |
12ਵੀਂ ਸ਼ਤਾਬਦੀ ਦੇ ਅਰੰਭ ਵਿੱਚ, ਭਾਰਤ ਉੱਤੇ ਇਸਲਾਮੀ ਹਮਲਿਆਂ ਦੇ ਬਾਅਦ, ਉੱਤਰੀ ਅਤੇ ਕੇਂਦਰੀ ਭਾਰਤ ਦਾ ਸਾਰਾ ਹਿੱਸਾ [[ਦਿੱਲੀ]] ਸਲਤਨਤ ਦੇ ਸ਼ਾਸਨ ਅਧੀਨ ਹੋ ਗਿਆ; ਅਤੇ ਬਾਅਦ ਵਿੱਚ, ਸਾਰਾ [[ਉੱਪ-ਮਹਾਂਦੀਪ]] [[ਮੁਗਲ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ]] ਦੇ ਅਧੀਨ। ਦੱਖਣ ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ [[ਵਿਜੇਨਗਰ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ]] ਸ਼ਕਤੀਸ਼ਾਲੀ ਨਿਕਲਿਆ। ਹਾਲਾਂਕਿ ਖਾਸ ਕਰਕੇ ਮੁਕਾਬਲਤਨ ਰੂਪ ਵਲੋਂ, ਦੱਖਣ ਵਿੱਚ ਅਨੇਕਾਂ ਰਾਜ ਬਾਕੀ ਰਹੇ, ਅਤੇ ਹੋਂਦ ਵਿੱਚ ਆਏ। ਮੁਗਲਾਂ ਦੇ ਸੰਖੇਪ ਅਧਿਕਾਰ ਦੇ ਬਾਅਦ ਸਤਾਰਵੀਂ ਸਦੀ ਵਿੱਚ ਦੱਖਣ ਅਤੇ ਮੱਧ ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ [[ਮਰਾਠਿਆਂ]] ਦਾ ਜੋਰ ਹੋਇਆ। ਉੱਤਰ ਪੱਛਮ ਵਿੱਚ ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਦਾ ਸ਼ਕਤੀਸ਼ਾਲੀ ਰਾਜ ਹੋਂਦ ਵਿੱਚ ਆਇਆ। |
||
17ਵੀਂ ਸ਼ਤਾਬਦੀ ਦੇ ਮੱਧ ਵਿੱਚ [[ਪੁਰਤਗਾਲ]], [[ਡੱਚ]], [[ਫ਼ਰਾਂਸ]], [[ਬ੍ਰਿਟੇਨ]] ਸਹਿਤ ਅਨੇਕਾਂ ਯੂਰਪੀ ਦੇਸ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ, ਜੋ ਭਾਰਤ ਨਾਲ ਵਪਾਰ ਕਰਨ ਦੇ ਇੱਛੁਕ ਸਨ, ਦੇਸ਼ ਦੀ ਅੰਦਰੂਨੀ ਸ਼ਾਸਕੀ ਅਰਾਜਕਤਾ ਦਾ ਫਾਇਦਾ ਚੁੱਕਿਆ। ਅੰਗ੍ਰੇਜ ਦੂਜੇ ਦੇਸ਼ਾਂ ਨਾਲ ਵਪਾਰ ਦੇ ਇੱਛੁਕ ਲੋਕਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਰੋਕਣ ਵਿੱਚ ਸਫ਼ਲ ਰਹੇ ਅਤੇ 1840 ਤੱਕ ਲਗਭਗ ਪੂਰੇ ਦੇਸ਼ ਉੱਤੇ ਸ਼ਾਸਨ ਕਰਣ ਵਿੱਚ ਸਫਲ ਹੋਏ। 1847 ਵਿੱਚ [[ਬ੍ਰਿਟਿਸ਼ ਈਸਟ ਇੰਡੀਆ ਕੰਪਨੀ]] ਦੇ ਵਿਰੁੱਧ ਅਸਫਲ ਬਗ਼ਾਵਤ, ਜੋ ਭਾਰਤੀ ਸੁਤੰਤਰਤਾ ਦੀ ਪਹਿਲੀ ਲੜਾਈ ਵਜੋਂ ਵੀ ਜਾਣੀ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ, ਦੇ ਬਾਅਦ ਭਾਰਤ ਦਾ ਸਾਰਾ ਭਾਗ ਸਿੱਧੇ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਸ਼ਾਸਨ ਦੇ ਪ੍ਰਬੰਧਕੀ ਕਾਬੂ ਵਿੱਚ ਆ ਗਿਆ। |
|||
ਕੋਣਾਰਕ ਚੱਕਰ |
ਕੋਣਾਰਕ ਚੱਕਰ – 13ਵੀਂ ਸ਼ਤਾਬਦੀ ਵਿੱਚ ਬਣੇ ਉੜੀਸਾ ਦੇ [[ਕੋਣਾਰਕ ਸੂਰਜ ਮੰਦਿਰ]] ਵਿੱਚ ਸਥਿਤ, ਇਹ ਦੁਨੀਆ ਦੇ ਪ੍ਰਸਿੱਧ ਇਤਿਹਾਸਿਕ ਸਮਾਰਕਾਂ ਵਿੱਚੋਂ ਇੱਕ ਹੈ। |
||
ਵੀਹਵੀਂ ਸਦੀ ਦੇ ਸ਼ੁਰੂ ਵਿੱਚ ਆਧੁਨਿਕ ਸਿੱਖਿਆ ਦੇ ਪ੍ਰਸਾਰ ਅਤੇ ਵਿਸ਼ਵਪਟਲ ਉੱਤੇ ਬਦਲਦੀ ਰਾਜਨੀਤਕ ਪਰੀਸਥਤੀਆਂ ਦੇ ਚਲਦੇ ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਇੱਕ ਬੌਧਿਕ ਅੰਦੋਲਨ ਦਾ ਸੂਤਰਪਾਤ ਹੋਇਆ ਜਿਨ੍ਹੇ ਸਮਾਜਕ ਅਤੇ ਰਾਜਨੀਤਕ ਪਧਰਾਂ ਉੱਤੇ ਅਨੇਕ ਪਰਿਵਰਤਨਾਂ ਅਤੇ ਅੰਦੋਲਨਾਂ ਦੀ ਨੀਂਹ ਰੱਖੀ। 1884 ਵਿੱਚ [[ਇੰਡੀਅਨ ਨੈਸ਼ਨਲ ਕਾਂਗਰਸ]] ਕਾਂਗਰੇਸ ਪਾਰਟੀ ਦੀ ਸਥਾਪਨਾ ਨੇ ਸਵਤੰਤਰਤਾ ਅੰਦੋਲਨ ਨੂੰ ਇੱਕ ਗਤੀਮਾਨ ਸਵਰੂਪ ਦਿੱਤਾ। ਵੀਹਵੀਂ ਸ਼ਤਾਬਦੀ ਦੇ ਅਰੰਭ ਵਿੱਚ ਲੰਬੇ ਸਮਾਂ ਤੱਕ ਅਜ਼ਾਦੀ ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤੀ ਲਈ ਵਿਸ਼ਾਲ ਅਹਿੰਸਾਵਾਦੀ ਸੰਘਰਸ਼ ਚੱਲਿਆ, ਜਿਸਦਾ ਨੇਤ੍ਰਤਅਲਤੇ [[ਮਹਾਤਮਾ ਗਾਂਧੀ]], ਜੋ ਆਧਿਕਾਰਿਕ ਰੁਪ ਵਲੋਂ ਆਧੁਨਿਕ ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰਪਿਤਾ ਦੇ ਰੂਪ ਵਿੱਚ ਸੰਬੋਧਿਤ ਕੀਤੇ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਹਨ, ਨੇ ਕੀਤਾ। ਇਸਦੇ ਨਾਲ |
ਵੀਹਵੀਂ ਸਦੀ ਦੇ ਸ਼ੁਰੂ ਵਿੱਚ ਆਧੁਨਿਕ ਸਿੱਖਿਆ ਦੇ ਪ੍ਰਸਾਰ ਅਤੇ ਵਿਸ਼ਵਪਟਲ ਉੱਤੇ ਬਦਲਦੀ ਰਾਜਨੀਤਕ ਪਰੀਸਥਤੀਆਂ ਦੇ ਚਲਦੇ ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਇੱਕ ਬੌਧਿਕ ਅੰਦੋਲਨ ਦਾ ਸੂਤਰਪਾਤ ਹੋਇਆ ਜਿਨ੍ਹੇ ਸਮਾਜਕ ਅਤੇ ਰਾਜਨੀਤਕ ਪਧਰਾਂ ਉੱਤੇ ਅਨੇਕ ਪਰਿਵਰਤਨਾਂ ਅਤੇ ਅੰਦੋਲਨਾਂ ਦੀ ਨੀਂਹ ਰੱਖੀ। 1884 ਵਿੱਚ [[ਇੰਡੀਅਨ ਨੈਸ਼ਨਲ ਕਾਂਗਰਸ]] ਕਾਂਗਰੇਸ ਪਾਰਟੀ ਦੀ ਸਥਾਪਨਾ ਨੇ ਸਵਤੰਤਰਤਾ ਅੰਦੋਲਨ ਨੂੰ ਇੱਕ ਗਤੀਮਾਨ ਸਵਰੂਪ ਦਿੱਤਾ। ਵੀਹਵੀਂ ਸ਼ਤਾਬਦੀ ਦੇ ਅਰੰਭ ਵਿੱਚ ਲੰਬੇ ਸਮਾਂ ਤੱਕ ਅਜ਼ਾਦੀ ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤੀ ਲਈ ਵਿਸ਼ਾਲ ਅਹਿੰਸਾਵਾਦੀ ਸੰਘਰਸ਼ ਚੱਲਿਆ, ਜਿਸਦਾ ਨੇਤ੍ਰਤਅਲਤੇ [[ਮਹਾਤਮਾ ਗਾਂਧੀ]], ਜੋ ਆਧਿਕਾਰਿਕ ਰੁਪ ਵਲੋਂ ਆਧੁਨਿਕ ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰਪਿਤਾ ਦੇ ਰੂਪ ਵਿੱਚ ਸੰਬੋਧਿਤ ਕੀਤੇ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਹਨ, ਨੇ ਕੀਤਾ। ਇਸਦੇ ਨਾਲ – ਨਾਲ [[ਸ਼ਿਵ ਆਜ਼ਾਦ]], ਸਰਦਾਰ [[ਭਗਤ ਸਿੰਘ]], [[ਸੁਖਦੇਵ ਥਾਪਰ]], [[ਰਾਜਗੁਰੂ]], ਨੇਤਾਜੀ [[ਸੁਭਾਸ਼ ਚੰਦਰ ਬੋਸ]], [[ਵੀਰ ਸਾਵਰਕਰ]] ਆਦਿ ਦੇ ਨੇਤ੍ਰਤਆਤੇ ਵਿੱਚ ਚਲੇ ਕ੍ਰਾਂਤੀਵਾਦੀ ਸੰਘਰਸ਼ ਦੇ ਫਲਸਰੁਪ [[16 ਜੂਨ]] 1946 ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਵਲੋਂ ਅੰਤਰਮ ਸਰਕਾਰ ਬਣਾਉਣ ਦਾ ਐਲਾਨ: ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀ ਦੋ ਗਰੁੱਪਾਂ (ਏ ਤੇ ਬੀ) ਵਿੱਚ ਵੰਡ ਦੀ ਹਮਾਇਤ ਕੀਤੀ। ਮਿਸ਼ਨ ਨੇ ਬੀ ਗਰੁੱਪ ਵਿੱਚ [[ਪੰਜਾਬ]], [[ਸਿੰਧ]], [[ਬਲੋਚਿਸਤਾਨ]] ਤੇ [[ਸੂਬਾ ਸਰਹੱਦ]] ਰੱਖੇ ਸਨ। ਕੈਬਨਿਟ ਮਿਸ਼ਨ ਤੇ ਵਾਇਸਰਾਏ ਨੇ ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਅੰਤਰਮ ਸਰਕਾਰ ਬਣਾਉਣ ਦਾ ਐਲਾਨ ਕੀਤਾ। ਇਸ ਵਿੱਚ 6 ਕਾਂਗਰਸੀ, 5 ਮੁਸਲਿਮ ਲੀਗ, 1 ਸਿੱਖ, 1 ਪਾਰਸੀ ਤੇ 1 ਭਾਰਤੀ ਈਸਾਈ ਵਜ਼ੀਰ ਲੈਣ ਦਾ ਫ਼ੈਸਲਾ ਹੋਇਆ। ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਵਿੱਚੋਂ ਬਲਦੇਵ ਸਿਘ (ਅਕਾਲੀ) ਨੂੰ ਵਜ਼ਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਸ਼ਾਮਲ ਹੋਣ ਵਾਸਤੇ ਸੱਦਾ ਦਿਤਾ ਗਿਆ। 15 ਅਗਸਤ 1947 ਭਾਰਤ ਨੇ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਸ਼ਾਸਨ ਵਲੋਂ ਪੂਰਣਤਯਾ ਅਜ਼ਾਦੀ ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤ ਕੀਤੀ। ਤਦੁਪਰਾਂਤ 26 ਜਨਵਰੀ 1950 ਨੂੰ ਭਾਰਤ ਇੱਕ ਲੋਕ-ਰਾਜ ਬਣਾ। |
||
ਇੱਕ ਬਹੁਜਾਤੀਏ ਅਤੇ ਬਹੁਧਾਰਮਿਕ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰ ਹੋਣ ਦੇ ਕਾਰਨ ਭਾਰਤ ਨੂੰ ਸਮਾਂ – ਸਮਾਂ ਉੱਤੇ ਸਾੰਪ੍ਰਦਾਇਿਕ ਅਤੇ ਜਾਤੀ ਵੈਰ ਦਾ ਸ਼ਿਕਾਰ ਹੋਣਾ ਪਿਆ ਹੈ। ਖੇਤਰੀ ਅਸੰਤੋਸ਼ ਅਤੇ ਬਗ਼ਾਵਤ ਵੀ ਹਾਲਾਂਕਿ ਦੇਸ਼ ਦੇ ਵੱਖ - ਵੱਖ ਹਿੱਸੀਆਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਰਹੇ ਹਨ, ਉੱਤੇ ਇਸਦੀ ਧਰਮਨਿਰਪੇਕਸ਼ਤਾ ਅਤੇ ਜਨਤਾਂਤਰਿਕਤਾ, ਕੇਵਲ 1975 – 77 ਨੂੰ ਛੱਡ, ਜਦੋਂ ਤਤਕਾਲੀਨ ਪ੍ਰਧਾਨਮੰਤਰੀ [[ਇੰਦਰਾ ਗਾਂਧੀ]] ਨੇ [[ਐਮਰਜੈਂਸੀ (ਭਾਰਤ)|ਐਮਰਜੈਂਸੀ]] ਦੀ ਘੋਸ਼ਣਾ ਕਰ ਦਿੱਤੀ ਸੀ, ਅਖੰਡਤ ਰਹੀ ਹੈ। |
|||
ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਗੁਆਂਢੀ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੋਂ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ਅਨਸੁਲਝੇ ਸੀਮਾ ਵਿਵਾਦ ਹਨ। ਇਸਦੇ ਕਾਰਨ ਇਸਨੂੰ ਛੋਟੇ ਪੈਮਾਨੀਆਂ ਉੱਤੇ ਲੜਾਈ ਦਾ ਵੀ ਸਾਮਣਾ ਕਰਣਾ ਪਿਆ ਹੈ। 1962 ਵਿੱਚ ਚੀਨ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ, ਅਤੇ 1947, 1965, 1971 ਏਵੰ 1999 ਵਿੱਚ [[ਪਾਕਿਸਤਾਨ]] ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ਲੜਾਇਆਂ ਹੋ ਚੁੱਕੀ ਹਨ।<br /> |
ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਗੁਆਂਢੀ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੋਂ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ਅਨਸੁਲਝੇ ਸੀਮਾ ਵਿਵਾਦ ਹਨ। ਇਸਦੇ ਕਾਰਨ ਇਸਨੂੰ ਛੋਟੇ ਪੈਮਾਨੀਆਂ ਉੱਤੇ ਲੜਾਈ ਦਾ ਵੀ ਸਾਮਣਾ ਕਰਣਾ ਪਿਆ ਹੈ। 1962 ਵਿੱਚ ਚੀਨ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ, ਅਤੇ 1947, 1965, 1971 ਏਵੰ 1999 ਵਿੱਚ [[ਪਾਕਿਸਤਾਨ]] ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ਲੜਾਇਆਂ ਹੋ ਚੁੱਕੀ ਹਨ।<br /> |
||
ਭਾਰਤ ਗੁਟਨਿਰਪੇਕਸ਼ ਅੰਦੋਲਨ ਅਤੇ ਸੰਯੁਕਤ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰ ਸੰਘ ਦੇ ਸੰਸਥਾਪਕ ਮੈਂਬਰ ਦੇਸ਼ਾਂ ਵਿੱਚੋਂ ਇੱਕ ਹੈ। |
ਭਾਰਤ ਗੁਟਨਿਰਪੇਕਸ਼ ਅੰਦੋਲਨ ਅਤੇ ਸੰਯੁਕਤ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰ ਸੰਘ ਦੇ ਸੰਸਥਾਪਕ ਮੈਂਬਰ ਦੇਸ਼ਾਂ ਵਿੱਚੋਂ ਇੱਕ ਹੈ। |
||
1974 ਵਿੱਚ ਭਾਰਤ ਨੇ ਆਪਣਾ ਪਹਿਲਾ ਪਰਮਾਣੁ ਪ੍ਰੀਖਿਆ ਕੀਤਾ ਸੀ ਜਿਸਦੇ ਬਾਅਦ 1998 ਵਿੱਚ 5 ਅਤੇ ਪ੍ਰੀਖਿਆ ਕੀਤੇ ਗਏ। 1990 ਦੇ ਦਸ਼ਕ ਵਿੱਚ ਕੀਤੇ ਗਏ ਆਰਥਕ ਸੁਧਾਰੀਕਰਣ ਦੀ ਬਦੌਲਤ ਅੱਜ ਦੇਸ਼ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਤੇਜੀ ਵਲੋਂ ਵਿਕਾਸਸ਼ੀਲ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੋਂ ਦੀ ਸੂਚੀ ਵਿੱਚ ਆ ਗਿਆ ਹੈ। |
|||
==ਭੂਗੋਲਿਕ ਸਥਿਤੀ== |
==ਭੂਗੋਲਿਕ ਸਥਿਤੀ== |
||
ਭਾਰਤ, ਭਾਰਤੀ ਉਪ-ਮਹਾਂਦੀਪ ਦਾ ਜ਼ਿਆਦਾਤਰ ਹਿੱਸਾ, ਭਾਰਤੀ ਟੈਕਟੋਨਿਕ ਪਲੇਟ ਦੇ ਉੱਪਰ ਸਥਿਤ ਹੈ, ਥੋੜੀ ਪਲੇਟ ਹਿੰਦ-ਆਸਟ੍ਰੇਲੀਆਈ ਪਲੇਟ ਨਾਲ ਲੱਗਦੀ ਹੈ। ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀ ਪਰਿਭਾਸ਼ਤ ਭੂ-ਵਿਗਿਆਨਿਕ ਪ੍ਰਕਿਰਿਆਵਾਂ ੭ ਕਰੋੜ ਸਾਲ ਪਹਿਲਾਂ ਸ਼ੁਰੂ ਹੋਈਆਂ ਜਦੋਂ ਭਾਰਤੀ ਉਪਮਹਾਂਦੀਪ, ਜੋ ਉਸ ਸਮੇਂ ਦੇ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਵੱਡੇ ਮਹਾਂਦੀਪ ਗੋਂਡਵਾਨਾ ਦਾ ਦੱਖਣੀ ਹਿੱਸਾ ਸੀ, ਉੱਤਰ-ਪੂਰਬ ਵੱਲ ਨੂੰ ਵਧਣ ਲੱਗਾ। ਉਪ-ਮਹਾਂਦੀਪ ਦੇ ਯੁਰੇਸ਼ਿਅਨ ਪਲੇਟ ਨਾਲ ਹੋਏ ਟਕਰਾਅ ਨਾਲ ਹਿਮਾਲਾ ਦਾ ਜਨਮ ਹੋਇਆ। ਹਿਮਾਲਾ ਚੋਂ ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਵੱਡੇ ਦਰਿਆ ਨਿਕਲਦੇ ਹਨ। ਇਸ ਦੇ ਪੱਛਮ 'ਚ ਥਾਰ ਮਾਰੂਥਲ ਹੈ, ਜਿਸ ਨੂੰ ਅਰਾਵਲੀ ਨੇ ਬਾਰਿਸ਼ਾਂ ਤੋ ਵਾਂਝਾ ਕੀਤਾ ਹੋਇਆ ਹੈ। ਉੱਤਰ 'ਚ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਦੀ ਉਪਜਾਊ ਧਰਤੀ ਤੇ ਦੱਖਣ 'ਚ ਕਠੋਰ ਪਠਾਰ ਇਸ ਨੂੰ ਭਿੰਨਤਾ ਦਾ ਪੁਤਲਾ ਬਣਾਉਂਦੇ ਹਨ। ਗੰਗਾ, ਜਮਨਾ, ਸਤਲੁਜ, ਬ੍ਰਹਮਪੁੱਤਰ ਆਦਿ ਵੱਡੀਆਂ ਨਦੀਆਂ ਭਾਰਤ 'ਚ ਹੀ ਹਨ। ਸਾਰਾ ਦੇਸ਼ ਮਾਨਸੂਨ ਦੀ ਵਰਖਾ ਤੋਂ ਹੀ ਝੜੀ ਦਾ ਸੁੱਖ ਮਾਣਦਾ ਹੈ। |
|||
===ਮੌਸਮ=== |
===ਮੌਸਮ=== |
||
ਹਿਮਾਲਾ ਜਵਾਬ ਵਿੱਚ ਜੰਮੂ ਅਤੇ ਕਾਸ਼ਮੀਰ ਵਲੋਂ ਲੈ ਕੇ ਪੂਰਵ ਵਿੱਚ ਅਰੁਣਾਂਚਲ ਪ੍ਰਦੇਸ਼ ਤੱਕ ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀ ਜਿਆਦਾਤਰ ਪੂਰਵੀ ਸੀਮਾ ਬਣਾਉਂਦਾ ਹੈ |
|||
ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਜਿਆਦਾਤਰ ਉੱਤਰੀ ਅਤੇ ਜਵਾਬ |
ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਜਿਆਦਾਤਰ ਉੱਤਰੀ ਅਤੇ ਜਵਾਬ – ਪਸ਼ਚਿਮੀਏ ਪ੍ਰਾਂਤ ਹਿਮਾਲਾ ਦੇ ਪਹਾੜਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਸਥਿਤ ਹਨ। ਬਾਕੀ ਭਾਗ ਉੱਤਰੀ, ਵਿਚਕਾਰ ਅਤੇ ਪੂਰਵੀ ਭਾਰਤ ਗੰਗਾ ਦੇ ਉਪਜਾਊ ਮੈਦਾਨਾਂ ਵਲੋਂ ਬਣਿਆ ਹੈ। ਉੱਤਰੀ - ਪੂਰਵੀ ਪਾਕਿਸਤਾਨ ਵਲੋਂ ਚੋਟੀ ਹੋਇਆ, ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਪੱਛਮ ਵਿੱਚ ਥਾਰ ਦਾ ਮਾਰੂਥਲ ਹੈ। ਦੱਖਣ ਭਾਰਤ ਲਗਭਗ ਸੰਪੂਰਣ ਹੀ ਦੱਖਣ ਦੇ ਪਠਾਰ ਵੱਲੋਂ ਨਿਰਮਿਤ ਹੈ। ਇਹ ਪਠਾਰ ਪੂਰਵੀ ਅਤੇ ਪੱਛਮ ਵੱਲ ਘਾਟਾਂ ਦੇ ਵਿੱਚ ਸਥਿਤ ਹੈ। |
||
ਕਈ ਮਹੱਤਵਪੂਰਣ ਅਤੇ ਵੱਡੀਆਂ ਨਦੀਆਂ ਜਿਵੇਂ ਗੰਗਾ, ਬ੍ਰਹਮਪੁਤਰ, ਜਮੁਨਾ, ਗੋਦਾਵਰੀ ਅਤੇ ਕ੍ਰਿਸ਼ਣਾ ਭਾਰਤ ਵਲੋਂ ਹੋਕੇ ਵਗਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ। ਇਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨਦੀਆਂ ਦੇ ਕਾਰਨ ਉੱਤਰ ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀ ਭੂਮੀ ਖੇਤੀਬਾੜੀ ਲਈ ਉਪਜਾਊ ਹੈ। ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਵਿਸਥਾਰ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ਹੀ ਇਸਦੇ ਮੌਸਮ ਵਿੱਚ ਵੀ ਬਹੁਤ ਭਿੰਨਤਾ ਹੈ। ਦੱਖਣ ਵਿੱਚ ਜਿੱਥੇ ਕਿਨਾਰੀ ਅਤੇ ਗਰਮ ਮਾਹੌਲ ਰਹਿੰਦਾ ਹੈ ਉਥੇ ਹੀ ਜਵਾਬ ਵਿੱਚ ਕੜੀ ਸਰਦੀ, ਪੂਰਵ ਵਿੱਚ ਜਿੱਥੇ ਜਿਆਦਾ ਵਰਖਾ ਹੈ ਉਥੇ ਹੀ ਪੱਛਮ ਵਿੱਚ ਰੇਗਿਸਤਾਨ ਦੀ ਖੁਸ਼ਕੀ। ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਵਰਖਾ ਮੁੱਖਤਆ ਮਾਨਸੂਨ ਹਵਾਵਾਂ ਵਲੋਂ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ। |
|||
===ਜੀਵ ਵਖਰੇਵਾਂ=== |
===ਜੀਵ ਵਖਰੇਵਾਂ=== |
||
| ਲਕੀਰ 183: | ਲਕੀਰ 226: | ||
==ਰਾਜ== |
==ਰਾਜ== |
||
{{main| |
{{main|ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਰਾਜ ਅਤੇ ਕੇਂਦਰ ਸ਼ਾਸਿਤ ਪ੍ਰਦੇਸ਼}} |
||
[[File:Political map of India EN.svg|thumb|{{#if:{{{image-width|}}}|{{{image-width}}}|500}}px{{!}}A clickable map of the 29 states and 9 union territories of India]] |
[[File:Political map of India EN.svg|thumb|{{#if:{{{image-width|}}}|{{{image-width}}}|500}}px{{!}}A clickable map of the 29 states and 9 union territories of India]] |
||
[[ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਾਸਕੀ]] ਮਕਸਦ ਲਈ, ਭਾਰਤ ਨੂੰ ਛੋਟੇ ਹਿੱਸਿਆਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਵੰਡਿਆ ਗਿਆ ਹੈ। ਜ਼ਿਆਦਾਤਰ ਹਿੱਸਿਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਰਾਜ ਜਾਂ ਪ੍ਰਾਂਤ ਕਿਹਾ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ਅਤੇ ਕੁੱਝ ਹਿੱਸਿਆਂ ਨੂੰ [[ਕੇਂਦਰੀ |
[[ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਾਸਕੀ]] ਮਕਸਦ ਲਈ, ਭਾਰਤ ਨੂੰ ਛੋਟੇ ਹਿੱਸਿਆਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਵੰਡਿਆ ਗਿਆ ਹੈ। ਜ਼ਿਆਦਾਤਰ ਹਿੱਸਿਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਰਾਜ ਜਾਂ ਪ੍ਰਾਂਤ ਕਿਹਾ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ਅਤੇ ਕੁੱਝ ਹਿੱਸਿਆਂ ਨੂੰ [[ਕੇਂਦਰੀ ਸ਼ਾਸ਼ਤ ਪ੍ਰਦੇਸ]] ਕਿਹਾ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ। ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਕੁਲ 28 ਰਾਜ ਅਤੇ 9 ਕੇਂਦਰੀ ਸ਼ਾਸਤ ਪ੍ਰਦੇਸ਼ ਹਨ। |
||
=== ਰਾਜ-ਸਾਰਣੀ === |
=== ਰਾਜ-ਸਾਰਣੀ === |
||
| ਲਕੀਰ 198: | ਲਕੀਰ 241: | ||
| [[ਆਂਧਰਾ ਪ੍ਰਦੇਸ਼]] |
| [[ਆਂਧਰਾ ਪ੍ਰਦੇਸ਼]] |
||
| AP |
| AP |
||
| [[ਅਮਰਾਵਤੀ (ਰਾਜਧਾਨੀ )|ਅਮਰਾਵਤੀ]] |
|||
| [[ਹੈਦਰਾਬਾਦ, ਭਾਰਤ|ਹੈਦਰਾਬਾਦ]] |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| 2 |
| 2 |
||
| ਲਕੀਰ 279: | ਲਕੀਰ 322: | ||
| [[ਮਿਜ਼ੋਰਮ]] |
| [[ਮਿਜ਼ੋਰਮ]] |
||
| MZ |
| MZ |
||
| [[ਆਇਜੋਲ ਜ਼ਿਲਾ|ਆਇਜੋਲ]] |
|||
| [[ਇੰਜ਼ੌਲ]] |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| 18 |
| 18 |
||
| ਲਕੀਰ 342: | ਲਕੀਰ 385: | ||
! ਸੰਖਿਆ |
! ਸੰਖਿਆ |
||
! ਰਾਜ-ਖੇਤਰ |
! ਰਾਜ-ਖੇਤਰ |
||
! ਕੋਡ |
|||
! ਰਾਜਧਾਨੀ |
! ਰਾਜਧਾਨੀ |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| A |
| A |
||
| [[ਅੰਡੇਮਾਨ ਅਤੇ ਨਿਕੋਬਾਰ ਦੀਪ ਸਮੂਹ]] |
| [[ਅੰਡੇਮਾਨ ਅਤੇ ਨਿਕੋਬਾਰ ਦੀਪ ਸਮੂਹ]] |
||
| AN |
|||
| [[ਪੋਰਟ ਬਲੇਅਰ]] |
| [[ਪੋਰਟ ਬਲੇਅਰ]] |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| B |
| B |
||
| [[ਚੰਡੀਗੜ੍ਹ]] |
| [[ਚੰਡੀਗੜ੍ਹ]] |
||
| CH |
|||
| [[ਚੰਡੀਗੜ੍ਹ]] |
| [[ਚੰਡੀਗੜ੍ਹ]] |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| C |
| C |
||
| [[ਦਾਦਰਾ ਅਤੇ ਨਗਰ ਹਵੇਲੀ]] |
| [[ਦਾਦਰਾ ਅਤੇ ਨਗਰ ਹਵੇਲੀ]] ਅਤੇ [[ਦਮਨ ਅਤੇ ਦਿਉ]] |
||
| DN |
|||
| [[ਸਿਲਵਾਸਾ]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| D |
|||
| [[ਦਮਨ ਅਤੇ ਦਿਉ]] |
|||
| DD |
|||
| [[ਦਮਨ]] |
| [[ਦਮਨ]] |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
| D |
||
| [[ਲਕਸ਼ਦੀਪ]] |
| [[ਲਕਸ਼ਦੀਪ]] |
||
| LD |
|||
| [[ਕਵਰੱਤੀ]] |
| [[ਕਵਰੱਤੀ]] |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
| E |
||
| [[ਦਿੱਲੀ]] |
| [[ਦਿੱਲੀ]] |
||
| DL |
|||
| [[ਨਵੀਂ ਦਿੱਲੀ]] |
| [[ਨਵੀਂ ਦਿੱਲੀ]] |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
| F |
||
| [[ਪਾਂਡੀਚਰੀ]] |
| [[ਪਾਂਡੀਚਰੀ]] |
||
| PY |
|||
| [[ਪਾਂਡੀਚਰੀ|ਪਾਂਡੀਚਰੀ (ਸ਼ਹਿਰ)]] |
| [[ਪਾਂਡੀਚਰੀ|ਪਾਂਡੀਚਰੀ (ਸ਼ਹਿਰ)]] |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
| G |
||
| [[ਜੰਮੂ ਅਤੇ ਕਸ਼ਮੀਰ]] |
| [[ਜੰਮੂ ਅਤੇ ਕਸ਼ਮੀਰ (ਰਾਜ)|ਜੰਮੂ ਅਤੇ ਕਸ਼ਮੀਰ]] |
||
| [[ਸ੍ਰੀਨਗਰ]] ਅਤੇ [[ਜੰਮੂ]] |
|||
| JK |
|||
| [[ਸ਼੍ਰੀ ਨਗਰ]] ਅਤੇ [[ਜੰਮੂ]] |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
| H |
||
| [[ਲੱਦਾਖ]] |
| [[ਲੱਦਾਖ]] |
||
| |
|||
| [[ਲੇਹ]] |
| [[ਲੇਹ]] |
||
|- |
|||
|} |
|} |
||
==ਸਰਕਾਰ== |
|||
{{main|ਭਾਰਤ ਸਰਕਾਰ}} |
{{main|ਭਾਰਤ ਸਰਕਾਰ}} |
||
ਭਾਰਤ ਦੁਨੀਆ ਦਾ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਵੱਡਾ [[ਗਣਰਾਜ]] ਹੈ। ਇਸ ਦੀ [[ਸਰਕਾਰ]] (ਹਕੂਮਤ) ਤਿੰਨ ਸ਼ਾਖ਼ਾਵਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਵੰਡਿਆ ਹੋਇਆ:[[ਵਿਧਾਇਕਾ]] / ਕਨੂੰਨਸਾਜ (ਜੋ ਕਨੂੰਨ ਬਣਾਉਂਦੀ ਹੈ, [[ਸੰਸਦ]]), [[ਕਾਰਜਪਾਲਿਕਾ]]/ ਹਕੂਮਤਿ ਮੁਲਕ ([[ਸਰਕਾਰ]]) ਅਤੇ [[ਨਿਆਪਾਲਿਕਾ]]/ ਅਦਾਲਤ (ਜੋ ਕਨੂੰਨ ਨੂੰ ਲਾਗੂ ਰਹਿਣ 'ਚ ਸਹਾਈ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ)। |
|||
== ਰਾਜਨੀਤੀ ਅਤੇ ਸਰਕਾਰ == |
|||
ਕਨੂੰਨਸਾਜ ਸ਼ਾਖਾ ਵਿੱਚ ਭਾਰਤੀ ਸੰਸਦ ਆਉਂਦੀ ਹੈ, ਜੋ ਕਿ ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀ ਰਾਜਧਾਨੀ (ਦਾਰ-ਅਲ-ਹਕੂਮਤ), ਨਵੀਂ ਦਿੱਲੀ ਵਿਖੇ ਹੈ। ਸੰਸਦ ਦੋ ਹਿੱਸਿਆਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਵੰਡੀ ਹੋਈ ਹੈ: ਉੱਪਰਲਾ ਸਦਨ, [[ਰਾਜ ਸਭਾ]] (ਰਿਆਸਤੀ ਪਰਿਸ਼ਦ); ਹੇਠਲਾ ਸਦਨ, [[ਲੋਕ ਸਭਾ]] (ਲੋਕਾਂ ਸਦਨ)। ਰਾਜ ਸਭਾ ਦੇ ੨੫੦ [[ਸਭਾਸਦ]] ਹਨ ਅਤੇ ਲੋਕ ਸਭਾ ਦੇ ੫੪੫ ਸਭਾਸਦ ਹਨ। |
|||
=== ਰਾਜਨੀਤੀ === |
|||
ਭਾਰਤ ਦੁਨੀਆ ਦਾ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਵੱਧ ਆਬਾਦੀ ਵਾਲਾ [[ਲੋਕਰਾਜ|ਲੋਕਤੰਤਰ]] ਹੈ। {{Sfn|United Nations Population Division}} [[ਬਹੁ-ਪਾਰਟੀ ਪ੍ਰਣਾਲੀ]] ਵਾਲਾ ਇੱਕ ਸੰਸਦੀ ਗਣਰਾਜ, {{Sfn|Burnell|Calvert|1999}} ਇਸਦੇ ਅੱਠ ਹਨ ਮਾਨਤਾ ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਪਾਰਟੀਆਂ, ਜਿਸ ਵਿੱਚ [[ਭਾਰਤੀ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਕਾਂਗਰਸ]] ਅਤੇ [[ਭਾਰਤੀ ਜਨਤਾ ਪਾਰਟੀ]] (ਭਾਜਪਾ), ਅਤੇ 40 ਤੋਂ ਵੱਧ ਖੇਤਰੀ ਪਾਰਟੀਆਂ {{Sfn|Election Commission of India}} ਕਾਂਗਰਸ ਨੂੰ ਭਾਰਤੀ ਰਾਜਨੀਤਿਕ ਸੰਸਕ੍ਰਿਤੀ ਵਿੱਚ ਕੇਂਦਰ-ਖੱਬੇ ਮੰਨਿਆ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ,<ref>{{Cite journal|last=Sáez|first=Lawrence|last2=Sinha|first2=Aseema|year=2010|title=Political cycles, political institutions and public expenditure in India, 1980–2000|url=https://archive.org/details/sim_british-journal-of-political-science_2010-01_40_1/page/91|journal=[[British Journal of Political Science]]|volume=40|issue=1|pages=91–113|doi=10.1017/s0007123409990226}}</ref> ਅਤੇ ਭਾਜਪਾ ਨੂੰ [[ਸੱਜੇ-ਪੱਖੀ ਰਾਜਨੀਤੀ|ਸੱਜੇ-ਪੱਖੀ]] ਮੰਨਿਆ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ। {{Sfn|Malik|Singh|1992}} {{Sfn|Banerjee|2005}} <ref>{{Cite news|url=https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-asia-india-18352532|title=Narendra Modi makes his move|last=Halarnkar|first=Samar|date=13 June 2012|work=[[BBC News]]|quote=The right-wing Hindu nationalist Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP), India's primary opposition party}}</ref> 1950-ਜਦੋਂ ਭਾਰਤ ਪਹਿਲੀ ਵਾਰ ਗਣਤੰਤਰ ਬਣਿਆ-ਅਤੇ 1980ਵਿਆਂ ਦੇ ਅਖੀਰ ਤੱਕ, ਕਾਂਗਰਸ ਨੇ ਸੰਸਦ ਵਿੱਚ ਬਹੁਮਤ ਹਾਸਲ ਕੀਤਾ। ਉਦੋਂ ਤੋਂ, ਹਾਲਾਂਕਿ, ਇਸ ਨੇ ਭਾਜਪਾ {{Sfn|Sarkar|2007}} ਦੇ ਨਾਲ-ਨਾਲ ਸ਼ਕਤੀਸ਼ਾਲੀ ਖੇਤਰੀ ਪਾਰਟੀਆਂ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ਵੱਧ ਤੋਂ ਵੱਧ ਸਿਆਸੀ ਸਟੇਜ ਸਾਂਝੀ ਕੀਤੀ ਹੈ, ਜਿਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੇ ਅਕਸਰ ਕੇਂਦਰ ਵਿੱਚ ਬਹੁ-ਪਾਰਟੀ ਗੱਠਜੋੜ ਸਰਕਾਰਾਂ ਬਣਾਉਣ ਲਈ ਮਜ਼ਬੂਰ ਕੀਤਾ ਹੈ। {{Sfn|Chander|2004}} |
|||
ਭਾਰਤੀ ਗਣਰਾਜ ਦੀਆਂ ਪਹਿਲੀਆਂ ਤਿੰਨ ਆਮ ਚੋਣਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ, 1951, 1957 ਅਤੇ 1962 ਵਿੱਚ, [[ਜਵਾਹਰ ਲਾਲ ਨਹਿਰੂ]] ਦੀ ਅਗਵਾਈ ਵਾਲੀ ਕਾਂਗਰਸ ਨੇ ਆਸਾਨ ਜਿੱਤਾਂ ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤ ਕੀਤੀਆਂ। 1964 ਵਿਚ ਨਹਿਰੂ ਦੀ ਮੌਤ 'ਤੇ, [[ਲਾਲ ਬਹਾਦਰ ਸ਼ਾਸਤਰੀ]] ਥੋੜ੍ਹੇ ਸਮੇਂ ਲਈ ਪ੍ਰਧਾਨ ਮੰਤਰੀ ਬਣੇ; ਨਹਿਰੂ ਦੀ ਧੀ [[ਇੰਦਰਾ ਗਾਂਧੀ]] ਦੁਆਰਾ, 1966 ਵਿੱਚ ਉਸਦੀ ਆਪਣੀ ਅਚਾਨਕ ਮੌਤ ਤੋਂ ਬਾਅਦ, ਉਸਨੂੰ ਸਫ਼ਲ ਬਣਾਇਆ ਗਿਆ ਸੀ, ਜਿਸਨੇ 1967 ਅਤੇ 1971 ਵਿੱਚ ਕਾਂਗਰਸ ਨੂੰ ਚੋਣ ਜਿੱਤਾਂ ਤੱਕ ਪਹੁੰਚਾਉਣ ਲਈ ਅਗਵਾਈ ਕੀਤੀ ਸੀ। ਉਸਨੇ 1975 ਵਿੱਚ ਐਲਾਨੀ [[ਐਮਰਜੈਂਸੀ (ਭਾਰਤ)|ਐਮਰਜੈਂਸੀ ਦੀ ਸਥਿਤੀ]] ਤੋਂ ਜਨਤਕ ਅਸੰਤੋਸ਼ ਦੇ ਬਾਅਦ, 1977 ਵਿੱਚ ਕਾਂਗਰਸ ਨੂੰ ਸੱਤਾ ਤੋਂ ਬਾਹਰ ਕਰ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਗਿਆ ਸੀ; ਉਸ ਸਮੇਂ ਦੀ ਨਵੀਂ [[ਜਨਤਾ ਪਾਰਟੀ]], ਜਿਸ ਨੇ ਐਮਰਜੈਂਸੀ ਦਾ ਵਿਰੋਧ ਕੀਤਾ ਸੀ, ਨੂੰ ਵੋਟ ਦਿੱਤੀ ਗਈ ਸੀ। ਇਸ ਦੀ ਸਰਕਾਰ ਸਿਰਫ਼ ਦੋ ਸਾਲ ਹੀ ਚੱਲੀ। 1980 ਵਿੱਚ ਮੁੜ ਸੱਤਾ ਵਿੱਚ ਆਈ, ਕਾਂਗਰਸ ਨੇ 1984 ਵਿੱਚ ਲੀਡਰਸ਼ਿਪ ਵਿੱਚ ਬਦਲਾਅ ਦੇਖਿਆ, ਜਦੋਂ ਇੰਦਰਾ ਗਾਂਧੀ ਦੀ ਹੱਤਿਆ ਕਰ ਦਿੱਤੀ ਗਈ ਸੀ; ਉਸ ਤੋਂ ਬਾਅਦ ਉਸ ਦਾ ਪੁੱਤਰ [[ਰਾਜੀਵ ਗਾਂਧੀ]] ਬਣਿਆ, ਜਿਸ ਨੇ ਉਸ ਸਾਲ ਬਾਅਦ ਵਿੱਚ ਆਮ ਚੋਣਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਆਸਾਨ ਜਿੱਤ ਹਾਸਲ ਕੀਤੀ। 1989 ਵਿੱਚ ਕਾਂਗਰਸ ਨੂੰ ਫਿਰ ਤੋਂ ਬਾਹਰ ਕਰ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਗਿਆ ਜਦੋਂ [[ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀ ਕਮਿਊਨਿਸਟ ਪਾਰਟੀ (ਮਾਰਕਸਵਾਦੀ)|ਖੱਬੇ ਮੋਰਚੇ]] ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ਗਠਜੋੜ ਵਿੱਚ ਨਵੇਂ ਬਣੇ ਜਨਤਾ ਦਲ ਦੀ ਅਗਵਾਈ ਵਿੱਚ ਇੱਕ ਨੈਸ਼ਨਲ ਫਰੰਟ ਗੱਠਜੋੜ ਨੇ ਚੋਣਾਂ ਜਿੱਤੀਆਂ; ਉਹ ਸਰਕਾਰ ਵੀ ਮੁਕਾਬਲਤਨ ਥੋੜ੍ਹੇ ਸਮੇਂ ਲਈ ਸਾਬਤ ਹੋਈ, ਸਿਰਫ ਦੋ ਸਾਲਾਂ ਤੋਂ ਘੱਟ ਸਮੇਂ ਲਈ। {{Sfn|Bhambhri|1992}} 1991 ਵਿੱਚ ਦੁਬਾਰਾ ਚੋਣਾਂ ਹੋਈਆਂ; ਕਿਸੇ ਵੀ ਪਾਰਟੀ ਨੂੰ ਪੂਰਨ ਬਹੁਮਤ ਨਹੀਂ ਮਿਲਿਆ। ਕਾਂਗਰਸ, ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਵੱਡੀ ਇਕੱਲੀ ਪਾਰਟੀ ਦੇ ਰੂਪ ਵਿੱਚ, [[ਪੀ ਵੀ ਨਰਸਿਮਾ ਰਾਓ|ਪੀਵੀ ਨਰਸਿਮਹਾ ਰਾਓ]] ਦੀ ਅਗਵਾਈ ਵਿੱਚ ਘੱਟ ਗਿਣਤੀ ਸਰਕਾਰ ਬਣਾਉਣ ਵਿੱਚ ਕਾਮਯਾਬ ਰਹੀ। <ref>{{Cite news|url=https://www.hindu.com/2004/12/24/stories/2004122408870100.htm|title=Narasimha Rao Passes Away|date=24 December 2004|work=[[The Hindu]]|access-date=2 November 2008|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090213181659/https://www.hindu.com/2004/12/24/stories/2004122408870100.htm|archive-date=13 February 2009}}</ref> |
|||
1996 ਦੀਆਂ ਆਮ ਚੋਣਾਂ ਤੋਂ ਬਾਅਦ ਸਿਆਸੀ ਉਥਲ-ਪੁਥਲ ਦਾ ਦੋ ਸਾਲਾਂ ਦਾ ਦੌਰ ਚੱਲਿਆ। ਕਈ ਥੋੜ੍ਹੇ ਸਮੇਂ ਲਈ ਗਠਜੋੜਾਂ ਨੇ ਕੇਂਦਰ ਵਿੱਚ ਸੱਤਾ ਸਾਂਝੀ ਕੀਤੀ। ਭਾਜਪਾ ਨੇ 1996 ਵਿਚ ਥੋੜ੍ਹੇ ਸਮੇਂ ਲਈ ਸਰਕਾਰ ਬਣਾਈ; ਇਸਦੇ ਬਾਅਦ ਦੋ ਤੁਲਨਾਤਮਕ ਤੌਰ 'ਤੇ ਲੰਬੇ ਸਮੇਂ ਤੱਕ ਚੱਲਣ ਵਾਲੇ ਸੰਯੁਕਤ ਮੋਰਚੇ ਦੇ ਗੱਠਜੋੜ ਸਨ, ਜੋ ਬਾਹਰੀ ਸਮਰਥਨ 'ਤੇ ਨਿਰਭਰ ਸਨ। 1998 ਵਿੱਚ, ਭਾਜਪਾ ਇੱਕ ਸਫਲ ਗੱਠਜੋੜ, [[ਕੌਮੀ ਜਮਹੂਰੀ ਗਠਜੋੜ|ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਜਮਹੂਰੀ ਗਠਜੋੜ]] (ਐਨ.ਡੀ.ਏ.) ਬਣਾਉਣ ਵਿੱਚ ਕਾਮਯਾਬ ਰਹੀ। [[ਅਟਲ ਬਿਹਾਰੀ ਬਾਜਪਾਈ|ਅਟਲ ਬਿਹਾਰੀ ਵਾਜਪਾਈ]] ਦੀ ਅਗਵਾਈ ਵਿੱਚ, NDA ਪੰਜ ਸਾਲ ਦਾ ਕਾਰਜਕਾਲ ਪੂਰਾ ਕਰਨ ਵਾਲੀ ਪਹਿਲੀ ਗੈਰ-ਕਾਂਗਰਸੀ, ਗੱਠਜੋੜ ਸਰਕਾਰ ਬਣ ਗਈ। {{Sfn|Dunleavy|Diwakar|Dunleavy|2007}} ਫਿਰ [[ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀਆਂ ਆਮ ਚੋਣਾਂ 2004|2004 ਦੀਆਂ ਭਾਰਤੀ ਆਮ ਚੋਣਾਂ]] ਵਿੱਚ, ਕਿਸੇ ਵੀ ਪਾਰਟੀ ਨੇ ਪੂਰਨ ਬਹੁਮਤ ਨਹੀਂ ਜਿੱਤਿਆ, ਪਰ ਕਾਂਗਰਸ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਵੱਡੀ ਸਿੰਗਲ ਪਾਰਟੀ ਵਜੋਂ ਉੱਭਰੀ, ਇੱਕ ਹੋਰ ਸਫਲ ਗੱਠਜੋੜ: [[ਸੰਯੁਕਤ ਪ੍ਰਗਤੀਸ਼ੀਲ ਗਠਜੋੜ]] (ਯੂਪੀਏ)। ਇਸ ਨੂੰ ਖੱਬੇ ਪੱਖੀ ਪਾਰਟੀਆਂ ਅਤੇ ਭਾਜਪਾ ਦਾ ਵਿਰੋਧ ਕਰਨ ਵਾਲੇ ਸੰਸਦ ਮੈਂਬਰਾਂ ਦਾ ਸਮਰਥਨ ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤ ਸੀ। ਯੂਪੀਏ [[ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀਆਂ ਆਮ ਚੋਣਾਂ 2009|2009 ਦੀਆਂ ਆਮ ਚੋਣਾਂ]] ਵਿੱਚ ਵਧੀ ਹੋਈ ਗਿਣਤੀ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ਸੱਤਾ ਵਿੱਚ ਵਾਪਸ ਪਰਤਿਆ, ਅਤੇ ਇਸਨੂੰ ਹੁਣ ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀਆਂ ਕਮਿਊਨਿਸਟ ਪਾਰਟੀਆਂ ਤੋਂ ਬਾਹਰੀ ਸਮਰਥਨ ਦੀ ਲੋੜ ਨਹੀਂ ਰਹੀ। {{Sfn|Kulke|Rothermund|2004}} ਉਸ ਸਾਲ, [[ਮਨਮੋਹਨ ਸਿੰਘ]] [[ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀਆਂ ਆਮ ਚੋਣਾਂ 1957|1957]] ਅਤੇ [[ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀਆਂ ਆਮ ਚੋਣਾਂ 1962|1962]] ਵਿੱਚ [[ਜਵਾਹਰ ਲਾਲ ਨਹਿਰੂ]] ਤੋਂ ਬਾਅਦ ਲਗਾਤਾਰ ਪੰਜ ਸਾਲਾਂ ਦੇ ਕਾਰਜਕਾਲ ਲਈ ਦੁਬਾਰਾ ਚੁਣੇ ਜਾਣ ਵਾਲੇ ਪਹਿਲੇ ਪ੍ਰਧਾਨ ਮੰਤਰੀ ਬਣੇ। {{Sfn|Business Standard|2009}} [[ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀਆਂ ਆਮ ਚੋਣਾਂ 2014|2014 ਦੀਆਂ ਆਮ ਚੋਣਾਂ]] ਵਿੱਚ, ਭਾਜਪਾ 1984 ਤੋਂ ਬਾਅਦ ਪਹਿਲੀ ਸਿਆਸੀ ਪਾਰਟੀ ਬਣ ਗਈ ਜਿਸ ਨੇ ਬਹੁਮਤ ਹਾਸਲ ਕੀਤਾ ਅਤੇ ਦੂਜੀਆਂ ਪਾਰਟੀਆਂ ਦੇ ਸਮਰਥਨ ਤੋਂ ਬਿਨਾਂ ਸ਼ਾਸਨ ਕੀਤਾ। <ref>{{Cite news|url=https://www.dnaindia.com/india/report-bjp-first-party-since-1984-to-win-parliamentary-majority-on-its-own-1988981|title=BJP first party since 1984 to win parliamentary majority on its own|date=16 May 2014|work=[[Daily News and Analysis|DNA]]|access-date=20 May 2014|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140521032413/https://www.dnaindia.com/india/report-bjp-first-party-since-1984-to-win-parliamentary-majority-on-its-own-1988981|archive-date=21 May 2014|agency=Indo-Asian News Service}}</ref> ਮੌਜੂਦਾ ਪ੍ਰਧਾਨ ਮੰਤਰੀ [[ਨਰਿੰਦਰ ਮੋਦੀ]] [[ਗੁਜਰਾਤ]] ਦੇ ਸਾਬਕਾ [[ਮੁੱਖ ਮੰਤਰੀ (ਭਾਰਤ)|ਮੁੱਖ ਮੰਤਰੀ]] ਹਨ। 22 ਜੁਲਾਈ 2022 ਨੂੰ, [[ਦ੍ਰੋਪਦੀ ਮੁਰਮੂ]] ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀ 15ਵੀਂ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰਪਤੀ ਚੁਣੀ ਗਈ ਅਤੇ 25 ਜੁਲਾਈ 2022 ਨੂੰ ਅਹੁਦੇ ਦੀ ਸਹੁੰ ਚੁੱਕੀ। <ref>{{Cite news|url=https://indianexpress.com/article/india/droupadi-murmu-swearing-in-live-updates-8049577/|title=Droupadi Murmu Swearing-in Live: My election is the greatness of India, mother of democracy, says President Murmu|date=25 July 2022|access-date=26 July 2022|publisher=The Indian Express}}</ref> |
|||
ਕਾਰਜਪਾਲਕਾ ਸ਼ਾਖਾ ਵਿੱਚ [[ਸਦਰ]] (ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰਪਤੀ), [[ਨਾਇਬ ਸਦਰ]] (ਉਪਰਾਸ਼ਟਰਪਤੀ), [[ਵਾਜ਼ੀਰਿਆਜ਼ਾਮ]] (ਪ੍ਰਧਾਨਮੰਤਰੀ) ਅਤੇ [[ਵਜ਼ੀਰਾਂ ਦੀ ਪਰਿਸ਼ਦ]] ਆਉਂਦੇ ਹਨ। ਭਾਰਤ ਦਾ ਸਦਰ ੫ ਸਾਲਾਂ ਲਈ ਚੁਣਿਆ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ। ਜਿਸ ਕੋਲ ਲੋਕ ਸਭਾ ਵਿੱਚ ਵਧੇਰੇ ਤਾਕਤ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ, ਸਦਰ ਉਸ ਨੂੰ ਪ੍ਰਧਾਨਮੰਤਰੀ ਵਜੋਂ ਚੁਣ ਸਕਦਾ ਹੈ। |
|||
=== ਸਰਕਾਰ === |
|||
ਨਿਆਪਾਲਿਕਾ ਸ਼ਾਖਾ ਵਿੱਚ ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀਆਂ ਸਾਰੀਆਂ ਅਦਾਲਤਾਂ ਆਉਂਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ, ਜਿਸ ਵਿੱਚ ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀ [[ਭਾਰਤੀ ਸੁਪਰੀਮ ਕੋਰਟ|ਸਰਵਉੱਚ ਅਦਾਲਤ]] ਵੀ ਸ਼ਾਮਿਲ ਹੈ। ਭਾਰਤ ਕੋਲ 21 [[ਉੱਚ ਅਦਾਲਤਾਂ]] ਹਨ। |
|||
ਭਾਰਤ ਇੱਕ ਸੰਘ ਹੈ ਜਿਸਦਾ ਸੰਚਾਲਨ ਇੱਕ ਸੰਸਦੀ ਪ੍ਰਣਾਲੀ ਹੈ [[ਭਾਰਤੀ ਸੰਵਿਧਾਨ|ਜੋ ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਸੰਵਿਧਾਨ ਦੇ]] ਅਧੀਨ ਹੈ - ਦੇਸ਼ ਦਾ ਸਰਵਉੱਚ ਕਾਨੂੰਨੀ ਦਸਤਾਵੇਜ਼। ਇਹ ਇੱਕ ਸੰਵਿਧਾਨਕ ਗਣਰਾਜ ਅਤੇ [[ਅਪ੍ਰਤੱਖ ਲੋਕਰਾਜ|ਪ੍ਰਤੀਨਿਧ ਲੋਕਤੰਤਰ]] ਹੈ, ਜਿਸ ਵਿੱਚ " ਬਹੁਗਿਣਤੀ ਸ਼ਾਸਨ [[ਭਾਰਤ ਦਾ ਕਾਨੂੰਨ|ਕਾਨੂੰਨ]] ਦੁਆਰਾ ਸੁਰੱਖਿਅਤ ਘੱਟ ਗਿਣਤੀ ਦੇ ਅਧਿਕਾਰਾਂ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਸੰਜੀਦਾ ਹੈ"। ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਸੰਘਵਾਦ ਸੰਘ ਅਤੇ [[ਭਾਰਤੀ ਸੂਬੇ ਅਤੇ ਕੇਂਦਰੀ ਸ਼ਾਸ਼ਤ ਪ੍ਰਦੇਸ਼|ਰਾਜਾਂ]] ਵਿਚਕਾਰ ਸ਼ਕਤੀ ਦੀ ਵੰਡ ਨੂੰ ਪਰਿਭਾਸ਼ਿਤ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ। ਭਾਰਤ ਦਾ ਸੰਵਿਧਾਨ, ਜੋ ਕਿ 26 ਜਨਵਰੀ 1950 ਨੂੰ ਲਾਗੂ ਹੋਇਆ, {{Sfn|Pylee|2003a}} ਨੇ ਮੂਲ ਰੂਪ ਵਿੱਚ ਭਾਰਤ ਨੂੰ ਇੱਕ "[[ਖ਼ੁਦਮੁਖ਼ਤਿਆਰੀ|ਪ੍ਰਭੁਸੱਤਾ ਸੰਪੰਨ]], ਜਮਹੂਰੀ [[ਗਣਰਾਜ]]" ਕਿਹਾ। ਇਸ ਵਿਸ਼ੇਸ਼ਤਾ ਨੂੰ 1971 ਵਿੱਚ "ਇੱਕ ਪ੍ਰਭੂਸੱਤਾ ਸੰਪੰਨ, ਸਮਾਜਵਾਦੀ, [[ਧਰਮ ਨਿਰਪੱਖਤਾ|ਧਰਮ ਨਿਰਪੱਖ]], ਜਮਹੂਰੀ ਗਣਰਾਜ" ਵਿੱਚ ਸੋਧਿਆ ਗਿਆ ਸੀ। {{Sfn|Dutt|1998}} ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀ ਸਰਕਾਰ ਦਾ ਰੂਪ, ਜਿਸ ਨੂੰ ਰਵਾਇਤੀ ਤੌਰ 'ਤੇ ਇੱਕ ਮਜ਼ਬੂਤ ਕੇਂਦਰ ਅਤੇ ਕਮਜ਼ੋਰ ਰਾਜਾਂ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ "ਅਰਧ-ਸੰਘੀ" ਵਜੋਂ ਦਰਸਾਇਆ ਗਿਆ ਹੈ, {{Sfn|Wheare|1980}} ਸਿਆਸੀ, ਆਰਥਿਕ ਅਤੇ ਸਮਾਜਿਕ ਤਬਦੀਲੀਆਂ ਦੇ ਨਤੀਜੇ ਵਜੋਂ 1990 ਦੇ ਦਹਾਕੇ ਦੇ ਅਖੀਰ ਤੋਂ ਸੰਘੀ ਰੂਪ ਵਿੱਚ ਵਧਿਆ ਹੈ। {{Sfn|Echeverri-Gent|2002}} {{Sfn|Sinha|2004}} |
|||
==ਸਮੱਸਿਆਵਾਂ== |
==ਸਮੱਸਿਆਵਾਂ== |
||
ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀਆਂ ਹੱਦਾਂ ਦੇ ਕਈ ਹਿੱਸਿਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਲੈ ਕੇ ਕਈ [[ਵਿਵਾਦ]] ਪਏ ਹੋਏ ਹਨ। ਕਈ ਦੇਸ਼ ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀ ਆਪਣੀ ਮਾਨਤ ਹੱਦਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਨਹੀਂ ਮੰਨਦੇ। ਪਾਕਿਸਤਾਨ ਅਤੇ ਚੀਨ ਭਾਰਤੀ ਕਬਜ਼ੇ ਦੇ [[ਕਸ਼ਮੀਰ]] ਅਤੇ [[ਅਰੁਣਾਚਲ]] ਨੂੰ ਭਾਰਤੀ ਰਿਆਸਤ ਹੋਣ ਦੀ ਮਾਨਤਾ ਨਹੀਂ ਦਿੰਦੇ। ਇਸੇ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਭਾਰਤ ਵੀ ਪਾਕਿਸਤਾਨ ਅਤੇ ਚੀਨ ਦੇ ਕਬਜ਼ੇ ਵਾਲੇ ਕਸ਼ਮੀਰ ਅਤੇ ਅਰੁਣਾਚਲ ਨੂੰ ਉਹਨਾਂ ਦਾ ਹੋਣ ਦੀ ਮਾਨਤਾ ਨਹੀਂ ਦਿੰਦਾ। |
|||
੧੯ ੧੪ ਵਿਚ, [[ਬਰਤਾਨਵੀ ਭਾਰਤ]] ਅਤੇ [[ਤਿੱਬਤ]] ਵਿਚਕਾਰ [[ਮਕਮਹੋਨ]] ਰੇਖਾ ਨੂੰ ਭਾਰਤ ਨਾਲ ਲੱਗਦੀ ਤਿਬਤ ਦੀ ਹੱਦ ਹੋਣ ਦਾ ਕਰਾਰ ਹੋਇਆ ਸੀ, [[ਸ਼ਿਮਲਾ ਸੰਧੀ]] ਦਾ ਹਿੱਸਾ। ਤਿਬਤ ਦੀ ਵਿਸਥਾਪਤ ਸਰਕਾਰ ਇਸ ਰੇਖਾ ਨੂੰ ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀ ਤਿੱਬਤ ਨਾਲ ਲੱਗਦੀ ਹੱਦ ਮੰਨਦੀ ਹੈ। ਪਰ ਚੀਨ ਇਸ ਸੰਧੀ ਨੂੰ ਨਹੀਂ ਮੰਨਦਾ। ਸਿੱਟੇ ਵੱਜੋਂ, ਚੀਨ ਅਰੁਣਾਚਲ ਨੂੰ [[ਦੱਖਣੀ ਤਿੱਬਤ]] ਜਾਂ ਤਿੱਬਤ ਦਾ ਦੱਖਣੀ ਹਿੱਸਾ ਕਹਿੰਦਾ ਹੈ। |
|||
==ਘਰੇਲੂ ਉਤਪਾਦਨ ਦਰ== |
==ਘਰੇਲੂ ਉਤਪਾਦਨ ਦਰ== |
||
ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀ '''ਅਕਤਸਾਦ''' ਵੱਧ ਰਹੀ ਹੈ। ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀ ਅਕਤਸਾਦ [[$]]੫੬੮੦੦ ਕਰੋੜ (''Gross domestic product'' ਜਾਂ GDP) ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ਦੁਨੀਆ ਦੀ ੧੧ਵੀਂ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਵੱਡੀ ਅਕਤਸਾਦ ਹੈ। PPP ਅਨੁਸਾਰ ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀ ਅਕਤਸਾਦ ਚੌਥੇ ਸਥਾਨ 'ਤੇ ਹੈ। |
|||
ਇੱਥੇ ਜ਼ਿਕਰਯੋਗ ਹੈ ਕਿ ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀ ਬਹੁਤੀ ਅਬਾਦੀ [[ਗਰੀਬ]] ਹੈ। ੨੭.੫% ਅਬਾਦੀ ਗਰੀਬੀ ਰੇਖਾ ਤੋ ਹੇਠਾਂ ਹੈ। ੮੦.੪% ਆਬਾਦੀ ਰੋਜ਼ਾਨਾ ਦੀ $੨ ਤੋਂ ਘੱਟ ਦੀ ਕਮਾਈ ਕਰਦੀ ਹੈ। |
ਇੱਥੇ ਜ਼ਿਕਰਯੋਗ ਹੈ ਕਿ ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀ ਬਹੁਤੀ ਅਬਾਦੀ [[ਗਰੀਬ]] ਹੈ। ੨੭.੫% ਅਬਾਦੀ ਗਰੀਬੀ ਰੇਖਾ ਤੋ ਹੇਠਾਂ ਹੈ। ੮੦.੪% ਆਬਾਦੀ ਰੋਜ਼ਾਨਾ ਦੀ $੨ ਤੋਂ ਘੱਟ ਦੀ ਕਮਾਈ ਕਰਦੀ ਹੈ। |
||
==ਸਮਾਜ== |
==ਸਮਾਜ== |
||
ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ੧੨੧ ਕਰੋੜ ਦੀ ਆਬਾਦੀ ਰਹਿੰਦੀ ਹੈ। ਭਾਰਤ ਅਬਾਦੀ ਦੇ ਲਿਹਾਜ਼ ਤੋਂ ਦੁਨੀਆ ਦਾ ਦੂਜਾਂ ਸਭ ਤੋ ਵੱਡਾ ਦੇਸ਼ ਹੈ। ਤਕਰੀਬਨ ੭੦% ਲੋਕ ਕਿਰਸਾਨੀ ਕਰਦੇ ਹਨ। ਇਸ ਦੇਸ਼ ਵਿੱਚ ਪੰਜਾਬੀ, ਕਸ਼ਮੀਰੀ, ਰਾਜਪੂਤ, ਦ੍ਰਵਿੜ, ਤੇਲਗੂ, ਮਰਹੱਟੇ, ਅਸਾਮੀ ਆਦਿ ਖੇਤਰ ਪੱਖ ਤੋਂ ਲੋਕ ਰਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ। ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀਆਂ ੨੩ ਕੰਮਕਾਜੀ ਬੋਲੀਆਂ ਹਨ। ਪਰ ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਕੁਲ ੧੬੨੫ ਬੋਲੀਆਂ ਤੇ ਲਹਿਜੇ ਬੋਲੇ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਹਨ। |
|||
===ਸੱਭਿਆਚਾਰ=== |
===ਸੱਭਿਆਚਾਰ=== |
||
ਪੱਥਰ ਯੁੱਗ ਦੀਆਂ ਨਕਾਸ਼ੀ ਦਰ ਗੁਫ਼ਾਵਾਂ ਸਾਰੇ ਭਾਰਤ 'ਚੋ ਮਿਲਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ। ਇਹ ਨਕਾਸ਼ੀਆਂ ਉਸ ਵੇਲੇ ਦੇ ਨਾਚ ਅਤੇ ਵਿਰਸੇ ਨੂੰ ਦਰਸਾਉਂਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ ਜੋ ਆਦਿ ਧਰਮ ਦੀ ਪੁਸ਼ਟੀ ਕਰਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ। ਲਿਪਿਕ ਅਤੇ ਪੁਰਾਣਕ ਸਮੇਂ, ਰਮਾਇਣ ਅਤੇ ਮਹਾਂਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਆਦਿ ਰੂਪ ਤਕਰੀਬਨ ੫੦੦-੧੦੦ ਈਸਾ ਦੇ ਜਨਮ ਤੋਂ ਪਹਿਲਾਂ ਲਿਖੇ ਗਏ। |
|||
ਕਈ ਆਧੁਨਿਕ ਧਰਮ ਵੀ ਭਾਰਤ ਨਾਲ ਜੁੜੇ ਹੋਏ ਹਨ, ਇਹਨਾਂ ਦੇ ਨਾਂ ਹਨ: [[ਹਿੰਦੂ|ਹਿੰਦੂ ਧਰਮ]], [[ਜੈਨ ਧਰਮ]], [[ਬੁੱਧ ਧਰਮ]] ਅਤੇ [[ਸਿੱਖ ਧਰਮ]]। ਇਹਨਾਂ ਸਾਰੇ ਧਰਮਾਂ ਕੋਲ ਅਲੱਗ ਵਿਰਾਸਤਾਂ ਅਤੇ ਮਾਨਤਾਵਾਂ ਹਨ। ਇਹਨਾਂ ਧਰਮਾਂ ਨੂੰ '''ਪੂਰਬੀ ਧਰਮ''' ਕਿਹਾ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ। ਇਹਨਾਂ ਧਰਮਾਂ ਦੀ ਵਿਚਾਰਧਾਰਾਵਾਂ ਦਾ ਕੁਝ ਹਿੱਸਾ ਆਪਸ 'ਚ ਮੇਲ ਖਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ, ਜਿਸ ਤੋਂ ਇਹ ਪਤਾ ਲਗਦਾ ਹੈ ਕਿ ਇਹਨਾਂ ਧਰਮਾਂ ਦਾ ਪਿਛੋਕੜ ਇੱਕੋ ਹੀ ਹੈ ਅਤੇ ਇਹਨਾਂ ਨੇ ਇੱਕ ਦੂਜੇ ਨੂੰ ਵੱਡੇ ਪੱਧਰ ਤੇ ਪ੍ਰਭਾਵਿਤ ਕੀਤਾ ਹੈ। |
|||
ਹਿੰਦੂ ਧਰਮ ਭਾਰਤ ਦਾ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਵੱਡਾ ਧਰਮ ਹੈ; ਇਸਲਾਮ ਦੇ ੧੨.੮ %; ਇਸਾਈਅਤ ਦੇ ੨.੯ %; ਸਿੱਖ ਧਰਮ ਦੇ ੧.੯ %; ਬੁੱਧ ਧਰਨ ਦੇ ੦.੮ % ਅਤੇ ਜੈਨ ਧਰਮ ਦੇ ੦.੪ % ਲੋਕ ਧਾਰਨੀ ਹਨ। |
ਹਿੰਦੂ ਧਰਮ ਭਾਰਤ ਦਾ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਵੱਡਾ ਧਰਮ ਹੈ; ਇਸਲਾਮ ਦੇ ੧੨.੮ %; ਇਸਾਈਅਤ ਦੇ ੨.੯ %; ਸਿੱਖ ਧਰਮ ਦੇ ੧.੯ %; ਬੁੱਧ ਧਰਨ ਦੇ ੦.੮ % ਅਤੇ ਜੈਨ ਧਰਮ ਦੇ ੦.੪ % ਲੋਕ ਧਾਰਨੀ ਹਨ। |
||
| ਲਕੀਰ 424: | ਲਕੀਰ 456: | ||
===ਅਬਾਦੀ ਅੰਕੜੇ=== |
===ਅਬਾਦੀ ਅੰਕੜੇ=== |
||
ਹਿੰਦੂ ਧਰਮ ਭਾਰਤ ਦਾ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਬਡਾ ਧਰਮ ਹੈ - ਇਸ ਚਿੱਤਰ ਵਿੱਚ ਗੋਆ ਦਾ ਇੱਕ ਮੰਦਿਰ ਵਿਖਾਇਆ ਗਿਆ ਹੈ |
|||
ਭਾਰਤ ਚੀਨ ਦੇ ਬਾਅਦ ਸੰਸਾਰ ਦਾ ਦੂਜਾ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਜਿਆਦਾ ਜਨਸੰਖਿਆ ਵਾਲਾ ਦੇਸ਼ ਹੈ। ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀਆਂਵਿਭਿੰਨਤਾਵਾਂਵਲੋਂ ਭਰੀ ਜਨਤਾ ਵਿੱਚ ਭਾਸ਼ਾ, ਜਾਤੀ ਅਤੇ ਧਰਮ, ਸਮਾਜਕ ਅਤੇ ਰਾਜਨੀਤਕ ਸੌਹਾਰਦਰ ਅਤੇ ਸਮਰਸਤਾ ਦੇ ਮੁੱਖ ਵੈਰੀ ਹਨ। |
ਭਾਰਤ ਚੀਨ ਦੇ ਬਾਅਦ ਸੰਸਾਰ ਦਾ ਦੂਜਾ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਜਿਆਦਾ ਜਨਸੰਖਿਆ ਵਾਲਾ ਦੇਸ਼ ਹੈ। ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀਆਂਵਿਭਿੰਨਤਾਵਾਂਵਲੋਂ ਭਰੀ ਜਨਤਾ ਵਿੱਚ ਭਾਸ਼ਾ, ਜਾਤੀ ਅਤੇ ਧਰਮ, ਸਮਾਜਕ ਅਤੇ ਰਾਜਨੀਤਕ ਸੌਹਾਰਦਰ ਅਤੇ ਸਮਰਸਤਾ ਦੇ ਮੁੱਖ ਵੈਰੀ ਹਨ। |
||
ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ੬੪ . ੮ ਫ਼ੀਸਦੀ ਸਾਕਸ਼ਰਤਾ ਹੈ ਜਿਸ ਵਿੱਚੋਂ ੭੫ . ੩ % ਪੁਰਖ ਅਤੇ ੫੩ . ੭ % ਔਰਤਾਂ ਸਾਕਸ਼ਰ ਹਨ। ਲਿੰਗ ਅਨਪਾਤ ਦੀ ਨਜ਼ਰ ਵਲੋਂ ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਹਰ ਇੱਕ ੧੦੦੦ ਪੁਰਸ਼ਾਂ ਦੇ ਪਿੱਛੇ ਸਿਰਫ ੯੩੩ ਔਰਤਾਂ ਹਨ। ਕਾਰਜ ਭਾਗੀਦਾਰੀ ਦਰ (ਕੁਲ ਜਨਸੰਖਿਆ ਵਿੱਚ ਕਾਰਜ ਕਰਣ ਵਾਲੀਆਂ ਦਾ ਭਾਗ) ੩੯ . ੧ % ਹੈ। ਪੁਰਸ਼ਾਂ ਲਈ ਇਹ ਦਰ ੫੧ . ੭ % ਅਤੇ ਸਤਰੀਆਂ ਲਈ ੨੫ . ੬ % ਹੈ। ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀ ੧੦੦੦ ਜਨਸੰਖਿਆ ਵਿੱਚ ੨੨ . ੩੨ ਜਨਮਾਂ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ਵੱਧਦੀ ਜਨਸੰਖਿਆ ਦੇ ਅੱਧੇ ਲੋਕ ੨੨ . ੬੬ ਸਾਲ ਵਲੋਂ ਘੱਟ ਉਮਰ ਦੇ ਹਨ। |
|||
ਹਾਲਾਂਕਿ ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀ ੮੦ . ੫ ਫ਼ੀਸਦੀ ਜਨਸੰਖਿਆ ਹਿੰਦੂ ਹੈ, ੧੩ . ੪ ਫ਼ੀਸਦੀ ਜਨਸੰਖਿਆ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ਭਾਰਤ ਸੰਸਾਰ ਵਿੱਚ ਮੁਸਲਮਾਨਾਂ ਦੀ ਗਿਣਤੀ ਵਿੱਚ ਵੀ ਇੰਡੋਨੇਸ਼ਿਆ ਅਤੇ ਪਾਕਿਸਤਾਨ ਦੇ ਬਾਅਦ ਤੀਸਰੇ ਸਥਾਨ ਉੱਤੇ ਹੈ। ਹੋਰ ਧਰਮਾਵਲੰਬੀਆਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਈਸਾਈ (੨ . ੩੩ %), ਸਿੱਖ (੧ . ੮੪ %), ਬੋਧੀ (੦ . ੭੬ %), ਜੈਨ (੦ . ੪੦ %), ਅਇਯਾਵਲਿ (੦ . ੧੨ %), ਯਹੂਦੀ, ਪਾਰਸੀ, ਅਹਮਦੀ ਅਤੇ ਬਹਾਈ ਆਦਿ ਸਮਿੱਲਤ ਹਨ। |
ਹਾਲਾਂਕਿ ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀ ੮੦ . ੫ ਫ਼ੀਸਦੀ ਜਨਸੰਖਿਆ ਹਿੰਦੂ ਹੈ, ੧੩ . ੪ ਫ਼ੀਸਦੀ ਜਨਸੰਖਿਆ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ਭਾਰਤ ਸੰਸਾਰ ਵਿੱਚ ਮੁਸਲਮਾਨਾਂ ਦੀ ਗਿਣਤੀ ਵਿੱਚ ਵੀ ਇੰਡੋਨੇਸ਼ਿਆ ਅਤੇ ਪਾਕਿਸਤਾਨ ਦੇ ਬਾਅਦ ਤੀਸਰੇ ਸਥਾਨ ਉੱਤੇ ਹੈ। ਹੋਰ ਧਰਮਾਵਲੰਬੀਆਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਈਸਾਈ (੨ . ੩੩ %), ਸਿੱਖ (੧ . ੮੪ %), ਬੋਧੀ (੦ . ੭੬ %), ਜੈਨ (੦ . ੪੦ %), ਅਇਯਾਵਲਿ (੦ . ੧੨ %), ਯਹੂਦੀ, ਪਾਰਸੀ, ਅਹਮਦੀ ਅਤੇ ਬਹਾਈ ਆਦਿ ਸਮਿੱਲਤ ਹਨ। |
||
ਭਾਰਤ ਦੋ ਮੁੱਖ ਭਾਸ਼ਾ - ਸੂਤਰਾਂ: ਆਰਿਆ ਅਤੇ ਦਰਵਿੜਭਾਸ਼ਾਵਾਂਦਾ ਸਰੋਤ ਵੀ ਹੈ। ਭਾਰਤ ਦਾ ਸੰਵਿਧਾਨ ਕੁਲ ੨੩ਭਾਸ਼ਾਵਾਂਨੂੰ ਮਾਨਤਾ ਦਿੰਦਾ ਹੈ। ਹਿੰਦੀ ਅਤੇ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਕੇਂਦਰੀ ਸਰਕਾਰ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਸਰਕਾਰੀ ਕੰਮਧੰਦਾ ਲਈ ਵਰਤੋ ਦੀ ਜਾਂਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ . ਸੰਸਕ੍ਰਿਤ ਅਤੇ ਤਮਿਲ ਵਰਗੀ ਅਤਿ ਪ੍ਰਾਚੀਨ ਭਾਸ਼ਾਵਾਂ ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਹੀ ਜੰਮੀ ਹਨ। ਸੰਸਕ੍ਰਿਤ, ਸੰਸਾਰ ਦੀ ਸਬਤੋਂ ਜਿਆਦਾ ਪ੍ਰਾਚੀਨਭਾਸ਼ਾਵਾਂਵਿੱਚੋਂ ਇੱਕ ਹੈ, ਜਿਸਦਾ ਵਿਕਾਸ ਪਥਿਆਸਵਸਤੀ ਨਾਮ ਦੀ ਅਤਿ ਪ੍ਰਾਚੀਨ ਭਾਸ਼ਾ / ਬੋਲੀ ਵਲੋਂ ਹੋਇਆ ਸੀ . ਤਮਿਲ ਦੇ ਇਲਾਵਾ ਸਾਰੀ ਭਾਰਤੀਭਾਸ਼ਾਵਾਂਸੰਸਕ੍ਰਿਤ ਵਲੋਂ ਹੀ ਵਿਕਸਿਤ ਹੋਈਆਂ ਹਨ, ਹਾਲਾਂਕਿ ਸੰਸਕ੍ਰਿਤ ਅਤੇ ਤਮਿਲ ਵਿੱਚ ਕਈ ਸ਼ਬਦ ਸਮਾਨ ਹਨ ! ਕੁਲ ਮਿਲਿਆ ਕਰ ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ੧੬੫੨ ਵਲੋਂ ਵੀ ਜਿਆਦਾ ਭਾਸ਼ਾਵਾਂ ਅਤੇ ਬੋਲੀਆਂ ਬੋਲੀ ਜਾਤੀਂ ਹਨ। |
|||
===ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰ ਦੇ ਰੂਪ ਵਿੱਚ ਉਠਾਅ=== |
===ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰ ਦੇ ਰੂਪ ਵਿੱਚ ਉਠਾਅ=== |
||
| ਲਕੀਰ 441: | ਲਕੀਰ 473: | ||
੧੯੪੭ ਵਿੱਚ ਆਪਣੀ ਆਜ਼ਾਦੀ ਦੇ ਬਾਅਦ ਵਲੋਂ, ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਜਿਆਦਾਤਰ ਦੇਸ਼ਾਂ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ਸੌਹਾਰਦਪੂਰਣ ਸੰਬੰਧ ਬਣਾਇ ਰੱਖਿਆ ਹੈ। ੧੯੫੦ ਦੇ ਦਹਾਕੇ ਵਿੱਚ, ਇਹ ਮਜ਼ਬੂਤੀ ਵਲੋਂ ਅਫਰੀਕਾ ਅਤੇ ਏਸ਼ਿਆ ਵਿੱਚ ਯੂਰਪੀ ਕਲੋਨੀਆਂ ਦੀ ਆਜ਼ਾਦੀ ਦਾ ਸਮਰਥਨ ਕੀਤਾ ਅਤੇ ਗੁਟ-ਨਿਰਲੇਪ ਅੰਦੋਲਨ ਵਿੱਚ ਇੱਕ ਆਗੂ ਭੂਮਿਕਾ ਨਿਭਾਈ। ੧੯੮੦ ਦੇ ਦਹਾਕੇ ਵਿੱਚ ਭਾਰਤ ਗੁਆਂਢੀ ਦੇ ਸੱਦੇ ਉੱਤੇ ਦੋ ਦੇਸ਼ਾਂ ਸੰਖਿਪਤ ਫੌਜੀ ਹਸਤੱਕਖੇਪ ਕੀਤਾ, ਮਾਲਦੀਵ, ਸ਼੍ਰੀਲੰਕਾ ਅਤੇ ਹੋਰ ਦੇਸ਼ਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਆਪਰੇਸ਼ਨ ਥੋਹਰ ਵਿੱਚ ਭਾਰਤੀ ਸ਼ਾਂਤੀ ਫੌਜ ਭੇਜਿਆ। ਹਾਲਾਂਕਿ, ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਗੁਆਂਢੀ ਦੇਸ਼ ਪਾਕਿਸਤਾਨ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ਇੱਕ ਤਨਾਵ ਸੰਬੰਧ ਪਿਆ ਰਿਹਾ, ਅਤੇ ਦੋਨਾਂ ਦੇਸ਼ ਚਾਰ ਵਾਰ ਯੁਧਦਰ (੧੯੪੭, ੧੯੬੫, ੧੯੭੧ ਅਤੇ ੧੯੯੯ ਵਿੱਚ) ਲਈ ਚਲਾ ਹੈ। ਕਸ਼ਮੀਰ ਵਿਵਾਦ ਇਸ ਯੁੱਧਾਂ ਦੇ ਪ੍ਰਮੁੱਖ ਕਾਰਨ ਸੀ, ੧੯੭੧ ਨੂੰ ਛੱਡਕੇ ਜੋ ਤਤਕਾਲੀਨ ਪੂਰਵੀ ਪਾਕਿਸਤਾਨ ਵਿੱਚ ਨਾਗਰਿਕ ਅਸ਼ਾਂਤਿ ਲਈ ਕੀਤਾ ਗਿਆ ਸੀ। ੧੯੬੨ ਦੇ ਭਾਰਤ - ਚੀਨ ਲੜਾਈ ਅਤੇ ਪਾਕਿਸਤਾਨ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ੧੯੬੫ ਦੇ ਲੜਾਈ ਦੇ ਬਾਅਦ ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਕਰੀਬ ਫੌਜੀ ਅਤੇ ਆਰਥਕ ਵਿਕਾਸ ਦਿੱਤੀ। ਸੋਵਿਅਤ ਸੰਘ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ਸਬੰਧਾਂ, ਸੰਨ ੧੯੬੦ ਦੇ ਦਸ਼ਕ ਵਲੋਂ, ਸੋਵਿਅਤ ਸੰਘ ਭਾਰਤ ਦਾ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਬਹੁਤ ਹਥਿਆਰ ਆਪੂਰਤੀਕਰਤਾ ਦੇ ਰੂਪ ਵਿੱਚ ਉਭਰੀ ਸੀ। |
੧੯੪੭ ਵਿੱਚ ਆਪਣੀ ਆਜ਼ਾਦੀ ਦੇ ਬਾਅਦ ਵਲੋਂ, ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਜਿਆਦਾਤਰ ਦੇਸ਼ਾਂ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ਸੌਹਾਰਦਪੂਰਣ ਸੰਬੰਧ ਬਣਾਇ ਰੱਖਿਆ ਹੈ। ੧੯੫੦ ਦੇ ਦਹਾਕੇ ਵਿੱਚ, ਇਹ ਮਜ਼ਬੂਤੀ ਵਲੋਂ ਅਫਰੀਕਾ ਅਤੇ ਏਸ਼ਿਆ ਵਿੱਚ ਯੂਰਪੀ ਕਲੋਨੀਆਂ ਦੀ ਆਜ਼ਾਦੀ ਦਾ ਸਮਰਥਨ ਕੀਤਾ ਅਤੇ ਗੁਟ-ਨਿਰਲੇਪ ਅੰਦੋਲਨ ਵਿੱਚ ਇੱਕ ਆਗੂ ਭੂਮਿਕਾ ਨਿਭਾਈ। ੧੯੮੦ ਦੇ ਦਹਾਕੇ ਵਿੱਚ ਭਾਰਤ ਗੁਆਂਢੀ ਦੇ ਸੱਦੇ ਉੱਤੇ ਦੋ ਦੇਸ਼ਾਂ ਸੰਖਿਪਤ ਫੌਜੀ ਹਸਤੱਕਖੇਪ ਕੀਤਾ, ਮਾਲਦੀਵ, ਸ਼੍ਰੀਲੰਕਾ ਅਤੇ ਹੋਰ ਦੇਸ਼ਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਆਪਰੇਸ਼ਨ ਥੋਹਰ ਵਿੱਚ ਭਾਰਤੀ ਸ਼ਾਂਤੀ ਫੌਜ ਭੇਜਿਆ। ਹਾਲਾਂਕਿ, ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਗੁਆਂਢੀ ਦੇਸ਼ ਪਾਕਿਸਤਾਨ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ਇੱਕ ਤਨਾਵ ਸੰਬੰਧ ਪਿਆ ਰਿਹਾ, ਅਤੇ ਦੋਨਾਂ ਦੇਸ਼ ਚਾਰ ਵਾਰ ਯੁਧਦਰ (੧੯੪੭, ੧੯੬੫, ੧੯੭੧ ਅਤੇ ੧੯੯੯ ਵਿੱਚ) ਲਈ ਚਲਾ ਹੈ। ਕਸ਼ਮੀਰ ਵਿਵਾਦ ਇਸ ਯੁੱਧਾਂ ਦੇ ਪ੍ਰਮੁੱਖ ਕਾਰਨ ਸੀ, ੧੯੭੧ ਨੂੰ ਛੱਡਕੇ ਜੋ ਤਤਕਾਲੀਨ ਪੂਰਵੀ ਪਾਕਿਸਤਾਨ ਵਿੱਚ ਨਾਗਰਿਕ ਅਸ਼ਾਂਤਿ ਲਈ ਕੀਤਾ ਗਿਆ ਸੀ। ੧੯੬੨ ਦੇ ਭਾਰਤ - ਚੀਨ ਲੜਾਈ ਅਤੇ ਪਾਕਿਸਤਾਨ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ੧੯੬੫ ਦੇ ਲੜਾਈ ਦੇ ਬਾਅਦ ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਕਰੀਬ ਫੌਜੀ ਅਤੇ ਆਰਥਕ ਵਿਕਾਸ ਦਿੱਤੀ। ਸੋਵਿਅਤ ਸੰਘ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ਸਬੰਧਾਂ, ਸੰਨ ੧੯੬੦ ਦੇ ਦਸ਼ਕ ਵਲੋਂ, ਸੋਵਿਅਤ ਸੰਘ ਭਾਰਤ ਦਾ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਬਹੁਤ ਹਥਿਆਰ ਆਪੂਰਤੀਕਰਤਾ ਦੇ ਰੂਪ ਵਿੱਚ ਉਭਰੀ ਸੀ। |
||
ਅੱਜ ਰੂਸ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ਸਾਮਰਿਕ ਸਬੰਧਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਜਾਰੀ ਰੱਖਣ ਦੇ ਇਲਾਵਾ, ਭਾਰਤ ਫੈਲਿਆ ਇਜਰਾਇਲ ਅਤੇ ਫ਼ਰਾਂਸ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ਰੱਖਿਆ ਸੰਬੰਧ ਰੱਖਿਆ ਹੈ। ਹਾਲ ਦੇ ਸਾਲਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ, ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਖੇਤਰੀ ਸਹਿਯੋਗ ਅਤੇ ਸੰਸਾਰ ਵਪਾਰ ਸੰਗਠਨ ਲਈ ਇੱਕ ਦੱਖਣ ਏਸ਼ੀਆਈ ਏਸੋਸਿਏਸ਼ਨ ਵਿੱਚ ਪ੍ਰਭਾਵਸ਼ਾਲੀ ਭੂਮਿਕਾ ਨਿਭਾਈ ਹੈ। ੧੦, ੦੦੦ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰ ਫੌਜੀ ਅਤੇ ਪੁਲਿਸ ਕਰਮੀਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਚਾਰ ਮਹਾਂਦੀਪਾਂ ਭਰ ਵਿੱਚ ਪੈਂਤੀ ਸੰਯੁਕਤ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰ ਸ਼ਾਂਤੀ ਅਭਿਆਨਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਸੇਵਾ ਪ੍ਰਦਾਨ ਕੀਤੀ ਹੈ। ਭਾਰਤ ਵੀ ਵੱਖਰਾ ਬਹੁਪਕਸ਼ੀਏ ਮੰਚਾਂ, ਖਾਸਕਰ ਪੂਰਵੀ ਏਸ਼ਿਆ ਸਿਖਰ ਬੈਠਕ ਅਤੇ G – ੮੫ ਬੈਠਕ ਵਿੱਚ ਇੱਕ ਸਰਗਰਮ ਭਾਗੀਦਾਰ ਰਿਹਾ ਹੈ। ਆਰਥਕ ਖੇਤਰ ਵਿੱਚ ਭਾਰਤ ਦੱਖਣ ਅਮਰੀਕਾ, ਅਫਰੀਕਾ ਅਤੇ ਏਸ਼ਿਆ ਦੇ ਵਿਕਾਸਸ਼ੀਲ ਦੇਸ਼ਾਂ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ਘਨਿਸ਼ਠ ਸੰਬੰਧ ਰੱਖਦੇ ਹੈ। ਹੁਣ ਭਾਰਤ ਇੱਕ ਪੂਰਵ ਦੇ ਵੱਲ ਵੇਖੋ ਨੀਤੀ ਵਿੱਚ ਵੀ ਸੰਜੋਗ ਕੀਤਾ ਹੈ। ਇਹ ਆਸਿਆਨ ਦੇਸ਼ਾਂ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ਆਪਣੀ ਭਾਗੀਦਾਰੀ ਨੂੰ ਮਜ਼ਬੂਤ ਬਣਾਉਣ ਦੇ ਮੁੱਦੀਆਂ ਦੀ ਇੱਕ ਫੈਲਿਆ ਲੜੀ ਹੈ ਜਿਸ ਵਿੱਚ ਜਾਪਾਨ ਅਤੇ ਦੱਖਣ ਕੋਰੀਆ ਨੇ ਵੀ ਮਦਦ ਕੀਤਾ ਹੈ। ਇਹ ਵਿਸ਼ੇਸ਼ ਰੂਪ ਵਲੋਂ ਆਰਥਕ ਨਿਵੇਸ਼ ਅਤੇ ਖੇਤਰੀ ਸੁਰੱਖਿਆ ਦੀ ਕੋਸ਼ਿਸ਼ ਹੈ। |
|||
੧੯੭੪ ਵਿੱਚ ਭਾਰਤ ਆਪਣੀ ਪਹਿਲੀ ਪਰਮਾਣੁ ਹਥਿਆਰਾਂ ਦਾ ਪ੍ਰੀਖਿਆ ਕੀਤਾ ਅਤੇ ਅੱਗੇ ੧੯੯੮ ਵਿੱਚ ਭੂਮੀਗਤ ਪ੍ਰੀਖਿਆ ਕੀਤਾ। ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਕੋਲ ਹੁਣ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ – ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੇ ਪਰਮਾਣੁ ਹਥਿਆਰਾਂ ਹੈ। ਭਾਰਤ ਹੁਣੇ ਰੂਸ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ਮਿਲ ਕੇ ਪੰਜਵੀਂ ਪੀੜ ਦੇ ਜਹਾਜ਼ ਬਣਾ ਰਹੇ ਹੈ। |
|||
ਹਾਲ ਹੀ ਵਿੱਚ, ਭਾਰਤ ਦਾ ਸੰਯੁਕਤ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੇ ਅਮਰੀਕਾ ਅਤੇ ਯੂਰੋਪੀ ਸੰਘ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ਆਰਥਕ, ਸਾਮਰਿਕ ਅਤੇ ਫੌਜੀ ਸਹਿਯੋਗ ਵੱਧ ਗਿਆ ਹੈ। ੨੦੦੮ ਵਿੱਚ, ਭਾਰਤ ਅਤੇ ਸੰਯੁਕਤ ਰਾਜ ਅਮਰੀਕਾ ਦੇ ਵਿੱਚ ਗ਼ੈਰ ਫ਼ੌਜੀ ਪਰਮਾਣੁ ਸਮੱਝੌਤੇ ਹਸਤਾਖਰ ਕੀਤੇ ਗਏ ਸਨ। ਹਾਲਾਂਕਿ ਉਸ ਸਮੇਂ ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਕੋਲ ਪਰਮਾਣੁ ਹਥਿਆਰ ਸੀ ਅਤੇ ਪਰਮਾਣੁ ਅਪ੍ਰਸਾਰ ਸੁਲਾਹ (ਏਨਪੀਟੀ) ਦੇ ਪੱਖ ਵਿੱਚ ਨਹੀਂ ਸੀ ਇਹ ਅੰਤਰਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਪਰਮਾਣੁ ਊਰਜਾ ਏਜੰਸੀ ਅਤੇ ਨਿਊਕਲਿਅਰ ਸਪਲਾਇਰਸ ਗਰੁਪ (ਏਨਏਸਜੀ) ਵਲੋਂ ਛੁੱਟ ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤ ਹੈ, ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀ ਪਰਮਾਣੁ ਤਕਨੀਕੀ ਅਤੇ ਵਣਜ ਉੱਤੇ ਪਹਿਲਾਂ ਰੋਕ ਖ਼ਤਮ . ਭਾਰਤ ਸੰਸਾਰ ਦਾ ਛੇਵਾਂ ਅਸਲੀ ਪਰਮਾਣੁ ਹਥਿਆਰ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰਤ ਬੰਨ ਗਿਆ ਹੈ। ਏਨਏਸਜੀ ਛੁੱਟ ਦੇ ਬਾਅਦ ਭਾਰਤ ਵੀ ਰੂਸ, ਫ਼ਰਾਂਸ, ਯੂਨਾਇਟੇਡ ਕਿੰਗਡਮ, ਅਤੇ ਕਨਾਡਾ ਸਹਿਤ ਦੇਸ਼ਾਂ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ਗ਼ੈਰ ਫ਼ੌਜੀ ਪਰਮਾਣੁ ਊਰਜਾ ਸਹਿਯੋਗ ਸਮੱਝੌਤੇ ਉੱਤੇ ਹਸਤਾਖਰ ਕਰਣ ਵਿੱਚ ਸਮਰੱਥਾਵਾਨ ਹੈ। |
|||
ਲਗਭਗ ੧ . ੩ ਮਿਲਿਅਨ ਸਰਗਰਮ ਸੈਨਿਕਾਂ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ, ਭਾਰਤੀ ਫੌਜ ਦੁਨੀਆ ਵਿੱਚ ਤੀਜਾ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਬਹੁਤ ਹੈ। ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀ ਸ਼ਸਤਰਬੰਦ ਫੌਜ ਵਿੱਚ ਇੱਕ ਭਾਰਤੀ ਫੌਜ, ਨੌਸੇਨਾ, ਹਵਾ ਫੌਜ, ਅਤੇ ਅਰੱਧਸੈਨਿਕ ਜੋਰ, ਤਟਰਕਸ਼ਕ, ਅਤੇ ਸਾਮਰਿਕ ਜਿਵੇਂ ਸਹਾਇਕ ਜੋਰ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ। ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰਪਤੀ ਭਾਰਤੀ ਸ਼ਸਤਰਬੰਦ ਬਲਾਂ ਦੇ ਸਰਵੋੱਚ ਕਮਾਂਡਰ ਹੈ। ਸਾਲ ੨੦੧੧ ਵਿੱਚ ਭਾਰਤੀ ਰੱਖਿਆ ਬਜਟ ੩੬ . ੦੩ ਅਰਬ ਅਮਰਿਕੀ ਡਾਲਰ ਰਿਹਾ (ਜਾਂ ਸਕਲ ਘਰੇਲੂ ਉਤਪਾਦ ਦਾ ੧ . ੮੩ %)। ੨੦੦੮ ਦੇ ਇੱਕ SIPRI ਰਿਪੋਰਟ ਦੇ ਅਨੁਸਾਰ, ਭਾਰਤ ਖਰੀਦ ਸ਼ਕਤੀ ਦੇ ਮਾਮਲੇ ਵਿੱਚ ਭਰਤੀਏ ਫੌਜ ਦੇ ਫੌਜੀ ਖਰਚ ੭੨ . ੭ ਅਰਬ ਅਮਰੀਕੀ ਡਾਲਰ ਰਿਹਾ। ਸਾਲ 2011 ਵਿੱਚ ਭਾਰਤੀ ਰੱਖਿਆ ਮੰਤਰਾਲਾ ਦੇ ਵਾਰਸ਼ਿਕ ਰੱਖਿਆ ਬਜਟ ਵਿੱਚ ੧੧ . ੬ ਫ਼ੀਸਦੀ ਦਾ ਵਾਧਾ ਹੋਇਆ, ਹਾਲਾਂਕਿ ਇਹ ਪੈਸਾ ਸਰਕਾਰ ਦੀ ਹੋਰਸ਼ਾਖਾਵਾਂਦੇ ਮਾਧਿਅਮ ਵਲੋਂ ਫੌਜੀ ਦੇ ਵੱਲ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਹੋਏ ਪੈਸੀਆਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਸ਼ਮਿਲ ਨਹੀਂ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ। ਭਾਰਤ ਦੁਨੀਆ ਦੇ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਵੱਡੇ ਹਥਿਆਰ ਆਯਾਤਕ ਬੰਨ ਗਿਆ ਹੈ। |
|||
==ਸਮੱਸਿਆਵਾਂ== |
==ਸਮੱਸਿਆਵਾਂ== |
||
===ਅੰਦਰੂਨੀ ਸਮੱਸਿਆਵਾਂ=== |
===ਅੰਦਰੂਨੀ ਸਮੱਸਿਆਵਾਂ=== |
||
* '''ਅੱਤਵਾਦ''' |
* '''ਅੱਤਵਾਦ''' – ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਡਰ ਤੇ ਦਹਿਸ਼ਤ ਦਾ ਮਹੌਲ ਕਾਇਮ ਕਰਨ ਲਈ ਕਈ ਅੱਤਵਾਦੀ ਸਮੂਹ ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿਰੋਧੀ ਕਾਰਵਾਈਆਂ ਕਰਦੇ ਰਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ ਜਿਸ ਕਾਰਨ ਦੇਸ਼ ਦਾ ਕਾਫੀ ਜਾਨੀ ਅਤੇ ਮਾਲੀ ਨੁਕਸਾਨ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ। ਅੱਤਵਾਦੀਆਂ ਨੇ ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀ [[ਸੰਸਦ]], ਤਾਜ ਹੋਟਲ, ਕਸ਼ਮੀਰ, [[ਪਠਾਨਕੋਟ]] ਏਅਰਬੇਸ ਸਮੇਤ ਹੋਰ ਵੀ ਕਈ ਅਜਿਮ ਜਗ੍ਹਾਹਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਨਿਸ਼ਾਨਾ ਬਣਾ ਦਹਿਸ਼ਤ ਫੈਲਾਉਣ ਦੀ ਕੋਸ਼ਿਸ਼ ਕੀਤੀ ਹੈ। |
||
* '''ਨਕਸਲਵਾਦ''' |
* '''ਨਕਸਲਵਾਦ''' |
||
* '''ਨਸ਼ੇ''' |
* '''ਨਸ਼ੇ''' – ਦੇਸ਼ਾਂ-ਵਿਦੇਸ਼ਾਂ 'ਚੋਂ ਹੋ ਰਹੀ ਨਸ਼ਾ ਤਸਕਰੀ ਕਾਰਨ ਕਾਫੀ ਤੇਜ਼ੀ ਨਾਲ ਨਸ਼ਾ ਕਰਨ ਵਾਲਿਆਂ ਦੀ ਗਿਣਤੀ ਵਧੀ ਹੈ। ਸਰਹੱਦੀ ਇਲਾਕਿਆਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਇਹ ਸਮੱਸਿਆ ਕਾਫੀ ਗੰਭੀਰ ਹੈ। |
||
===ਬਾਹਰੀ ਸਮੱਸਿਆਵਾਂ=== |
===ਬਾਹਰੀ ਸਮੱਸਿਆਵਾਂ=== |
||
* '''ਕਸ਼ਮੀਰ ਮੁੱਦਾ''' |
* '''ਕਸ਼ਮੀਰ ਮੁੱਦਾ''' – ਕਸ਼ਮੀਰ ਦੇ ਝਗੜੇ ਕਾਰਨ ਭਾਰਤ ਪਾਕਿਸਤਾਨ ਦੇ ਸਬੰਧ ਹਮੇਸ਼ਾ ਤੋ ਹੀ ਉਲਝੇ ਅਤੇ ਤਣਾਅਪੂਰਣ ਰਹੇ ਹਨ। ਕਦੇ ਪਾਣੀ ਦੀ ਵੰਡ, ਕਦੇ ਕਰਜੇ ਦੀ ਵੰਡ ਤੇ ਕਦੇ ਕਸ਼ਮੀਰੀ ਲੋਕਾਂ ਦੀਆਂ ਜਾਇਦਾਦਾਂ ਦੀ ਵੰਡ ਕਾਰਨ ਮਤਭੇਦ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੀ ਰਹਿੰਦਾ ਹੈ। ਸੰਨ 1947-48 ਦੌਰਾਨ ਪਾਕਿਸਤਾਨ ਨੇ ਹਜ਼ਾਰਾਂ ਚੀਨੀਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਪਾਕਿਸਤਾਨੀ ਬਣਾ ਕੇ ਘੁਸਪੈਠ ਕਰਵਾਈ ਗਈ। 1999 ਵਿੱਚ ਪਾਕਿਸਤਾਨ ਨੇ ਅਫ਼ਗਾਨ ਗੁਜਬਦੀਨ ਪਾਕ ਸੈਨਿਕਾਂ ਅਤੇ ਸਿੱਖਿਅਤ ਕਸ਼ਮੀਰੀ ਅੱਤਵਾਦੀਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਭੇਜ ਕੇ ਕਾਰਗਿਲ 'ਤੇ ਕਬਜ਼ਾ ਕਰ ਲਿਆ ਜੋ ਕਿ ਬਾਅਦ ਵਿੱਚ ਭਾਰਤੀ ਸੈਨਾ ਨੇ ਫ਼ਿਰ ਆਪਣੇ ਕਬਜੇ ਹੇਠ ਕਰ ਲਿਆ। ਪਾਕਿਸਤਾਨ ਸ਼ੁਰੂ ਤੋਂ ਹਈ ਕਸ਼ਮੀਰ 'ਤੇ ਆਪਣਾ ਹੱਕ ਜਤਾਉਂਦਾ ਹੈ। ਇਸੇ ਕਰਕੇ ਭਾਰਤ-ਪਾਕਿਸਤਾਨ ਵਿੱਚ ਆਪਸੀ ਮਤਭੇਦ ਹੈ। ਇਸ ਮੁੱਦੇ ਦੇ ਹੱਲ ਲਈ 1950 ਵਿੱਚ ਨਹਿਰੂ-ਲਿਆਕਤ ਅਲੀ ਸਮਝੌਤਾ ਵੀ ਹੋਇਆ ਸੀ। ਹੁਣ ਇਸ ਮਾਮਲੇ ਸਬੰਧੀ ਯੂ.ਐਨ.ਓ ਨੂੰ ਦਰਖ਼ਾਸਤ ਕੀਤੀ ਗਈ ਹੈ। |
||
== ਨੋਟ == |
|||
{{notes|refs={{efn|name=remaining religions|Besides specific religions, the last two categories in the 2011 Census were "Other religions and persuasions" (0.65%) and "Religion not stated" (0.23%).}}|33em}} |
|||
== ਬਾਹਰੀ ਕੜੀਆਂ == |
== ਬਾਹਰੀ ਕੜੀਆਂ == |
||
{{ਹਵਾਲੇ|1=ਹਵਾਲੇ, ਨੋਟਸ ਅਤੇ ਮਾਖਜ਼ਾਂ}} |
|||
*{{Citation|title=There's No National Language in India: Gujarat High Court|publisher=Times Of India|date=6 January 2007|url=http://articles.timesofindia.indiatimes.com/2010-01-25/india/28148512_1_national-language-official-language-hindi|accessdate=17 July 2011|ref={{Sfnref|Times of India|2007}}|archivedate=29 ਜਨਵਰੀ 2014|archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20140129070149/http://articles.timesofindia.indiatimes.com/2010-01-25/india/28148512_1_national-language-official-language-hindi}} |
*{{Citation|title=There's No National Language in India: Gujarat High Court|publisher=Times Of India|date=6 January 2007|url=http://articles.timesofindia.indiatimes.com/2010-01-25/india/28148512_1_national-language-official-language-hindi|accessdate=17 July 2011|ref={{Sfnref|Times of India|2007}}|archivedate=29 ਜਨਵਰੀ 2014|archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20140129070149/http://articles.timesofindia.indiatimes.com/2010-01-25/india/28148512_1_national-language-official-language-hindi}} |
||
---- |
---- |
||
==ਹਵਾਲੇ== |
==ਹਵਾਲੇ== |
||
{{ਹਵਾਲੇ}} |
{{ਹਵਾਲੇ}} |
||
==ਹੋਰ ਵੇਖੋ== |
|||
* [[ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਖੇਤੀਬਾੜੀ]] |
|||
{{ਕਾਮਨਜ਼|India|ਭਾਰਤ}} |
{{ਕਾਮਨਜ਼|India|ਭਾਰਤ}} |
||
* [http://raisen.nic.in/admin.htm subdivisions] |
|||
Online Travel India - http://www.takeofftrip.com {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110621133845/http://www.takeofftrip.com/ |date=2011-06-21 }} |
|||
* http://www.citymayors.com/government/india_government.html#Anchor-Municipal-49575 |
|||
* [http://raisen.nic.in/admin.htm Example of district with different subdivisions] |
|||
* [http://www.SeasonsIndia.info Seasons, Climate, Global Warming in India - Reference Links Students Project] |
|||
{{ਏਸ਼ੀਆ ਦੇ ਦੇਸ਼}} |
{{ਏਸ਼ੀਆ ਦੇ ਦੇਸ਼}} |
||
| ਲਕੀਰ 477: | ਲਕੀਰ 507: | ||
[[ਸ਼੍ਰੇਣੀ:ਏਸ਼ੀਆ ਦੇ ਦੇਸ਼]] |
[[ਸ਼੍ਰੇਣੀ:ਏਸ਼ੀਆ ਦੇ ਦੇਸ਼]] |
||
[[ਸ਼੍ਰੇਣੀ:ਲੋਕਤੰਤਰ]] |
[[ਸ਼੍ਰੇਣੀ:ਲੋਕਤੰਤਰ]] |
||
[[ਸ਼੍ਰੇਣੀ: |
[[ਸ਼੍ਰੇਣੀ:ਬ੍ਰਿਕਸ ਦੇਸ਼]] |
||
[[ਸ਼੍ਰੇਣੀ:ਜੀ-20 ਦੇਸ਼]] |
|||
17:13, 3 ਜੁਲਾਈ 2024 ਮੁਤਾਬਕ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਨਵਾਂ ਦੁਹਰਾਅ
ਭਾਰਤ ਗਣਰਾਜ | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||
| ਮਾਟੋ: "ਸਤਿਅਮੇਵ ਜਯਤੇ" (Sanskrit) "Truth Alone Triumphs"[1] | |||||
| ਐਨਥਮ: "ਜਨ ਗਣ ਮਨ"[2][3] "Thou Art the Ruler of the Minds of All People"[4][2] | |||||
| ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਗੀਤ "ਵੰਦੇ ਮਾਤਰਮ" (Sanskrit) "I Bow to Thee, Mother"[lower-alpha 1][1][2] | |||||
 ਗੂੜ੍ਹੇ ਹਰੇ ਰੰਗ ਵਿੱਚ ਦਿਖਾਇਆ ਗਿਆ ਭਾਰਤ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਨਿਯੰਤਰਿਤ ਖੇਤਰ; ਹਲਕੇ ਹਰੇ ਵਿੱਚ ਦਿਖਾਇਆ ਗਿਆ ਖੇਤਰ ਦਾਅਵਾ ਕੀਤਾ ਗਿਆ ਪਰ ਨਿਯੰਤਰਿਤ ਨਹੀਂ ਕੀਤਾ ਗਿਆ | |||||
| ਰਾਜਧਾਨੀ | ਨਵੀਂ ਦਿੱਲੀ 28°36′50″N 77°12′30″E / 28.61389°N 77.20833°E | ||||
| ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਵੱਡਾ ਸ਼ਹਿਰ | |||||
| ਅਧਿਕਾਰਤ ਭਾਸ਼ਾਵਾਂ | |||||
| ਮਾਨਤਾ ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਭਾਸ਼ਾਵਾਂ | ਕੋਈ ਨਹੀਂ[9][10][11] | ||||
| ਮਾਨਤਾ ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤ ਖੇਤਰੀ ਭਾਸ਼ਾਵਾਂ | |||||
| ਮੂਲ ਭਾਸ਼ਾਵਾਂ | 447 ਭਾਸ਼ਾਵਾਂ[lower-alpha 3] | ||||
| ਧਰਮ (2011) | |||||
| ਵਸਨੀਕੀ ਨਾਮ | ਭਾਰਤੀ | ||||
| ਸਰਕਾਰ | ਸੰਘੀ ਸੰਸਦੀ ਸੰਵਿਧਾਨਕ ਗਣਰਾਜ | ||||
| ਦ੍ਰੋਪਦੀ ਮੁਰਮੂ | |||||
| ਜਗਦੀਪ ਧਨਖੜ | |||||
| ਨਰਿੰਦਰ ਮੋਦੀ | |||||
• ਮੁੱਖ ਜੱਜ | ਧਨੰਜਯ ਯਸ਼ਵੰਤ ਚੰਦਰਚੂੜ | ||||
| ਓਮ ਬਿਰਲਾ | |||||
| ਵਿਧਾਨਪਾਲਿਕਾ | ਸੰਸਦ | ||||
| ਰਾਜ ਸਭਾ | |||||
| ਲੋਕ ਸਭਾ | |||||
ਯੂਨਾਈਟਡ ਕਿੰਗਡਮ ਤੋਂ ਆਜ਼ਾਦੀ | |||||
• ਰਾਜ | 15 ਅਗਸਤ 1947 | ||||
• ਗਣਰਾਜ | 26 ਜਨਵਰੀ 1950 | ||||
| ਖੇਤਰ | |||||
• ਕੁੱਲ | 3,287,263[2] km2 (1,269,219 sq mi)[lower-alpha 4] (7ਵਾਂ) | ||||
• ਜਲ (%) | 9.6 | ||||
| ਆਬਾਦੀ | |||||
• 2022 ਅਨੁਮਾਨ | 1,375,586,000[17] (ਦੂਜਾ) | ||||
• 2011 ਜਨਗਣਨਾ | 1,210,854,977[18][19] (ਦੂਜਾ) | ||||
• ਘਣਤਾ | 426.4/km2 (1,104.4/sq mi) (19ਵਾਂ) | ||||
| ਜੀਡੀਪੀ (ਪੀਪੀਪੀ) | 2022 ਅਨੁਮਾਨ | ||||
• ਕੁੱਲ | |||||
• ਪ੍ਰਤੀ ਵਿਅਕਤੀ | |||||
| ਜੀਡੀਪੀ (ਨਾਮਾਤਰ) | 2022 ਅਨੁਮਾਨ | ||||
• ਕੁੱਲ | |||||
• ਪ੍ਰਤੀ ਵਿਅਕਤੀ | |||||
| ਗਿਨੀ (2011) | 35.7[21][22] ਮੱਧਮ | ||||
| ਐੱਚਡੀਆਈ (2021) | ਮੱਧਮ · 132ਵਾਂ | ||||
| ਮੁਦਰਾ | ਭਾਰਤੀ ਰੁਪਈਆ (₹) (INR) | ||||
| ਸਮਾਂ ਖੇਤਰ | UTC+05:30 (IST) | ||||
| DST ਨਹੀਂ ਦੇਖਿਆ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ | |||||
| ਮਿਤੀ ਫਾਰਮੈਟ |
| ||||
| ਡਰਾਈਵਿੰਗ ਸਾਈਡ | left[24] | ||||
| ਕਾਲਿੰਗ ਕੋਡ | +91 | ||||
| ਆਈਐਸਓ 3166 ਕੋਡ | IN | ||||
| ਇੰਟਰਨੈੱਟ ਟੀਐਲਡੀ | .in | ||||
ਭਾਰਤ, ਅਧਿਕਾਰਤ ਤੌਰ 'ਤੇ ਭਾਰਤ ਗਣਰਾਜ (ਆਈਐੱਸਓ: Bhārat Gaṇarājya),[25] ਦੱਖਣੀ ਏਸ਼ੀਆ ਵਿੱਚ ਇੱਕ ਦੇਸ਼ ਹੈ। ਇਹ ਖੇਤਰ ਦੇ ਹਿਸਾਬ ਨਾਲ ਸੱਤਵਾਂ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਵੱਡਾ ਦੇਸ਼; ਜੂਨ 2023 ਤੱਕ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਵੱਧ ਆਬਾਦੀ ਵਾਲਾ ਦੇਸ਼;[26][27] ਅਤੇ 1947 ਵਿੱਚ ਆਪਣੀ ਆਜ਼ਾਦੀ ਦੇ ਸਮੇਂ ਤੋਂ, ਦੁਨੀਆ ਦਾ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਵੱਧ ਆਬਾਦੀ ਵਾਲਾ ਲੋਕਤੰਤਰ ਹੈ।[28][29][30] ਦੱਖਣ ਵੱਲ ਹਿੰਦ ਮਹਾਸਾਗਰ, ਦੱਖਣ-ਪੱਛਮ ਵੱਲ ਅਰਬ ਸਾਗਰ ਅਤੇ ਦੱਖਣ-ਪੂਰਬ ਵੱਲ ਬੰਗਾਲ ਦੀ ਖਾੜੀ ਨਾਲ ਘਿਰਿਆ ਹੋਇਆ, ਇਹ ਪੱਛਮ ਵੱਲ ਪਾਕਿਸਤਾਨ ਨਾਲ ਜ਼ਮੀਨੀ ਸਰਹੱਦਾਂ ਸਾਂਝੀਆਂ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ।;[lower-alpha 6] ਉੱਤਰ ਵੱਲ ਚੀਨ, ਨੇਪਾਲ ਅਤੇ ਭੂਟਾਨ; ਅਤੇ ਪੂਰਬ ਵੱਲ ਬੰਗਲਾਦੇਸ਼ ਅਤੇ ਮਿਆਂਮਾਰ। ਹਿੰਦ ਮਹਾਸਾਗਰ ਵਿੱਚ, ਭਾਰਤ ਸ਼੍ਰੀਲੰਕਾ ਅਤੇ ਮਾਲਦੀਵ ਦੇ ਨੇੜੇ ਹੈ; ਇਸ ਦੇ ਅੰਡੇਮਾਨ ਅਤੇ ਨਿਕੋਬਾਰ ਟਾਪੂ ਥਾਈਲੈਂਡ, ਮਿਆਂਮਾਰ ਅਤੇ ਇੰਡੋਨੇਸ਼ੀਆ ਨਾਲ ਸਮੁੰਦਰੀ ਸਰਹੱਦ ਸਾਂਝੇ ਕਰਦੇ ਹਨ।
ਆਧੁਨਿਕ ਮਨੁੱਖ 55,000 ਸਾਲ ਪਹਿਲਾਂ ਅਫ਼ਰੀਕਾ ਤੋਂ ਭਾਰਤੀ ਉਪ-ਮਹਾਂਦੀਪ 'ਤੇ ਆਏ ਸਨ।[31][32][33]
ਉਹਨਾਂ ਦੇ ਲੰਬੇ ਕਿੱਤੇ, ਸ਼ੁਰੂ ਵਿੱਚ ਵੱਖੋ-ਵੱਖਰੇ ਰੂਪਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਸ਼ਿਕਾਰੀ-ਇਕੱਠੇ ਕਰਨ ਵਾਲਿਆਂ ਦੇ ਰੂਪ ਵਿੱਚ, ਨੇ ਖੇਤਰ ਨੂੰ ਬਹੁਤ ਹੀ ਵਿਭਿੰਨਤਾ ਬਣਾ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਹੈ, ਮਨੁੱਖੀ ਜੈਨੇਟਿਕ ਵਿਭਿੰਨਤਾ ਵਿੱਚ ਅਫਰੀਕਾ ਤੋਂ ਬਾਅਦ ਦੂਜੇ ਸਥਾਨ 'ਤੇ ਹੈ।[34] 9,000 ਸਾਲ ਪਹਿਲਾਂ ਸਿੰਧ ਨਦੀ ਬੇਸਿਨ ਦੇ ਪੱਛਮੀ ਹਾਸ਼ੀਏ ਵਿੱਚ ਉਪ-ਮਹਾਂਦੀਪ ਵਿੱਚ ਸੈਟਲਡ ਜੀਵਨ ਉਭਰਿਆ ਸੀ, ਹੌਲੀ ਹੌਲੀ ਤੀਜੀ ਹਜ਼ਾਰ ਸਾਲ ਬੀਸੀਈ ਦੀ ਸਿੰਧੂ ਘਾਟੀ ਸਭਿਅਤਾ ਵਿੱਚ ਵਿਕਸਤ ਹੋਇਆ।[35]
12000 ਈਸਾ ਪੂਰਵ ਤੱਕ, ਸੰਸਕ੍ਰਿਤ ਦਾ ਇੱਕ ਪੁਰਾਤਨ ਰੂਪ, ਇੱਕ ਇੰਡੋ-ਯੂਰਪੀਅਨ ਭਾਸ਼ਾ, ਉੱਤਰ ਪੱਛਮ ਤੋਂ ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਫੈਲ ਗਈ ਸੀ।[36][37] ਇਸ ਦਾ ਪ੍ਰਮਾਣ ਅੱਜ ਰਿਗਵੇਦ ਦੇ ਭਜਨਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਮਿਲਦਾ ਹੈ। ਇੱਕ ਮੌਖਿਕ ਪਰੰਪਰਾ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਸੁਰੱਖਿਅਤ ਰੱਖਿਆ ਗਿਆ ਸੀ ਜੋ ਪੂਰੀ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਚੌਕਸ ਸੀ, ਰਿਗਵੇਦ ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਹਿੰਦੂ ਧਰਮ ਦੀ ਸ਼ੁਰੂਆਤ ਨੂੰ ਰਿਕਾਰਡ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ।[38] ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀਆਂ ਦ੍ਰਾਵਿੜ ਭਾਸ਼ਾਵਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਉੱਤਰੀ ਅਤੇ ਪੱਛਮੀ ਖੇਤਰਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਬਦਲ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਗਿਆ ਸੀ।[39]
400 ਈਸਾ ਪੂਰਵ ਤੱਕ, ਹਿੰਦੂ ਧਰਮ ਦੇ ਅੰਦਰ ਜਾਤ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਪੱਧਰੀਕਰਨ ਅਤੇ ਬੇਦਖਲੀ ਉਭਰ ਕੇ ਸਾਹਮਣੇ ਆਈ ਸੀ, ਅਤੇ ਬੌਧ ਅਤੇ ਜੈਨ ਧਰਮ ਪੈਦਾ ਹੋ ਗਏ ਸਨ, ਸਮਾਜਿਕ ਵਿਵਸਥਾਵਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਖ਼ਾਨਦਾਨੀ ਨਾਲ ਜੋੜਿਆ ਨਹੀਂ ਗਿਆ ਸੀ।[40][41]
ਸ਼ੁਰੂਆਤੀ ਸਿਆਸੀ ਮਜ਼ਬੂਤੀ ਨੇ ਗੰਗਾ ਬੇਸਿਨ ਵਿੱਚ ਸਥਿਤ ਮੌਰੀਆ ਅਤੇ ਗੁਪਤ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਨੂੰ ਜਨਮ ਦਿੱਤਾ।[42]
ਉਹਨਾਂ ਦਾ ਸਮੂਹਿਕ ਯੁੱਗ ਵਿਆਪਕ ਰਚਨਾਤਮਕਤਾ ਨਾਲ ਭਰਿਆ ਹੋਇਆ ਸੀ, ਪਰ ਔਰਤਾਂ ਦੀ ਡਿੱਗਦੀ ਸਥਿਤੀ, ਅਤੇ ਵਿਸ਼ਵਾਸ ਦੀ ਇੱਕ ਸੰਗਠਿਤ ਪ੍ਰਣਾਲੀ ਵਿੱਚ ਛੂਤ-ਛਾਤ ਨੂੰ ਸ਼ਾਮਲ ਕਰਨ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਵੀ ਚਿੰਨ੍ਹਿਤ ਕੀਤਾ ਗਿਆ ਸੀ।[43][44][lower-alpha 7][45] ਦੱਖਣੀ ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ, ਮੱਧ ਰਾਜਾਂ ਨੇ ਦੱਖਣ-ਪੂਰਬੀ ਏਸ਼ੀਆ ਦੇ ਰਾਜਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਦ੍ਰਾਵਿੜ-ਭਾਸ਼ਾ ਦੀਆਂ ਲਿਪੀਆਂ ਅਤੇ ਧਾਰਮਿਕ ਸਭਿਆਚਾਰਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਨਿਰਯਾਤ ਕੀਤਾ।[46]
ਸ਼ੁਰੂਆਤੀ ਮੱਧਕਾਲੀ ਯੁੱਗ ਵਿੱਚ, ਈਸਾਈ ਧਰਮ, ਇਸਲਾਮ, ਯਹੂਦੀ ਧਰਮ, ਅਤੇ ਜੋਰਾਸਟ੍ਰੀਅਨ ਧਰਮ ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਦੱਖਣੀ ਅਤੇ ਪੱਛਮੀ ਤੱਟਾਂ ਉੱਤੇ ਸਥਾਪਿਤ ਹੋ ਗਏ ਸਨ।[47] ਮੱਧ ਏਸ਼ੀਆ ਦੀਆਂ ਮੁਸਲਿਮ ਫੌਜਾਂ ਨੇ ਰੁਕ-ਰੁਕ ਕੇ ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਉੱਤਰੀ ਮੈਦਾਨਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਆਪਣੇ ਕਬਜ਼ੇ ਵਿੱਚ ਕਰ ਲਿਆ, ਅੰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਦਿੱਲੀ ਸਲਤਨਤ ਦੀ ਸਥਾਪਨਾ ਕੀਤੀ, ਅਤੇ ਉੱਤਰੀ ਭਾਰਤ ਨੂੰ ਮੱਧਕਾਲੀ ਇਸਲਾਮ ਦੇ ਬ੍ਰਹਿਮੰਡੀ ਨੈਟਵਰਕ ਵਿੱਚ ਖਿੱਚ ਲਿਆ।[48][49]
15ਵੀਂ ਸਦੀ ਵਿੱਚ, ਵਿਜੈਨਗਰ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਨੇ ਦੱਖਣ ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਇੱਕ ਲੰਬੇ ਸਮੇਂ ਤੱਕ ਚੱਲਣ ਵਾਲੇ ਸੰਯੁਕਤ ਹਿੰਦੂ ਸੱਭਿਆਚਾਰ ਦੀ ਸਿਰਜਣਾ ਕੀਤੀ।[50]
ਪੰਜਾਬ ਵਿੱਚ, ਸਿੱਖ ਧਰਮ ਦਾ ਉਭਾਰ ਹੋਇਆ, ਸੰਸਥਾਗਤ ਧਰਮ ਨੂੰ ਰੱਦ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੋਇਆ।[51] ਮੁਗਲ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ, 1526 ਵਿੱਚ, ਦੋ ਸਦੀਆਂ ਦੀ ਸਾਪੇਖਿਕ ਸ਼ਾਂਤੀ ਦੀ ਸ਼ੁਰੂਆਤ ਕੀਤੀ, ਚਮਕਦਾਰ ਆਰਕੀਟੈਕਚਰ ਦੀ ਵਿਰਾਸਤ ਛੱਡ ਕੇ।[52][lower-alpha 8][53]
ਹੌਲੀ-ਹੌਲੀ ਬ੍ਰਿਟਿਸ਼ ਈਸਟ ਇੰਡੀਆ ਕੰਪਨੀ ਦੇ ਸ਼ਾਸਨ ਦਾ ਵਿਸਤਾਰ ਹੋਇਆ, ਜਿਸ ਨੇ ਭਾਰਤ ਨੂੰ ਇੱਕ ਬਸਤੀਵਾਦੀ ਆਰਥਿਕਤਾ ਵਿੱਚ ਬਦਲ ਦਿੱਤਾ, ਪਰ ਇਸਦੀ ਪ੍ਰਭੂਸੱਤਾ ਨੂੰ ਵੀ ਮਜ਼ਬੂਤ ਕੀਤਾ।[54] ਬ੍ਰਿਟਿਸ਼ ਕ੍ਰਾਊਨ ਸ਼ਾਸਨ 1858 ਵਿੱਚ ਸ਼ੁਰੂ ਹੋਇਆ। ਭਾਰਤੀਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਦਿੱਤੇ ਗਏ ਅਧਿਕਾਰ ਹੌਲੀ-ਹੌਲੀ ਦਿੱਤੇ ਗਏ,[55][56] ਪਰ ਤਕਨੀਕੀ ਤਬਦੀਲੀਆਂ ਪੇਸ਼ ਕੀਤੀਆਂ ਗਈਆਂ, ਅਤੇ ਸਿੱਖਿਆ ਅਤੇ ਜਨਤਕ ਜੀਵਨ ਦੇ ਆਧੁਨਿਕ ਵਿਚਾਰਾਂ ਨੇ ਜੜ੍ਹ ਫੜ ਲਈ।[57] ਇੱਕ ਮੋਹਰੀ ਅਤੇ ਪ੍ਰਭਾਵਸ਼ਾਲੀ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰਵਾਦੀ ਲਹਿਰ ਉਭਰੀ, ਜੋ ਅਹਿੰਸਕ ਵਿਰੋਧ ਲਈ ਮਸ਼ਹੂਰ ਸੀ ਅਤੇ ਬ੍ਰਿਟਿਸ਼ ਸ਼ਾਸਨ ਨੂੰ ਖਤਮ ਕਰਨ ਦਾ ਮੁੱਖ ਕਾਰਕ ਬਣ ਗਈ।[58][59] 1947 ਵਿੱਚ ਬ੍ਰਿਟਿਸ਼ ਭਾਰਤੀ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਨੂੰ ਦੋ ਆਜ਼ਾਦ ਰਾਜਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਵੰਡਿਆ ਗਿਆ ਸੀ,[60][61][62][63] ਹਿੰਦੂ-ਬਹੁਗਿਣਤੀ ਭਾਰਤ ਦਾ ਡੋਮੀਨੀਅਨ ਅਤੇ ਇੱਕ ਮੁਸਲਿਮ-ਬਹੁਗਿਣਤੀ ਪਾਕਿਸਤਾਨ ਦਾ ਡੋਮੀਨੀਅਨ, ਵੱਡੇ ਪੱਧਰ 'ਤੇ ਜਾਨੀ ਨੁਕਸਾਨ ਅਤੇ ਇੱਕ ਬੇਮਿਸਾਲ ਪਰਵਾਸ ਦੇ ਵਿਚਕਾਰ।[64]
ਭਾਰਤ 1950 ਤੋਂ ਇੱਕ ਸੰਘੀ ਗਣਰਾਜ ਰਿਹਾ ਹੈ, ਇੱਕ ਲੋਕਤੰਤਰੀ ਸੰਸਦੀ ਪ੍ਰਣਾਲੀ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਸ਼ਾਸਨ ਕੀਤਾ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ। ਇਹ ਬਹੁਲਵਾਦੀ, ਬਹੁ-ਭਾਸ਼ੀ ਅਤੇ ਬਹੁ-ਜਾਤੀ ਸਮਾਜ ਹੈ। ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀ ਆਬਾਦੀ 1951 ਵਿੱਚ 361 ਮਿਲੀਅਨ ਤੋਂ ਵਧ ਕੇ 2022 ਵਿੱਚ ਲਗਭਗ 1.4 ਬਿਲੀਅਨ ਹੋ ਗਈ।[65]
ਉਸੇ ਸਮੇਂ ਦੌਰਾਨ, ਇਸਦੀ ਨਾਮਾਤਰ ਪ੍ਰਤੀ ਵਿਅਕਤੀ ਆਮਦਨ US$64 ਸਾਲਾਨਾ ਤੋਂ US$2,601 ਤੱਕ ਵਧ ਗਈ, ਅਤੇ ਇਸਦੀ ਸਾਖਰਤਾ ਦਰ 16.6% ਤੋਂ 74% ਹੋ ਗਈ। 1951 ਵਿੱਚ ਮੁਕਾਬਲਤਨ ਬੇਸਹਾਰਾ ਦੇਸ਼ ਹੋਣ ਤੋਂ[66] ਭਾਰਤ ਇੱਕ ਤੇਜ਼ੀ ਨਾਲ ਵਧ ਰਹੀ ਮੁੱਖ ਅਰਥਵਿਵਸਥਾ ਅਤੇ ਸੂਚਨਾ ਤਕਨਾਲੋਜੀ ਸੇਵਾਵਾਂ ਦਾ ਇੱਕ ਕੇਂਦਰ ਬਣ ਗਿਆ ਹੈ, ਇੱਕ ਵਿਸਤ੍ਰਿਤ ਮੱਧ ਵਰਗ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ।[67] ਇਸਦਾ ਇੱਕ ਸਪੇਸ ਪ੍ਰੋਗਰਾਮ ਹੈ। ਭਾਰਤੀ ਫਿਲਮਾਂ, ਸੰਗੀਤ ਅਤੇ ਅਧਿਆਤਮਿਕ ਸਿੱਖਿਆਵਾਂ ਗਲੋਬਲ ਸੱਭਿਆਚਾਰ ਵਿੱਚ ਵਧਦੀ ਭੂਮਿਕਾ ਨਿਭਾਉਂਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ।[68] ਭਾਰਤ ਨੇ ਆਪਣੀ ਗਰੀਬੀ ਦੀ ਦਰ ਨੂੰ ਕਾਫ਼ੀ ਹੱਦ ਤੱਕ ਘਟਾ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਹੈ, ਹਾਲਾਂਕਿ ਆਰਥਿਕ ਅਸਮਾਨਤਾ ਵਧਣ ਦੀ ਕੀਮਤ 'ਤੇ।[69] ਭਾਰਤ ਇੱਕ ਪਰਮਾਣੂ-ਹਥਿਆਰ ਵਾਲਾ ਦੇਸ਼ ਹੈ, ਜੋ ਫੌਜੀ ਖਰਚਿਆਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਉੱਚ ਦਰਜੇ 'ਤੇ ਹੈ। ਇਸ ਦੇ ਆਪਣੇ ਗੁਆਂਢੀ ਦੇਸ਼ਾਂ ਪਾਕਿਸਤਾਨ ਅਤੇ ਚੀਨ ਨਾਲ ਕਸ਼ਮੀਰ ਨੂੰ ਲੈ ਕੇ ਵਿਵਾਦ ਹਨ, ਜੋ 20ਵੀਂ ਸਦੀ ਦੇ ਅੱਧ ਤੋਂ ਅਣਸੁਲਝੇ ਹੋਏ ਹਨ।[70] ਭਾਰਤ ਨੂੰ ਜਿਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਸਮਾਜਿਕ-ਆਰਥਿਕ ਚੁਣੌਤੀਆਂ ਦਾ ਸਾਹਮਣਾ ਕਰਨਾ ਪੈਂਦਾ ਹੈ, ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਲਿੰਗ ਅਸਮਾਨਤਾ, ਬਾਲ ਕੁਪੋਸ਼ਣ,[71] ਅਤੇ ਹਵਾ ਪ੍ਰਦੂਸ਼ਣ ਦੇ ਵਧਦੇ ਪੱਧਰ।[72] ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀ ਧਰਤੀ ਮੈਗਾਡਾਇਵਰਸ ਹੈ, ਚਾਰ ਜੈਵ ਵਿਭਿੰਨਤਾ ਦੇ ਹੌਟਸਪੌਟਸ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ।[73] ਇਸਦੇ ਜੰਗਲਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਇਸਦੇ ਖੇਤਰ ਦਾ 21.7% ਸ਼ਾਮਲ ਹੈ।[74] ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਜੰਗਲੀ ਜੀਵ, ਜਿਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀ ਸੰਸਕ੍ਰਿਤੀ ਵਿੱਚ ਪਰੰਪਰਾਗਤ ਤੌਰ 'ਤੇ ਸਹਿਣਸ਼ੀਲਤਾ ਨਾਲ ਦੇਖਿਆ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ, ਨੂੰ ਇਹਨਾਂ ਜੰਗਲਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ, ਅਤੇ ਕਿਤੇ ਹੋਰ, ਸੁਰੱਖਿਅਤ ਨਿਵਾਸ ਸਥਾਨਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਸਮਰਥਨ ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤ ਹੈ।.[75]
ਨਾਂ ਦੀ ਉਤਪੱਤੀ
[ਸੋਧੋ]ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਦੋ ਅਧਿਕਾਰਤ ਨਾਂ ਹਨ - ਹਿੰਦੀ ਵਿੱਚ ਭਾਰਤ (भारत) ਅਤੇ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਵਿੱਚ ਇੰਡੀਆ (India)। ਇਸ ਨੂੰ ਹਿੰਦੁਸਤਾਨ ਵੀ ਆਖਦੇ ਹਨ। ਇੰਡੀਆ ਨਾਂ ਦੀ ਉਤਪਤੀ ਸਿੰਧੂ ਨਦੀ ਦੇ ਅੰਗਰੇਜੀ ਨਾਂ "ਇੰਡਸ" ਤੋਂ ਹੋਈ ਹੈ। ਭਾਰਤ ਨਾਂ, ਇੱਕ ਪ੍ਰਾਚੀਨ ਹਿੰਦੂ ਸਮਰਾਟ ਭਰਤ ਜੋ ਕਿ ਮਨੂੰ ਦੇ ਵੰਸ਼ਜ ਰਿਸ਼ਭਦੇਵ ਦੇ ਜੇਠੇ ਪੁੱਤ ਸਨ ਅਤੇ ਜਿਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੀ ਕਥਾ ਸ੍ਰੀਮਦ ਭਾਗਵਤ ਪੁਰਾਣ ਵਿੱਚ ਹੈ, ਦੇ ਨਾਮ ਤੋਂ ਲਿਆ ਗਿਆ ਹੈ। ਭਾਰਤ (ਭਾ+ਰਤ) ਸ਼ਬਦ ਦਾ ਮਤਲਬ ਹੈ ਆਂਤਰਿਕ ਪ੍ਰਕਾਸ਼ ਜਾਂ ਵਿਵੇਕ-ਰੂਪੀ ਪ੍ਰਕਾਸ਼ ਵਿੱਚ ਲੀਨ। ਇੱਕ ਤੀਜਾ ਨਾਮ ਹਿੰਦੁਸਤਾਨ (ہندوستان) ਵੀ ਹੈ ਜਿਸਦਾ ਮਤਲਬ "ਹਿੰਦ ਦੀ ਭੂਮੀ" ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ਜੋ ਕਿ ਪ੍ਰਾਚੀਨ ਕਾਲ ਰਿਸ਼ੀਆਂ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਗਿਆ ਸੀ। ਪ੍ਰਾਚੀਨ ਕਾਲ ਵਿੱਚ ਇਹ ਘੱਟ ਪ੍ਰਚੱਲਤ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਸੀ ਅਤੇ ਬਾਅਦ ਵਿੱਚ ਜ਼ਿਆਦਾ ਪ੍ਰਚੱਲਤ ਹੋਇਆ ਖਾਸ ਤੌਰ ਉੱਤੇ ਅਰਬ/ਈਰਾਨ ਵਿੱਚ। ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਇਹ ਨਾਮ ਮੁਗਲ ਕਾਲ ਵਿੱਚ ਜ਼ਿਆਦਾ ਪ੍ਰਚੱਲਤ ਹੋਇਆ ਹਾਲਾਂਕਿ ਇਸਦੀ ਸਮਕਾਲੀ ਵਰਤੋਂ ਘੱਟ ਅਤੇ ਅਕਸਰ ਉੱਤਰੀ ਭਾਰਤ ਲਈ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ। ਇਸ ਤੋਂ ਇਲਾਵਾ ਹਿੰਦੁਸਤਾਨ ਨੂੰ ਵੇਦ-ਕਾਲ ਵਿੱਚ ਆਰਿਆਵਰਤ ਜੰਬੂਦੀਪ ਅਤੇ ਅਜਨਾਭ-ਦੇਸ ਦੇ ਨਾਮ ਵਜੋਂ ਵੀ ਜਾਣਿਆ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਰਿਹਾ ਹੈ। ਬਹੁਤ ਪਹਿਲਾਂ ਇਹ ਦੇਸ਼ ਸੋਨੇ ਦੀ ਚਿੜੀ ਦੇ ਰੂਪ ਵਿੱਚ ਜਾਣਿਆ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਸੀ।[76]
ਇਤਿਹਾਸ
[ਸੋਧੋ]
ਪੱਥਰ ਯੁੱਗ ਭੀਮਬੇਟਕਾ ਮੱਧ ਪ੍ਰਦੇਸ਼ ਦੀ ਗੁਫਾਵਾਂ ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਮਨੁੱਖੀ ਜੀਵਨ ਦਾ ਪ੍ਰਾਚੀਨਤਮ ਪ੍ਰਮਾਣ ਹਨ। ਪਹਿਲੀਆਂ ਸਥਾਈ ਬਸਤੀਆਂ ਨੇ 9000 ਸਾਲ ਪੂਰਵ ਵਿੱਚ ਰੂਪ ਧਾਰਿਆ। ਇਹੀ ਅੱਗੇ ਚੱਲ ਕੇ ਸਿੰਧੂ ਘਾਟੀ ਸੱਭਿਅਤਾ ਵਿੱਚ ਵਿਕਸਿਤ ਹੋਈਆਂ, ਜੋ 2600 ਈਸਾ ਪੂਰਵ ਅਤੇ 1900 ਈਸਾ ਪੂਰਵ ਦੇ ਵਿਚਕਾਰ ਆਪਣੇ ਸਿਖਰ ਉੱਤੇ ਸੀ। ਲਗਭਗ 1600 ਈਸਾ ਪੂਰਵ ਵਿੱਚ ਆਰਿਆ ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਆਏ ਅਤੇ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੇ ਉੱਤਰ-ਭਾਰਤੀ ਖੇਤਰਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਵੈਦਿਕ ਸੱਭਿਅਤਾ ਦਾ ਸੂਤਰਪਾਤ ਕੀਤਾ। ਇਸ ਸੱਭਿਅਤਾ ਦੇ ਸਰੋਤ ਵੇਦ ਅਤੇ ਪੁਰਾਣ ਹਨ। ਪਰ ਆਰਿਆ-ਹਮਲਾ-ਸਿੱਧਾਂਤ ਅਜੇ ਤੱਕ ਵਿਵਾਦਤ ਹੈ। ਬਾਲ ਗੰਗਾਧਰ ਸਹਿਤ ਸਹਿਤ ਕੁਝ ਵਿਦਵਾਨਾਂ ਦੀ ਮਾਨਤਾ ਇਹ ਹੈ ਕਿ ਆਰਿਆ ਹਿੰਦੁਸਤਾਨ ਦੇ ਹੀ ਸਥਾਈ ਨਿਵਾਸੀ ਰਹੇ ਹਨ ਅਤੇ ਵੈਦਿਕ ਇਤਹਾਸ ਕਰੀਬ 75000 ਸਾਲ ਪ੍ਰਾਚੀਨ ਹੈ ਜੋ ਕਿ ਗਲਤ ਸਾਬਤ ਹੋਇਆ ਹੈ। ਇਸ ਸਮੇਂ ਦੱਖਣ ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਦ੍ਰਵਿੜ ਸੱਭਿਅਤਾ ਦਾ ਵਿਕਾਸ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਰਿਹਾ। ਦੋਨਾਂ ਜਾਤੀਆਂ ਨੇ ਇੱਕ ਦੂਜੇ ਦੀਆਂ ਖੂਬੀਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਅਪਣਾਉਂਦੇ ਹੋਏ ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਇੱਕ ਮਿਸ਼ਰਤ-ਸੰਸਕ੍ਰਿਤੀ ਦੀ ਉਸਾਰੀ ਕੀਤੀ।
500 ਈਸਵੀ ਪੂਰਵ ਤੋਂ ਬਾਅਦ ਕਈ ਅਜ਼ਾਦ ਰਾਜ ਬਣ ਗਏ। ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਸ਼ੁਰੂਆਤੀ ਰਾਜ-ਵੰਸ਼ਾਂ ਵਿੱਚੋਂ ਉੱਤਰ-ਭਾਰਤ ਦਾ ਮੌਰਿਆ ਰਾਜਵੰਸ਼ ਜ਼ਿਕਰਯੋਗ ਹੈ ਜਿਸਦੇ ਸਮਰਾਟ ਅਸ਼ੋਕ ਦਾ ਵਿਸ਼ਵ ਇਤਹਾਸ ਵਿੱਚ ਵਿਸ਼ੇਸ਼ ਸਥਾਨ ਹੈ। 180 ਈਸਵੀ ਦੀ ਸ਼ੁਰੂਆਤ ਤੋਂ ਮੱਧ-ਏਸ਼ਿਆ ਵੱਲੋਂ ਕਈ ਹਮਲੇ ਹੋਏ, ਜਿਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੇ ਨਤੀਜੇ ਵਜੋਂ ਉੱਤਰ-ਭਾਰਤੀ ਉਪ-ਮਹਾਦੀਪ ਵਿੱਚ ਯੂਨਾਨੀ, ਸ਼ੱਕ, ਪਾਰਥੀ ਅਤੇ ਓੜਕ ਕੁਸ਼ਾਣ ਰਾਜ-ਵੰਸ਼ ਸਥਾਪਤ ਹੋਏ।
ਤੀਜੀ ਸ਼ਤਾਬਦੀ ਤੋਂ ਬਾਅਦ ਦਾ ਸਮਾਂ, ਜਦੋਂ ਭਾਰਤ ਉੱਤੇ ਗੁਪਤ ਸਲਤਨਤ ਦਾ ਸ਼ਾਸਨ ਸੀ, ਭਾਰਤ ਦਾ ਸੁਨਹਿਰੀ ਕਾਲ ਕਹਾਇਆ। ਦੱਖਣ ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਭਿੰਨ-ਭਿੰਨ ਕਾਲ-ਖੰਡਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਕਈ ਰਾਜਵੰਸ਼ ਜਿਵੇਂ ਕਿ ਚਾਲੁਕੀਆ ਰਾਜਵੰਸ਼, ਗੁਲਾਮ ਵੰਸ਼, ਚੋਲ, ਪੱਲਵ ਅਤੇ ਪਾਂਡੇ ਰਹੇ। ਈਸੇ ਦੇ ਆਸਪਾਸ ਸੰਗਮ-ਸਾਹਿਤ ਆਪਣੇ ਸਿਖਰਾਂ ਤੇ ਸੀ, ਜਿਸ ਵਿੱਚ ਤਮਿਲ ਭਾਸ਼ਾ ਦਾ ਵਿਕਾਸ ਹੋਇਆ। ਸਤਵਾਹਨਾਂ ਅਤੇ ਚਾਲੁਕੀਆ ਰਾਜਵੰਸ਼ ਨੇ ਮੱਧ-ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਆਪਣਾ ਰਾਜ ਸਥਾਪਤ ਕੀਤਾ। ਵਿਗਿਆਨ, ਕਲਾ, ਸਾਹਿਤ, ਹਿਸਾਬ, ਖਗੋਲ-ਸ਼ਾਸਤਰ, ਪ੍ਰਾਚੀਨ ਤਕਨੀਕਾਂ, ਧਰਮ-ਦਰਸ਼ਨ ਇਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਰਾਜਿਆਂ ਦੇ ਸ਼ਾਸਣਕਾਲ ਵਿੱਚ ਵਧੇ-ਫੁੱਲੇ।
12ਵੀਂ ਸ਼ਤਾਬਦੀ ਦੇ ਅਰੰਭ ਵਿੱਚ, ਭਾਰਤ ਉੱਤੇ ਇਸਲਾਮੀ ਹਮਲਿਆਂ ਦੇ ਬਾਅਦ, ਉੱਤਰੀ ਅਤੇ ਕੇਂਦਰੀ ਭਾਰਤ ਦਾ ਸਾਰਾ ਹਿੱਸਾ ਦਿੱਲੀ ਸਲਤਨਤ ਦੇ ਸ਼ਾਸਨ ਅਧੀਨ ਹੋ ਗਿਆ; ਅਤੇ ਬਾਅਦ ਵਿੱਚ, ਸਾਰਾ ਉੱਪ-ਮਹਾਂਦੀਪ ਮੁਗਲ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਦੇ ਅਧੀਨ। ਦੱਖਣ ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਵਿਜੇਨਗਰ ਸਾਮਰਾਜ ਸ਼ਕਤੀਸ਼ਾਲੀ ਨਿਕਲਿਆ। ਹਾਲਾਂਕਿ ਖਾਸ ਕਰਕੇ ਮੁਕਾਬਲਤਨ ਰੂਪ ਵਲੋਂ, ਦੱਖਣ ਵਿੱਚ ਅਨੇਕਾਂ ਰਾਜ ਬਾਕੀ ਰਹੇ, ਅਤੇ ਹੋਂਦ ਵਿੱਚ ਆਏ। ਮੁਗਲਾਂ ਦੇ ਸੰਖੇਪ ਅਧਿਕਾਰ ਦੇ ਬਾਅਦ ਸਤਾਰਵੀਂ ਸਦੀ ਵਿੱਚ ਦੱਖਣ ਅਤੇ ਮੱਧ ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਮਰਾਠਿਆਂ ਦਾ ਜੋਰ ਹੋਇਆ। ਉੱਤਰ ਪੱਛਮ ਵਿੱਚ ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਦਾ ਸ਼ਕਤੀਸ਼ਾਲੀ ਰਾਜ ਹੋਂਦ ਵਿੱਚ ਆਇਆ।
17ਵੀਂ ਸ਼ਤਾਬਦੀ ਦੇ ਮੱਧ ਵਿੱਚ ਪੁਰਤਗਾਲ, ਡੱਚ, ਫ਼ਰਾਂਸ, ਬ੍ਰਿਟੇਨ ਸਹਿਤ ਅਨੇਕਾਂ ਯੂਰਪੀ ਦੇਸ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ, ਜੋ ਭਾਰਤ ਨਾਲ ਵਪਾਰ ਕਰਨ ਦੇ ਇੱਛੁਕ ਸਨ, ਦੇਸ਼ ਦੀ ਅੰਦਰੂਨੀ ਸ਼ਾਸਕੀ ਅਰਾਜਕਤਾ ਦਾ ਫਾਇਦਾ ਚੁੱਕਿਆ। ਅੰਗ੍ਰੇਜ ਦੂਜੇ ਦੇਸ਼ਾਂ ਨਾਲ ਵਪਾਰ ਦੇ ਇੱਛੁਕ ਲੋਕਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਰੋਕਣ ਵਿੱਚ ਸਫ਼ਲ ਰਹੇ ਅਤੇ 1840 ਤੱਕ ਲਗਭਗ ਪੂਰੇ ਦੇਸ਼ ਉੱਤੇ ਸ਼ਾਸਨ ਕਰਣ ਵਿੱਚ ਸਫਲ ਹੋਏ। 1847 ਵਿੱਚ ਬ੍ਰਿਟਿਸ਼ ਈਸਟ ਇੰਡੀਆ ਕੰਪਨੀ ਦੇ ਵਿਰੁੱਧ ਅਸਫਲ ਬਗ਼ਾਵਤ, ਜੋ ਭਾਰਤੀ ਸੁਤੰਤਰਤਾ ਦੀ ਪਹਿਲੀ ਲੜਾਈ ਵਜੋਂ ਵੀ ਜਾਣੀ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ, ਦੇ ਬਾਅਦ ਭਾਰਤ ਦਾ ਸਾਰਾ ਭਾਗ ਸਿੱਧੇ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਸ਼ਾਸਨ ਦੇ ਪ੍ਰਬੰਧਕੀ ਕਾਬੂ ਵਿੱਚ ਆ ਗਿਆ।
ਕੋਣਾਰਕ ਚੱਕਰ – 13ਵੀਂ ਸ਼ਤਾਬਦੀ ਵਿੱਚ ਬਣੇ ਉੜੀਸਾ ਦੇ ਕੋਣਾਰਕ ਸੂਰਜ ਮੰਦਿਰ ਵਿੱਚ ਸਥਿਤ, ਇਹ ਦੁਨੀਆ ਦੇ ਪ੍ਰਸਿੱਧ ਇਤਿਹਾਸਿਕ ਸਮਾਰਕਾਂ ਵਿੱਚੋਂ ਇੱਕ ਹੈ।
ਵੀਹਵੀਂ ਸਦੀ ਦੇ ਸ਼ੁਰੂ ਵਿੱਚ ਆਧੁਨਿਕ ਸਿੱਖਿਆ ਦੇ ਪ੍ਰਸਾਰ ਅਤੇ ਵਿਸ਼ਵਪਟਲ ਉੱਤੇ ਬਦਲਦੀ ਰਾਜਨੀਤਕ ਪਰੀਸਥਤੀਆਂ ਦੇ ਚਲਦੇ ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਇੱਕ ਬੌਧਿਕ ਅੰਦੋਲਨ ਦਾ ਸੂਤਰਪਾਤ ਹੋਇਆ ਜਿਨ੍ਹੇ ਸਮਾਜਕ ਅਤੇ ਰਾਜਨੀਤਕ ਪਧਰਾਂ ਉੱਤੇ ਅਨੇਕ ਪਰਿਵਰਤਨਾਂ ਅਤੇ ਅੰਦੋਲਨਾਂ ਦੀ ਨੀਂਹ ਰੱਖੀ। 1884 ਵਿੱਚ ਇੰਡੀਅਨ ਨੈਸ਼ਨਲ ਕਾਂਗਰਸ ਕਾਂਗਰੇਸ ਪਾਰਟੀ ਦੀ ਸਥਾਪਨਾ ਨੇ ਸਵਤੰਤਰਤਾ ਅੰਦੋਲਨ ਨੂੰ ਇੱਕ ਗਤੀਮਾਨ ਸਵਰੂਪ ਦਿੱਤਾ। ਵੀਹਵੀਂ ਸ਼ਤਾਬਦੀ ਦੇ ਅਰੰਭ ਵਿੱਚ ਲੰਬੇ ਸਮਾਂ ਤੱਕ ਅਜ਼ਾਦੀ ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤੀ ਲਈ ਵਿਸ਼ਾਲ ਅਹਿੰਸਾਵਾਦੀ ਸੰਘਰਸ਼ ਚੱਲਿਆ, ਜਿਸਦਾ ਨੇਤ੍ਰਤਅਲਤੇ ਮਹਾਤਮਾ ਗਾਂਧੀ, ਜੋ ਆਧਿਕਾਰਿਕ ਰੁਪ ਵਲੋਂ ਆਧੁਨਿਕ ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰਪਿਤਾ ਦੇ ਰੂਪ ਵਿੱਚ ਸੰਬੋਧਿਤ ਕੀਤੇ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਹਨ, ਨੇ ਕੀਤਾ। ਇਸਦੇ ਨਾਲ – ਨਾਲ ਸ਼ਿਵ ਆਜ਼ਾਦ, ਸਰਦਾਰ ਭਗਤ ਸਿੰਘ, ਸੁਖਦੇਵ ਥਾਪਰ, ਰਾਜਗੁਰੂ, ਨੇਤਾਜੀ ਸੁਭਾਸ਼ ਚੰਦਰ ਬੋਸ, ਵੀਰ ਸਾਵਰਕਰ ਆਦਿ ਦੇ ਨੇਤ੍ਰਤਆਤੇ ਵਿੱਚ ਚਲੇ ਕ੍ਰਾਂਤੀਵਾਦੀ ਸੰਘਰਸ਼ ਦੇ ਫਲਸਰੁਪ 16 ਜੂਨ 1946 ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਵਲੋਂ ਅੰਤਰਮ ਸਰਕਾਰ ਬਣਾਉਣ ਦਾ ਐਲਾਨ: ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀ ਦੋ ਗਰੁੱਪਾਂ (ਏ ਤੇ ਬੀ) ਵਿੱਚ ਵੰਡ ਦੀ ਹਮਾਇਤ ਕੀਤੀ। ਮਿਸ਼ਨ ਨੇ ਬੀ ਗਰੁੱਪ ਵਿੱਚ ਪੰਜਾਬ, ਸਿੰਧ, ਬਲੋਚਿਸਤਾਨ ਤੇ ਸੂਬਾ ਸਰਹੱਦ ਰੱਖੇ ਸਨ। ਕੈਬਨਿਟ ਮਿਸ਼ਨ ਤੇ ਵਾਇਸਰਾਏ ਨੇ ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਅੰਤਰਮ ਸਰਕਾਰ ਬਣਾਉਣ ਦਾ ਐਲਾਨ ਕੀਤਾ। ਇਸ ਵਿੱਚ 6 ਕਾਂਗਰਸੀ, 5 ਮੁਸਲਿਮ ਲੀਗ, 1 ਸਿੱਖ, 1 ਪਾਰਸੀ ਤੇ 1 ਭਾਰਤੀ ਈਸਾਈ ਵਜ਼ੀਰ ਲੈਣ ਦਾ ਫ਼ੈਸਲਾ ਹੋਇਆ। ਸਿੱਖਾਂ ਵਿੱਚੋਂ ਬਲਦੇਵ ਸਿਘ (ਅਕਾਲੀ) ਨੂੰ ਵਜ਼ਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਸ਼ਾਮਲ ਹੋਣ ਵਾਸਤੇ ਸੱਦਾ ਦਿਤਾ ਗਿਆ। 15 ਅਗਸਤ 1947 ਭਾਰਤ ਨੇ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਸ਼ਾਸਨ ਵਲੋਂ ਪੂਰਣਤਯਾ ਅਜ਼ਾਦੀ ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤ ਕੀਤੀ। ਤਦੁਪਰਾਂਤ 26 ਜਨਵਰੀ 1950 ਨੂੰ ਭਾਰਤ ਇੱਕ ਲੋਕ-ਰਾਜ ਬਣਾ।
ਇੱਕ ਬਹੁਜਾਤੀਏ ਅਤੇ ਬਹੁਧਾਰਮਿਕ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰ ਹੋਣ ਦੇ ਕਾਰਨ ਭਾਰਤ ਨੂੰ ਸਮਾਂ – ਸਮਾਂ ਉੱਤੇ ਸਾੰਪ੍ਰਦਾਇਿਕ ਅਤੇ ਜਾਤੀ ਵੈਰ ਦਾ ਸ਼ਿਕਾਰ ਹੋਣਾ ਪਿਆ ਹੈ। ਖੇਤਰੀ ਅਸੰਤੋਸ਼ ਅਤੇ ਬਗ਼ਾਵਤ ਵੀ ਹਾਲਾਂਕਿ ਦੇਸ਼ ਦੇ ਵੱਖ - ਵੱਖ ਹਿੱਸੀਆਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਰਹੇ ਹਨ, ਉੱਤੇ ਇਸਦੀ ਧਰਮਨਿਰਪੇਕਸ਼ਤਾ ਅਤੇ ਜਨਤਾਂਤਰਿਕਤਾ, ਕੇਵਲ 1975 – 77 ਨੂੰ ਛੱਡ, ਜਦੋਂ ਤਤਕਾਲੀਨ ਪ੍ਰਧਾਨਮੰਤਰੀ ਇੰਦਰਾ ਗਾਂਧੀ ਨੇ ਐਮਰਜੈਂਸੀ ਦੀ ਘੋਸ਼ਣਾ ਕਰ ਦਿੱਤੀ ਸੀ, ਅਖੰਡਤ ਰਹੀ ਹੈ।
ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਗੁਆਂਢੀ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੋਂ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ਅਨਸੁਲਝੇ ਸੀਮਾ ਵਿਵਾਦ ਹਨ। ਇਸਦੇ ਕਾਰਨ ਇਸਨੂੰ ਛੋਟੇ ਪੈਮਾਨੀਆਂ ਉੱਤੇ ਲੜਾਈ ਦਾ ਵੀ ਸਾਮਣਾ ਕਰਣਾ ਪਿਆ ਹੈ। 1962 ਵਿੱਚ ਚੀਨ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ, ਅਤੇ 1947, 1965, 1971 ਏਵੰ 1999 ਵਿੱਚ ਪਾਕਿਸਤਾਨ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ਲੜਾਇਆਂ ਹੋ ਚੁੱਕੀ ਹਨ।
ਭਾਰਤ ਗੁਟਨਿਰਪੇਕਸ਼ ਅੰਦੋਲਨ ਅਤੇ ਸੰਯੁਕਤ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰ ਸੰਘ ਦੇ ਸੰਸਥਾਪਕ ਮੈਂਬਰ ਦੇਸ਼ਾਂ ਵਿੱਚੋਂ ਇੱਕ ਹੈ।
1974 ਵਿੱਚ ਭਾਰਤ ਨੇ ਆਪਣਾ ਪਹਿਲਾ ਪਰਮਾਣੁ ਪ੍ਰੀਖਿਆ ਕੀਤਾ ਸੀ ਜਿਸਦੇ ਬਾਅਦ 1998 ਵਿੱਚ 5 ਅਤੇ ਪ੍ਰੀਖਿਆ ਕੀਤੇ ਗਏ। 1990 ਦੇ ਦਸ਼ਕ ਵਿੱਚ ਕੀਤੇ ਗਏ ਆਰਥਕ ਸੁਧਾਰੀਕਰਣ ਦੀ ਬਦੌਲਤ ਅੱਜ ਦੇਸ਼ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਤੇਜੀ ਵਲੋਂ ਵਿਕਾਸਸ਼ੀਲ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੋਂ ਦੀ ਸੂਚੀ ਵਿੱਚ ਆ ਗਿਆ ਹੈ।
ਭੂਗੋਲਿਕ ਸਥਿਤੀ
[ਸੋਧੋ]ਭਾਰਤ, ਭਾਰਤੀ ਉਪ-ਮਹਾਂਦੀਪ ਦਾ ਜ਼ਿਆਦਾਤਰ ਹਿੱਸਾ, ਭਾਰਤੀ ਟੈਕਟੋਨਿਕ ਪਲੇਟ ਦੇ ਉੱਪਰ ਸਥਿਤ ਹੈ, ਥੋੜੀ ਪਲੇਟ ਹਿੰਦ-ਆਸਟ੍ਰੇਲੀਆਈ ਪਲੇਟ ਨਾਲ ਲੱਗਦੀ ਹੈ। ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀ ਪਰਿਭਾਸ਼ਤ ਭੂ-ਵਿਗਿਆਨਿਕ ਪ੍ਰਕਿਰਿਆਵਾਂ ੭ ਕਰੋੜ ਸਾਲ ਪਹਿਲਾਂ ਸ਼ੁਰੂ ਹੋਈਆਂ ਜਦੋਂ ਭਾਰਤੀ ਉਪਮਹਾਂਦੀਪ, ਜੋ ਉਸ ਸਮੇਂ ਦੇ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਵੱਡੇ ਮਹਾਂਦੀਪ ਗੋਂਡਵਾਨਾ ਦਾ ਦੱਖਣੀ ਹਿੱਸਾ ਸੀ, ਉੱਤਰ-ਪੂਰਬ ਵੱਲ ਨੂੰ ਵਧਣ ਲੱਗਾ। ਉਪ-ਮਹਾਂਦੀਪ ਦੇ ਯੁਰੇਸ਼ਿਅਨ ਪਲੇਟ ਨਾਲ ਹੋਏ ਟਕਰਾਅ ਨਾਲ ਹਿਮਾਲਾ ਦਾ ਜਨਮ ਹੋਇਆ। ਹਿਮਾਲਾ ਚੋਂ ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਵੱਡੇ ਦਰਿਆ ਨਿਕਲਦੇ ਹਨ। ਇਸ ਦੇ ਪੱਛਮ 'ਚ ਥਾਰ ਮਾਰੂਥਲ ਹੈ, ਜਿਸ ਨੂੰ ਅਰਾਵਲੀ ਨੇ ਬਾਰਿਸ਼ਾਂ ਤੋ ਵਾਂਝਾ ਕੀਤਾ ਹੋਇਆ ਹੈ। ਉੱਤਰ 'ਚ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਦੀ ਉਪਜਾਊ ਧਰਤੀ ਤੇ ਦੱਖਣ 'ਚ ਕਠੋਰ ਪਠਾਰ ਇਸ ਨੂੰ ਭਿੰਨਤਾ ਦਾ ਪੁਤਲਾ ਬਣਾਉਂਦੇ ਹਨ। ਗੰਗਾ, ਜਮਨਾ, ਸਤਲੁਜ, ਬ੍ਰਹਮਪੁੱਤਰ ਆਦਿ ਵੱਡੀਆਂ ਨਦੀਆਂ ਭਾਰਤ 'ਚ ਹੀ ਹਨ। ਸਾਰਾ ਦੇਸ਼ ਮਾਨਸੂਨ ਦੀ ਵਰਖਾ ਤੋਂ ਹੀ ਝੜੀ ਦਾ ਸੁੱਖ ਮਾਣਦਾ ਹੈ।
ਮੌਸਮ
[ਸੋਧੋ]ਹਿਮਾਲਾ ਜਵਾਬ ਵਿੱਚ ਜੰਮੂ ਅਤੇ ਕਾਸ਼ਮੀਰ ਵਲੋਂ ਲੈ ਕੇ ਪੂਰਵ ਵਿੱਚ ਅਰੁਣਾਂਚਲ ਪ੍ਰਦੇਸ਼ ਤੱਕ ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀ ਜਿਆਦਾਤਰ ਪੂਰਵੀ ਸੀਮਾ ਬਣਾਉਂਦਾ ਹੈ ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਜਿਆਦਾਤਰ ਉੱਤਰੀ ਅਤੇ ਜਵਾਬ – ਪਸ਼ਚਿਮੀਏ ਪ੍ਰਾਂਤ ਹਿਮਾਲਾ ਦੇ ਪਹਾੜਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਸਥਿਤ ਹਨ। ਬਾਕੀ ਭਾਗ ਉੱਤਰੀ, ਵਿਚਕਾਰ ਅਤੇ ਪੂਰਵੀ ਭਾਰਤ ਗੰਗਾ ਦੇ ਉਪਜਾਊ ਮੈਦਾਨਾਂ ਵਲੋਂ ਬਣਿਆ ਹੈ। ਉੱਤਰੀ - ਪੂਰਵੀ ਪਾਕਿਸਤਾਨ ਵਲੋਂ ਚੋਟੀ ਹੋਇਆ, ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਪੱਛਮ ਵਿੱਚ ਥਾਰ ਦਾ ਮਾਰੂਥਲ ਹੈ। ਦੱਖਣ ਭਾਰਤ ਲਗਭਗ ਸੰਪੂਰਣ ਹੀ ਦੱਖਣ ਦੇ ਪਠਾਰ ਵੱਲੋਂ ਨਿਰਮਿਤ ਹੈ। ਇਹ ਪਠਾਰ ਪੂਰਵੀ ਅਤੇ ਪੱਛਮ ਵੱਲ ਘਾਟਾਂ ਦੇ ਵਿੱਚ ਸਥਿਤ ਹੈ।
ਕਈ ਮਹੱਤਵਪੂਰਣ ਅਤੇ ਵੱਡੀਆਂ ਨਦੀਆਂ ਜਿਵੇਂ ਗੰਗਾ, ਬ੍ਰਹਮਪੁਤਰ, ਜਮੁਨਾ, ਗੋਦਾਵਰੀ ਅਤੇ ਕ੍ਰਿਸ਼ਣਾ ਭਾਰਤ ਵਲੋਂ ਹੋਕੇ ਵਗਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ। ਇਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨਦੀਆਂ ਦੇ ਕਾਰਨ ਉੱਤਰ ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀ ਭੂਮੀ ਖੇਤੀਬਾੜੀ ਲਈ ਉਪਜਾਊ ਹੈ। ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਵਿਸਥਾਰ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ਹੀ ਇਸਦੇ ਮੌਸਮ ਵਿੱਚ ਵੀ ਬਹੁਤ ਭਿੰਨਤਾ ਹੈ। ਦੱਖਣ ਵਿੱਚ ਜਿੱਥੇ ਕਿਨਾਰੀ ਅਤੇ ਗਰਮ ਮਾਹੌਲ ਰਹਿੰਦਾ ਹੈ ਉਥੇ ਹੀ ਜਵਾਬ ਵਿੱਚ ਕੜੀ ਸਰਦੀ, ਪੂਰਵ ਵਿੱਚ ਜਿੱਥੇ ਜਿਆਦਾ ਵਰਖਾ ਹੈ ਉਥੇ ਹੀ ਪੱਛਮ ਵਿੱਚ ਰੇਗਿਸਤਾਨ ਦੀ ਖੁਸ਼ਕੀ। ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਵਰਖਾ ਮੁੱਖਤਆ ਮਾਨਸੂਨ ਹਵਾਵਾਂ ਵਲੋਂ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ।
ਜੀਵ ਵਖਰੇਵਾਂ
[ਸੋਧੋ]ਭਾਰਤ 'ਚ ਬਹੁਤ ਸਾਰੀਆਂ ਜੀਵ-ਜਾਤੀਆਂ ਹਨ; ੭.੬% ਥਣਧਾਰੀ, ੧੨.੬% ਪੰਛੀ, ੬.੨% ਭੁਜੰਗੀ, ੪.੪% ਜਲਥਲ-ਚੱਲ, ੧੧.੭% ਮੱਛੀਆਂ ਅਤੇ ੬.੦% ਫ਼ੁੱਲਾਂ ਵਾਲੇ ਪੌਦੇ ਹਨ।
ਅਰਥ-ਵਿਵਸਥਾ
[ਸੋਧੋ]ਰਾਜ
[ਸੋਧੋ]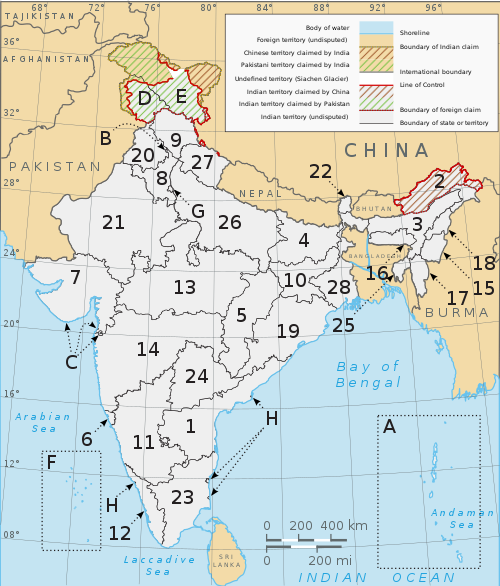
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਾਸਕੀ ਮਕਸਦ ਲਈ, ਭਾਰਤ ਨੂੰ ਛੋਟੇ ਹਿੱਸਿਆਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਵੰਡਿਆ ਗਿਆ ਹੈ। ਜ਼ਿਆਦਾਤਰ ਹਿੱਸਿਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਰਾਜ ਜਾਂ ਪ੍ਰਾਂਤ ਕਿਹਾ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ਅਤੇ ਕੁੱਝ ਹਿੱਸਿਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਕੇਂਦਰੀ ਸ਼ਾਸ਼ਤ ਪ੍ਰਦੇਸ ਕਿਹਾ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ। ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਕੁਲ 28 ਰਾਜ ਅਤੇ 9 ਕੇਂਦਰੀ ਸ਼ਾਸਤ ਪ੍ਰਦੇਸ਼ ਹਨ।
ਰਾਜ-ਸਾਰਣੀ
[ਸੋਧੋ]| ਸੰਖਿਆ | ਰਾਜ | ਕੋਡ | ਰਾਜਧਾਨੀ |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ਆਂਧਰਾ ਪ੍ਰਦੇਸ਼ | AP | ਅਮਰਾਵਤੀ |
| 2 | ਅਰੁਣਾਚਲ ਪ੍ਰਦੇਸ਼ | AR | ਈਟਾਨਗਰ |
| 3 | ਅਸਾਮ | AS | ਦਿਸਪੁਰ |
| 4 | ਬਿਹਾਰ | BR | ਪਟਨਾ |
| 5 | ਛੱਤੀਸਗੜ੍ਹ | CG | ਰਾਏਪੁਰ |
| 6 | ਗੋਆ | GA | ਪਣਜੀ |
| 7 | ਗੁਜਰਾਤ | GJ | ਗਾਂਧੀਨਗਰ |
| 8 | ਹਰਿਆਣਾ | HR | ਚੰਡੀਗੜ੍ਹ |
| 9 | ਹਿਮਾਚਲ ਪ੍ਰਦੇਸ਼ | HP | ਸ਼ਿਮਲਾ |
| 10 | ਝਾਰਖੰਡ | JH | ਰਾਂਚੀ |
| 11 | ਕਰਨਾਟਕ | KA | ਬੇਂਗਲੁਰੂ |
| 12 | ਕੇਰਲਾ | KL | ਤਿਰਵੰਦਰਮ ਜਾਂ ਤੀਰੂਵੰਥਪੁਰਮ |
| 13 | ਮੱਧ ਪ੍ਰਦੇਸ਼ | MP | ਭੋਪਾਲ |
| 14 | ਮਹਾਰਾਸ਼ਟਰ | MH | ਮੁੰਬਈ |
| 15 | ਮਨੀਪੁਰ | MN | ਇੰਫਾਲ |
| 16 | ਮੇਘਾਲਿਆ | ML | ਸ਼ਿਲਾਂਗ |
| 17 | ਮਿਜ਼ੋਰਮ | MZ | ਆਇਜੋਲ |
| 18 | ਨਾਗਾਲੈਂਡ | NL | ਕੋਹਿਮਾ |
| 19 | ਉੜੀਸਾ | OR | ਭੁਬਨੇਸ਼ਵਰ |
| 20 | ਪੰਜਾਬ | PB | ਚੰਡੀਗੜ੍ਹ |
| 21 | ਰਾਜਸਥਾਨ | RJ | ਜੈਪੁਰ |
| 22 | ਸਿੱਕਮ | SK | ਗੰਗਟੋਕ |
| 23 | ਤਾਮਿਲ ਨਾਡੂ | TN | ਚੇਨੱਈ |
| 24 | ਤੇਲੰਗਾਨਾ | TS | ਹੈਦਰਾਬਾਦ |
| 25 | ਤ੍ਰਿਪੁਰਾ | TR | ਅਗਰਤਲਾ |
| 26 | ਉੱਤਰ ਪ੍ਰਦੇਸ਼ | UP | ਲਖਨਊ |
| 27 | ਉੱਤਰਾਖੰਡ | UL | ਦੇਹਰਾਦੂਨ |
| 28 | ਪੱਛਮੀ ਬੰਗਾਲ | WB | ਕੋਲਕਾਤਾ |
ਕੇਂਦਰੀ ਸ਼ਾਸ਼ਤ ਪ੍ਰਦੇਸ਼
[ਸੋਧੋ]| ਸੰਖਿਆ | ਰਾਜ-ਖੇਤਰ | ਰਾਜਧਾਨੀ |
|---|---|---|
| A | ਅੰਡੇਮਾਨ ਅਤੇ ਨਿਕੋਬਾਰ ਦੀਪ ਸਮੂਹ | ਪੋਰਟ ਬਲੇਅਰ |
| B | ਚੰਡੀਗੜ੍ਹ | ਚੰਡੀਗੜ੍ਹ |
| C | ਦਾਦਰਾ ਅਤੇ ਨਗਰ ਹਵੇਲੀ ਅਤੇ ਦਮਨ ਅਤੇ ਦਿਉ | ਦਮਨ |
| D | ਲਕਸ਼ਦੀਪ | ਕਵਰੱਤੀ |
| E | ਦਿੱਲੀ | ਨਵੀਂ ਦਿੱਲੀ |
| F | ਪਾਂਡੀਚਰੀ | ਪਾਂਡੀਚਰੀ (ਸ਼ਹਿਰ) |
| G | ਜੰਮੂ ਅਤੇ ਕਸ਼ਮੀਰ | ਸ੍ਰੀਨਗਰ ਅਤੇ ਜੰਮੂ |
| H | ਲੱਦਾਖ | ਲੇਹ |
ਰਾਜਨੀਤੀ ਅਤੇ ਸਰਕਾਰ
[ਸੋਧੋ]ਰਾਜਨੀਤੀ
[ਸੋਧੋ]ਭਾਰਤ ਦੁਨੀਆ ਦਾ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਵੱਧ ਆਬਾਦੀ ਵਾਲਾ ਲੋਕਤੰਤਰ ਹੈ। [77] ਬਹੁ-ਪਾਰਟੀ ਪ੍ਰਣਾਲੀ ਵਾਲਾ ਇੱਕ ਸੰਸਦੀ ਗਣਰਾਜ, [78] ਇਸਦੇ ਅੱਠ ਹਨ ਮਾਨਤਾ ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਪਾਰਟੀਆਂ, ਜਿਸ ਵਿੱਚ ਭਾਰਤੀ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਕਾਂਗਰਸ ਅਤੇ ਭਾਰਤੀ ਜਨਤਾ ਪਾਰਟੀ (ਭਾਜਪਾ), ਅਤੇ 40 ਤੋਂ ਵੱਧ ਖੇਤਰੀ ਪਾਰਟੀਆਂ [79] ਕਾਂਗਰਸ ਨੂੰ ਭਾਰਤੀ ਰਾਜਨੀਤਿਕ ਸੰਸਕ੍ਰਿਤੀ ਵਿੱਚ ਕੇਂਦਰ-ਖੱਬੇ ਮੰਨਿਆ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ,[80] ਅਤੇ ਭਾਜਪਾ ਨੂੰ ਸੱਜੇ-ਪੱਖੀ ਮੰਨਿਆ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ। [81] [82] [83] 1950-ਜਦੋਂ ਭਾਰਤ ਪਹਿਲੀ ਵਾਰ ਗਣਤੰਤਰ ਬਣਿਆ-ਅਤੇ 1980ਵਿਆਂ ਦੇ ਅਖੀਰ ਤੱਕ, ਕਾਂਗਰਸ ਨੇ ਸੰਸਦ ਵਿੱਚ ਬਹੁਮਤ ਹਾਸਲ ਕੀਤਾ। ਉਦੋਂ ਤੋਂ, ਹਾਲਾਂਕਿ, ਇਸ ਨੇ ਭਾਜਪਾ [84] ਦੇ ਨਾਲ-ਨਾਲ ਸ਼ਕਤੀਸ਼ਾਲੀ ਖੇਤਰੀ ਪਾਰਟੀਆਂ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ਵੱਧ ਤੋਂ ਵੱਧ ਸਿਆਸੀ ਸਟੇਜ ਸਾਂਝੀ ਕੀਤੀ ਹੈ, ਜਿਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੇ ਅਕਸਰ ਕੇਂਦਰ ਵਿੱਚ ਬਹੁ-ਪਾਰਟੀ ਗੱਠਜੋੜ ਸਰਕਾਰਾਂ ਬਣਾਉਣ ਲਈ ਮਜ਼ਬੂਰ ਕੀਤਾ ਹੈ। [85]
ਭਾਰਤੀ ਗਣਰਾਜ ਦੀਆਂ ਪਹਿਲੀਆਂ ਤਿੰਨ ਆਮ ਚੋਣਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ, 1951, 1957 ਅਤੇ 1962 ਵਿੱਚ, ਜਵਾਹਰ ਲਾਲ ਨਹਿਰੂ ਦੀ ਅਗਵਾਈ ਵਾਲੀ ਕਾਂਗਰਸ ਨੇ ਆਸਾਨ ਜਿੱਤਾਂ ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤ ਕੀਤੀਆਂ। 1964 ਵਿਚ ਨਹਿਰੂ ਦੀ ਮੌਤ 'ਤੇ, ਲਾਲ ਬਹਾਦਰ ਸ਼ਾਸਤਰੀ ਥੋੜ੍ਹੇ ਸਮੇਂ ਲਈ ਪ੍ਰਧਾਨ ਮੰਤਰੀ ਬਣੇ; ਨਹਿਰੂ ਦੀ ਧੀ ਇੰਦਰਾ ਗਾਂਧੀ ਦੁਆਰਾ, 1966 ਵਿੱਚ ਉਸਦੀ ਆਪਣੀ ਅਚਾਨਕ ਮੌਤ ਤੋਂ ਬਾਅਦ, ਉਸਨੂੰ ਸਫ਼ਲ ਬਣਾਇਆ ਗਿਆ ਸੀ, ਜਿਸਨੇ 1967 ਅਤੇ 1971 ਵਿੱਚ ਕਾਂਗਰਸ ਨੂੰ ਚੋਣ ਜਿੱਤਾਂ ਤੱਕ ਪਹੁੰਚਾਉਣ ਲਈ ਅਗਵਾਈ ਕੀਤੀ ਸੀ। ਉਸਨੇ 1975 ਵਿੱਚ ਐਲਾਨੀ ਐਮਰਜੈਂਸੀ ਦੀ ਸਥਿਤੀ ਤੋਂ ਜਨਤਕ ਅਸੰਤੋਸ਼ ਦੇ ਬਾਅਦ, 1977 ਵਿੱਚ ਕਾਂਗਰਸ ਨੂੰ ਸੱਤਾ ਤੋਂ ਬਾਹਰ ਕਰ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਗਿਆ ਸੀ; ਉਸ ਸਮੇਂ ਦੀ ਨਵੀਂ ਜਨਤਾ ਪਾਰਟੀ, ਜਿਸ ਨੇ ਐਮਰਜੈਂਸੀ ਦਾ ਵਿਰੋਧ ਕੀਤਾ ਸੀ, ਨੂੰ ਵੋਟ ਦਿੱਤੀ ਗਈ ਸੀ। ਇਸ ਦੀ ਸਰਕਾਰ ਸਿਰਫ਼ ਦੋ ਸਾਲ ਹੀ ਚੱਲੀ। 1980 ਵਿੱਚ ਮੁੜ ਸੱਤਾ ਵਿੱਚ ਆਈ, ਕਾਂਗਰਸ ਨੇ 1984 ਵਿੱਚ ਲੀਡਰਸ਼ਿਪ ਵਿੱਚ ਬਦਲਾਅ ਦੇਖਿਆ, ਜਦੋਂ ਇੰਦਰਾ ਗਾਂਧੀ ਦੀ ਹੱਤਿਆ ਕਰ ਦਿੱਤੀ ਗਈ ਸੀ; ਉਸ ਤੋਂ ਬਾਅਦ ਉਸ ਦਾ ਪੁੱਤਰ ਰਾਜੀਵ ਗਾਂਧੀ ਬਣਿਆ, ਜਿਸ ਨੇ ਉਸ ਸਾਲ ਬਾਅਦ ਵਿੱਚ ਆਮ ਚੋਣਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਆਸਾਨ ਜਿੱਤ ਹਾਸਲ ਕੀਤੀ। 1989 ਵਿੱਚ ਕਾਂਗਰਸ ਨੂੰ ਫਿਰ ਤੋਂ ਬਾਹਰ ਕਰ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਗਿਆ ਜਦੋਂ ਖੱਬੇ ਮੋਰਚੇ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ਗਠਜੋੜ ਵਿੱਚ ਨਵੇਂ ਬਣੇ ਜਨਤਾ ਦਲ ਦੀ ਅਗਵਾਈ ਵਿੱਚ ਇੱਕ ਨੈਸ਼ਨਲ ਫਰੰਟ ਗੱਠਜੋੜ ਨੇ ਚੋਣਾਂ ਜਿੱਤੀਆਂ; ਉਹ ਸਰਕਾਰ ਵੀ ਮੁਕਾਬਲਤਨ ਥੋੜ੍ਹੇ ਸਮੇਂ ਲਈ ਸਾਬਤ ਹੋਈ, ਸਿਰਫ ਦੋ ਸਾਲਾਂ ਤੋਂ ਘੱਟ ਸਮੇਂ ਲਈ। [86] 1991 ਵਿੱਚ ਦੁਬਾਰਾ ਚੋਣਾਂ ਹੋਈਆਂ; ਕਿਸੇ ਵੀ ਪਾਰਟੀ ਨੂੰ ਪੂਰਨ ਬਹੁਮਤ ਨਹੀਂ ਮਿਲਿਆ। ਕਾਂਗਰਸ, ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਵੱਡੀ ਇਕੱਲੀ ਪਾਰਟੀ ਦੇ ਰੂਪ ਵਿੱਚ, ਪੀਵੀ ਨਰਸਿਮਹਾ ਰਾਓ ਦੀ ਅਗਵਾਈ ਵਿੱਚ ਘੱਟ ਗਿਣਤੀ ਸਰਕਾਰ ਬਣਾਉਣ ਵਿੱਚ ਕਾਮਯਾਬ ਰਹੀ। [87]
1996 ਦੀਆਂ ਆਮ ਚੋਣਾਂ ਤੋਂ ਬਾਅਦ ਸਿਆਸੀ ਉਥਲ-ਪੁਥਲ ਦਾ ਦੋ ਸਾਲਾਂ ਦਾ ਦੌਰ ਚੱਲਿਆ। ਕਈ ਥੋੜ੍ਹੇ ਸਮੇਂ ਲਈ ਗਠਜੋੜਾਂ ਨੇ ਕੇਂਦਰ ਵਿੱਚ ਸੱਤਾ ਸਾਂਝੀ ਕੀਤੀ। ਭਾਜਪਾ ਨੇ 1996 ਵਿਚ ਥੋੜ੍ਹੇ ਸਮੇਂ ਲਈ ਸਰਕਾਰ ਬਣਾਈ; ਇਸਦੇ ਬਾਅਦ ਦੋ ਤੁਲਨਾਤਮਕ ਤੌਰ 'ਤੇ ਲੰਬੇ ਸਮੇਂ ਤੱਕ ਚੱਲਣ ਵਾਲੇ ਸੰਯੁਕਤ ਮੋਰਚੇ ਦੇ ਗੱਠਜੋੜ ਸਨ, ਜੋ ਬਾਹਰੀ ਸਮਰਥਨ 'ਤੇ ਨਿਰਭਰ ਸਨ। 1998 ਵਿੱਚ, ਭਾਜਪਾ ਇੱਕ ਸਫਲ ਗੱਠਜੋੜ, ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਜਮਹੂਰੀ ਗਠਜੋੜ (ਐਨ.ਡੀ.ਏ.) ਬਣਾਉਣ ਵਿੱਚ ਕਾਮਯਾਬ ਰਹੀ। ਅਟਲ ਬਿਹਾਰੀ ਵਾਜਪਾਈ ਦੀ ਅਗਵਾਈ ਵਿੱਚ, NDA ਪੰਜ ਸਾਲ ਦਾ ਕਾਰਜਕਾਲ ਪੂਰਾ ਕਰਨ ਵਾਲੀ ਪਹਿਲੀ ਗੈਰ-ਕਾਂਗਰਸੀ, ਗੱਠਜੋੜ ਸਰਕਾਰ ਬਣ ਗਈ। [88] ਫਿਰ 2004 ਦੀਆਂ ਭਾਰਤੀ ਆਮ ਚੋਣਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ, ਕਿਸੇ ਵੀ ਪਾਰਟੀ ਨੇ ਪੂਰਨ ਬਹੁਮਤ ਨਹੀਂ ਜਿੱਤਿਆ, ਪਰ ਕਾਂਗਰਸ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਵੱਡੀ ਸਿੰਗਲ ਪਾਰਟੀ ਵਜੋਂ ਉੱਭਰੀ, ਇੱਕ ਹੋਰ ਸਫਲ ਗੱਠਜੋੜ: ਸੰਯੁਕਤ ਪ੍ਰਗਤੀਸ਼ੀਲ ਗਠਜੋੜ (ਯੂਪੀਏ)। ਇਸ ਨੂੰ ਖੱਬੇ ਪੱਖੀ ਪਾਰਟੀਆਂ ਅਤੇ ਭਾਜਪਾ ਦਾ ਵਿਰੋਧ ਕਰਨ ਵਾਲੇ ਸੰਸਦ ਮੈਂਬਰਾਂ ਦਾ ਸਮਰਥਨ ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤ ਸੀ। ਯੂਪੀਏ 2009 ਦੀਆਂ ਆਮ ਚੋਣਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਵਧੀ ਹੋਈ ਗਿਣਤੀ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ਸੱਤਾ ਵਿੱਚ ਵਾਪਸ ਪਰਤਿਆ, ਅਤੇ ਇਸਨੂੰ ਹੁਣ ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀਆਂ ਕਮਿਊਨਿਸਟ ਪਾਰਟੀਆਂ ਤੋਂ ਬਾਹਰੀ ਸਮਰਥਨ ਦੀ ਲੋੜ ਨਹੀਂ ਰਹੀ। [89] ਉਸ ਸਾਲ, ਮਨਮੋਹਨ ਸਿੰਘ 1957 ਅਤੇ 1962 ਵਿੱਚ ਜਵਾਹਰ ਲਾਲ ਨਹਿਰੂ ਤੋਂ ਬਾਅਦ ਲਗਾਤਾਰ ਪੰਜ ਸਾਲਾਂ ਦੇ ਕਾਰਜਕਾਲ ਲਈ ਦੁਬਾਰਾ ਚੁਣੇ ਜਾਣ ਵਾਲੇ ਪਹਿਲੇ ਪ੍ਰਧਾਨ ਮੰਤਰੀ ਬਣੇ। [90] 2014 ਦੀਆਂ ਆਮ ਚੋਣਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ, ਭਾਜਪਾ 1984 ਤੋਂ ਬਾਅਦ ਪਹਿਲੀ ਸਿਆਸੀ ਪਾਰਟੀ ਬਣ ਗਈ ਜਿਸ ਨੇ ਬਹੁਮਤ ਹਾਸਲ ਕੀਤਾ ਅਤੇ ਦੂਜੀਆਂ ਪਾਰਟੀਆਂ ਦੇ ਸਮਰਥਨ ਤੋਂ ਬਿਨਾਂ ਸ਼ਾਸਨ ਕੀਤਾ। [91] ਮੌਜੂਦਾ ਪ੍ਰਧਾਨ ਮੰਤਰੀ ਨਰਿੰਦਰ ਮੋਦੀ ਗੁਜਰਾਤ ਦੇ ਸਾਬਕਾ ਮੁੱਖ ਮੰਤਰੀ ਹਨ। 22 ਜੁਲਾਈ 2022 ਨੂੰ, ਦ੍ਰੋਪਦੀ ਮੁਰਮੂ ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀ 15ਵੀਂ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰਪਤੀ ਚੁਣੀ ਗਈ ਅਤੇ 25 ਜੁਲਾਈ 2022 ਨੂੰ ਅਹੁਦੇ ਦੀ ਸਹੁੰ ਚੁੱਕੀ। [92]
ਸਰਕਾਰ
[ਸੋਧੋ]ਭਾਰਤ ਇੱਕ ਸੰਘ ਹੈ ਜਿਸਦਾ ਸੰਚਾਲਨ ਇੱਕ ਸੰਸਦੀ ਪ੍ਰਣਾਲੀ ਹੈ ਜੋ ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਸੰਵਿਧਾਨ ਦੇ ਅਧੀਨ ਹੈ - ਦੇਸ਼ ਦਾ ਸਰਵਉੱਚ ਕਾਨੂੰਨੀ ਦਸਤਾਵੇਜ਼। ਇਹ ਇੱਕ ਸੰਵਿਧਾਨਕ ਗਣਰਾਜ ਅਤੇ ਪ੍ਰਤੀਨਿਧ ਲੋਕਤੰਤਰ ਹੈ, ਜਿਸ ਵਿੱਚ " ਬਹੁਗਿਣਤੀ ਸ਼ਾਸਨ ਕਾਨੂੰਨ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਸੁਰੱਖਿਅਤ ਘੱਟ ਗਿਣਤੀ ਦੇ ਅਧਿਕਾਰਾਂ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਸੰਜੀਦਾ ਹੈ"। ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਸੰਘਵਾਦ ਸੰਘ ਅਤੇ ਰਾਜਾਂ ਵਿਚਕਾਰ ਸ਼ਕਤੀ ਦੀ ਵੰਡ ਨੂੰ ਪਰਿਭਾਸ਼ਿਤ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ। ਭਾਰਤ ਦਾ ਸੰਵਿਧਾਨ, ਜੋ ਕਿ 26 ਜਨਵਰੀ 1950 ਨੂੰ ਲਾਗੂ ਹੋਇਆ, [93] ਨੇ ਮੂਲ ਰੂਪ ਵਿੱਚ ਭਾਰਤ ਨੂੰ ਇੱਕ "ਪ੍ਰਭੁਸੱਤਾ ਸੰਪੰਨ, ਜਮਹੂਰੀ ਗਣਰਾਜ" ਕਿਹਾ। ਇਸ ਵਿਸ਼ੇਸ਼ਤਾ ਨੂੰ 1971 ਵਿੱਚ "ਇੱਕ ਪ੍ਰਭੂਸੱਤਾ ਸੰਪੰਨ, ਸਮਾਜਵਾਦੀ, ਧਰਮ ਨਿਰਪੱਖ, ਜਮਹੂਰੀ ਗਣਰਾਜ" ਵਿੱਚ ਸੋਧਿਆ ਗਿਆ ਸੀ। [94] ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀ ਸਰਕਾਰ ਦਾ ਰੂਪ, ਜਿਸ ਨੂੰ ਰਵਾਇਤੀ ਤੌਰ 'ਤੇ ਇੱਕ ਮਜ਼ਬੂਤ ਕੇਂਦਰ ਅਤੇ ਕਮਜ਼ੋਰ ਰਾਜਾਂ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ "ਅਰਧ-ਸੰਘੀ" ਵਜੋਂ ਦਰਸਾਇਆ ਗਿਆ ਹੈ, [95] ਸਿਆਸੀ, ਆਰਥਿਕ ਅਤੇ ਸਮਾਜਿਕ ਤਬਦੀਲੀਆਂ ਦੇ ਨਤੀਜੇ ਵਜੋਂ 1990 ਦੇ ਦਹਾਕੇ ਦੇ ਅਖੀਰ ਤੋਂ ਸੰਘੀ ਰੂਪ ਵਿੱਚ ਵਧਿਆ ਹੈ। [96] [97]
ਸਮੱਸਿਆਵਾਂ
[ਸੋਧੋ]ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀਆਂ ਹੱਦਾਂ ਦੇ ਕਈ ਹਿੱਸਿਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਲੈ ਕੇ ਕਈ ਵਿਵਾਦ ਪਏ ਹੋਏ ਹਨ। ਕਈ ਦੇਸ਼ ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀ ਆਪਣੀ ਮਾਨਤ ਹੱਦਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਨਹੀਂ ਮੰਨਦੇ। ਪਾਕਿਸਤਾਨ ਅਤੇ ਚੀਨ ਭਾਰਤੀ ਕਬਜ਼ੇ ਦੇ ਕਸ਼ਮੀਰ ਅਤੇ ਅਰੁਣਾਚਲ ਨੂੰ ਭਾਰਤੀ ਰਿਆਸਤ ਹੋਣ ਦੀ ਮਾਨਤਾ ਨਹੀਂ ਦਿੰਦੇ। ਇਸੇ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਭਾਰਤ ਵੀ ਪਾਕਿਸਤਾਨ ਅਤੇ ਚੀਨ ਦੇ ਕਬਜ਼ੇ ਵਾਲੇ ਕਸ਼ਮੀਰ ਅਤੇ ਅਰੁਣਾਚਲ ਨੂੰ ਉਹਨਾਂ ਦਾ ਹੋਣ ਦੀ ਮਾਨਤਾ ਨਹੀਂ ਦਿੰਦਾ।
੧੯ ੧੪ ਵਿਚ, ਬਰਤਾਨਵੀ ਭਾਰਤ ਅਤੇ ਤਿੱਬਤ ਵਿਚਕਾਰ ਮਕਮਹੋਨ ਰੇਖਾ ਨੂੰ ਭਾਰਤ ਨਾਲ ਲੱਗਦੀ ਤਿਬਤ ਦੀ ਹੱਦ ਹੋਣ ਦਾ ਕਰਾਰ ਹੋਇਆ ਸੀ, ਸ਼ਿਮਲਾ ਸੰਧੀ ਦਾ ਹਿੱਸਾ। ਤਿਬਤ ਦੀ ਵਿਸਥਾਪਤ ਸਰਕਾਰ ਇਸ ਰੇਖਾ ਨੂੰ ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀ ਤਿੱਬਤ ਨਾਲ ਲੱਗਦੀ ਹੱਦ ਮੰਨਦੀ ਹੈ। ਪਰ ਚੀਨ ਇਸ ਸੰਧੀ ਨੂੰ ਨਹੀਂ ਮੰਨਦਾ। ਸਿੱਟੇ ਵੱਜੋਂ, ਚੀਨ ਅਰੁਣਾਚਲ ਨੂੰ ਦੱਖਣੀ ਤਿੱਬਤ ਜਾਂ ਤਿੱਬਤ ਦਾ ਦੱਖਣੀ ਹਿੱਸਾ ਕਹਿੰਦਾ ਹੈ।
ਘਰੇਲੂ ਉਤਪਾਦਨ ਦਰ
[ਸੋਧੋ]ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀ ਅਕਤਸਾਦ ਵੱਧ ਰਹੀ ਹੈ। ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀ ਅਕਤਸਾਦ $੫੬੮੦੦ ਕਰੋੜ (Gross domestic product ਜਾਂ GDP) ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ਦੁਨੀਆ ਦੀ ੧੧ਵੀਂ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਵੱਡੀ ਅਕਤਸਾਦ ਹੈ। PPP ਅਨੁਸਾਰ ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀ ਅਕਤਸਾਦ ਚੌਥੇ ਸਥਾਨ 'ਤੇ ਹੈ।
ਇੱਥੇ ਜ਼ਿਕਰਯੋਗ ਹੈ ਕਿ ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀ ਬਹੁਤੀ ਅਬਾਦੀ ਗਰੀਬ ਹੈ। ੨੭.੫% ਅਬਾਦੀ ਗਰੀਬੀ ਰੇਖਾ ਤੋ ਹੇਠਾਂ ਹੈ। ੮੦.੪% ਆਬਾਦੀ ਰੋਜ਼ਾਨਾ ਦੀ $੨ ਤੋਂ ਘੱਟ ਦੀ ਕਮਾਈ ਕਰਦੀ ਹੈ।
ਸਮਾਜ
[ਸੋਧੋ]ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ੧੨੧ ਕਰੋੜ ਦੀ ਆਬਾਦੀ ਰਹਿੰਦੀ ਹੈ। ਭਾਰਤ ਅਬਾਦੀ ਦੇ ਲਿਹਾਜ਼ ਤੋਂ ਦੁਨੀਆ ਦਾ ਦੂਜਾਂ ਸਭ ਤੋ ਵੱਡਾ ਦੇਸ਼ ਹੈ। ਤਕਰੀਬਨ ੭੦% ਲੋਕ ਕਿਰਸਾਨੀ ਕਰਦੇ ਹਨ। ਇਸ ਦੇਸ਼ ਵਿੱਚ ਪੰਜਾਬੀ, ਕਸ਼ਮੀਰੀ, ਰਾਜਪੂਤ, ਦ੍ਰਵਿੜ, ਤੇਲਗੂ, ਮਰਹੱਟੇ, ਅਸਾਮੀ ਆਦਿ ਖੇਤਰ ਪੱਖ ਤੋਂ ਲੋਕ ਰਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ। ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀਆਂ ੨੩ ਕੰਮਕਾਜੀ ਬੋਲੀਆਂ ਹਨ। ਪਰ ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਕੁਲ ੧੬੨੫ ਬੋਲੀਆਂ ਤੇ ਲਹਿਜੇ ਬੋਲੇ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਹਨ।
ਸੱਭਿਆਚਾਰ
[ਸੋਧੋ]ਪੱਥਰ ਯੁੱਗ ਦੀਆਂ ਨਕਾਸ਼ੀ ਦਰ ਗੁਫ਼ਾਵਾਂ ਸਾਰੇ ਭਾਰਤ 'ਚੋ ਮਿਲਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ। ਇਹ ਨਕਾਸ਼ੀਆਂ ਉਸ ਵੇਲੇ ਦੇ ਨਾਚ ਅਤੇ ਵਿਰਸੇ ਨੂੰ ਦਰਸਾਉਂਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ ਜੋ ਆਦਿ ਧਰਮ ਦੀ ਪੁਸ਼ਟੀ ਕਰਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ। ਲਿਪਿਕ ਅਤੇ ਪੁਰਾਣਕ ਸਮੇਂ, ਰਮਾਇਣ ਅਤੇ ਮਹਾਂਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਆਦਿ ਰੂਪ ਤਕਰੀਬਨ ੫੦੦-੧੦੦ ਈਸਾ ਦੇ ਜਨਮ ਤੋਂ ਪਹਿਲਾਂ ਲਿਖੇ ਗਏ।
ਕਈ ਆਧੁਨਿਕ ਧਰਮ ਵੀ ਭਾਰਤ ਨਾਲ ਜੁੜੇ ਹੋਏ ਹਨ, ਇਹਨਾਂ ਦੇ ਨਾਂ ਹਨ: ਹਿੰਦੂ ਧਰਮ, ਜੈਨ ਧਰਮ, ਬੁੱਧ ਧਰਮ ਅਤੇ ਸਿੱਖ ਧਰਮ। ਇਹਨਾਂ ਸਾਰੇ ਧਰਮਾਂ ਕੋਲ ਅਲੱਗ ਵਿਰਾਸਤਾਂ ਅਤੇ ਮਾਨਤਾਵਾਂ ਹਨ। ਇਹਨਾਂ ਧਰਮਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਪੂਰਬੀ ਧਰਮ ਕਿਹਾ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ। ਇਹਨਾਂ ਧਰਮਾਂ ਦੀ ਵਿਚਾਰਧਾਰਾਵਾਂ ਦਾ ਕੁਝ ਹਿੱਸਾ ਆਪਸ 'ਚ ਮੇਲ ਖਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ, ਜਿਸ ਤੋਂ ਇਹ ਪਤਾ ਲਗਦਾ ਹੈ ਕਿ ਇਹਨਾਂ ਧਰਮਾਂ ਦਾ ਪਿਛੋਕੜ ਇੱਕੋ ਹੀ ਹੈ ਅਤੇ ਇਹਨਾਂ ਨੇ ਇੱਕ ਦੂਜੇ ਨੂੰ ਵੱਡੇ ਪੱਧਰ ਤੇ ਪ੍ਰਭਾਵਿਤ ਕੀਤਾ ਹੈ।
ਹਿੰਦੂ ਧਰਮ ਭਾਰਤ ਦਾ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਵੱਡਾ ਧਰਮ ਹੈ; ਇਸਲਾਮ ਦੇ ੧੨.੮ %; ਇਸਾਈਅਤ ਦੇ ੨.੯ %; ਸਿੱਖ ਧਰਮ ਦੇ ੧.੯ %; ਬੁੱਧ ਧਰਨ ਦੇ ੦.੮ % ਅਤੇ ਜੈਨ ਧਰਮ ਦੇ ੦.੪ % ਲੋਕ ਧਾਰਨੀ ਹਨ।
ਅਬਾਦੀ ਅੰਕੜੇ
[ਸੋਧੋ]ਹਿੰਦੂ ਧਰਮ ਭਾਰਤ ਦਾ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਬਡਾ ਧਰਮ ਹੈ - ਇਸ ਚਿੱਤਰ ਵਿੱਚ ਗੋਆ ਦਾ ਇੱਕ ਮੰਦਿਰ ਵਿਖਾਇਆ ਗਿਆ ਹੈ ਭਾਰਤ ਚੀਨ ਦੇ ਬਾਅਦ ਸੰਸਾਰ ਦਾ ਦੂਜਾ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਜਿਆਦਾ ਜਨਸੰਖਿਆ ਵਾਲਾ ਦੇਸ਼ ਹੈ। ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀਆਂਵਿਭਿੰਨਤਾਵਾਂਵਲੋਂ ਭਰੀ ਜਨਤਾ ਵਿੱਚ ਭਾਸ਼ਾ, ਜਾਤੀ ਅਤੇ ਧਰਮ, ਸਮਾਜਕ ਅਤੇ ਰਾਜਨੀਤਕ ਸੌਹਾਰਦਰ ਅਤੇ ਸਮਰਸਤਾ ਦੇ ਮੁੱਖ ਵੈਰੀ ਹਨ।
ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ੬੪ . ੮ ਫ਼ੀਸਦੀ ਸਾਕਸ਼ਰਤਾ ਹੈ ਜਿਸ ਵਿੱਚੋਂ ੭੫ . ੩ % ਪੁਰਖ ਅਤੇ ੫੩ . ੭ % ਔਰਤਾਂ ਸਾਕਸ਼ਰ ਹਨ। ਲਿੰਗ ਅਨਪਾਤ ਦੀ ਨਜ਼ਰ ਵਲੋਂ ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਹਰ ਇੱਕ ੧੦੦੦ ਪੁਰਸ਼ਾਂ ਦੇ ਪਿੱਛੇ ਸਿਰਫ ੯੩੩ ਔਰਤਾਂ ਹਨ। ਕਾਰਜ ਭਾਗੀਦਾਰੀ ਦਰ (ਕੁਲ ਜਨਸੰਖਿਆ ਵਿੱਚ ਕਾਰਜ ਕਰਣ ਵਾਲੀਆਂ ਦਾ ਭਾਗ) ੩੯ . ੧ % ਹੈ। ਪੁਰਸ਼ਾਂ ਲਈ ਇਹ ਦਰ ੫੧ . ੭ % ਅਤੇ ਸਤਰੀਆਂ ਲਈ ੨੫ . ੬ % ਹੈ। ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀ ੧੦੦੦ ਜਨਸੰਖਿਆ ਵਿੱਚ ੨੨ . ੩੨ ਜਨਮਾਂ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ਵੱਧਦੀ ਜਨਸੰਖਿਆ ਦੇ ਅੱਧੇ ਲੋਕ ੨੨ . ੬੬ ਸਾਲ ਵਲੋਂ ਘੱਟ ਉਮਰ ਦੇ ਹਨ। ਹਾਲਾਂਕਿ ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀ ੮੦ . ੫ ਫ਼ੀਸਦੀ ਜਨਸੰਖਿਆ ਹਿੰਦੂ ਹੈ, ੧੩ . ੪ ਫ਼ੀਸਦੀ ਜਨਸੰਖਿਆ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ਭਾਰਤ ਸੰਸਾਰ ਵਿੱਚ ਮੁਸਲਮਾਨਾਂ ਦੀ ਗਿਣਤੀ ਵਿੱਚ ਵੀ ਇੰਡੋਨੇਸ਼ਿਆ ਅਤੇ ਪਾਕਿਸਤਾਨ ਦੇ ਬਾਅਦ ਤੀਸਰੇ ਸਥਾਨ ਉੱਤੇ ਹੈ। ਹੋਰ ਧਰਮਾਵਲੰਬੀਆਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਈਸਾਈ (੨ . ੩੩ %), ਸਿੱਖ (੧ . ੮੪ %), ਬੋਧੀ (੦ . ੭੬ %), ਜੈਨ (੦ . ੪੦ %), ਅਇਯਾਵਲਿ (੦ . ੧੨ %), ਯਹੂਦੀ, ਪਾਰਸੀ, ਅਹਮਦੀ ਅਤੇ ਬਹਾਈ ਆਦਿ ਸਮਿੱਲਤ ਹਨ।
ਭਾਰਤ ਦੋ ਮੁੱਖ ਭਾਸ਼ਾ - ਸੂਤਰਾਂ: ਆਰਿਆ ਅਤੇ ਦਰਵਿੜਭਾਸ਼ਾਵਾਂਦਾ ਸਰੋਤ ਵੀ ਹੈ। ਭਾਰਤ ਦਾ ਸੰਵਿਧਾਨ ਕੁਲ ੨੩ਭਾਸ਼ਾਵਾਂਨੂੰ ਮਾਨਤਾ ਦਿੰਦਾ ਹੈ। ਹਿੰਦੀ ਅਤੇ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਕੇਂਦਰੀ ਸਰਕਾਰ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਸਰਕਾਰੀ ਕੰਮਧੰਦਾ ਲਈ ਵਰਤੋ ਦੀ ਜਾਂਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ . ਸੰਸਕ੍ਰਿਤ ਅਤੇ ਤਮਿਲ ਵਰਗੀ ਅਤਿ ਪ੍ਰਾਚੀਨ ਭਾਸ਼ਾਵਾਂ ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਹੀ ਜੰਮੀ ਹਨ। ਸੰਸਕ੍ਰਿਤ, ਸੰਸਾਰ ਦੀ ਸਬਤੋਂ ਜਿਆਦਾ ਪ੍ਰਾਚੀਨਭਾਸ਼ਾਵਾਂਵਿੱਚੋਂ ਇੱਕ ਹੈ, ਜਿਸਦਾ ਵਿਕਾਸ ਪਥਿਆਸਵਸਤੀ ਨਾਮ ਦੀ ਅਤਿ ਪ੍ਰਾਚੀਨ ਭਾਸ਼ਾ / ਬੋਲੀ ਵਲੋਂ ਹੋਇਆ ਸੀ . ਤਮਿਲ ਦੇ ਇਲਾਵਾ ਸਾਰੀ ਭਾਰਤੀਭਾਸ਼ਾਵਾਂਸੰਸਕ੍ਰਿਤ ਵਲੋਂ ਹੀ ਵਿਕਸਿਤ ਹੋਈਆਂ ਹਨ, ਹਾਲਾਂਕਿ ਸੰਸਕ੍ਰਿਤ ਅਤੇ ਤਮਿਲ ਵਿੱਚ ਕਈ ਸ਼ਬਦ ਸਮਾਨ ਹਨ ! ਕੁਲ ਮਿਲਿਆ ਕਰ ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ੧੬੫੨ ਵਲੋਂ ਵੀ ਜਿਆਦਾ ਭਾਸ਼ਾਵਾਂ ਅਤੇ ਬੋਲੀਆਂ ਬੋਲੀ ਜਾਤੀਂ ਹਨ।
ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰ ਦੇ ਰੂਪ ਵਿੱਚ ਉਠਾਅ
[ਸੋਧੋ]ਭਾਰਤ ਨੂੰ ਇੱਕ ਸਨਾਤਨ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰ ਮੰਨਿਆ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ਕਿਉਂਕਿ ਇਹ ਮਨੁੱਖ-ਸੱਭਿਅਤਾ ਦਾ ਪਹਿਲਾ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰ ਸੀ। ਸ੍ਰੀਮਦਭਗਵਤ ਦੇ ਪੰਚਮ ਸਕੰਧ ਵਿੱਚ ਭਾਰਤ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰ ਦੀ ਸਥਾਪਨਾ ਦਾ ਵਰਣਨ ਆਉਂਦਾ ਹੈ।
ਭਾਰਤੀ ਦਰਸ਼ਨ ਦੇ ਅਨੁਸਾਰ ਸ੍ਰਿਸ਼ਟੀ ਉਤਪਤੀ ਦੇ ਬਾਅਦ ਬ੍ਰਹਮਾ ਦੇ ਮਾਨਸ ਪੁੱਤ ਸਵੰਭੂ ਮਨੂੰ ਨੇ ਵਿਵਸਥਾ ਸੰਭਾਲੀ। ਇਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੇ ਦੋ ਪੁੱਤ, ਪ੍ਰਿਅਵਰਤ ਅਤੇ ਉੱਤਾਨਪਾਦ ਸਨ। ਉੱਤਾਨਪਾਦ ਭਗਤ ਧਰੁਵ ਦਾ ਪਿਤ ਸੀ। ਪ੍ਰਿਅਵਰਤ ਦੇ ਦਸ ਪੁੱਤ ਸਨ। ਤਿੰਨ ਪੁੱਤ ਬਾਲਪਨ ਤੋਂ ਹੀ ਉਦਾਸੀਨ ਸਨ। ਇਸ ਕਰਕੇ ਪ੍ਰਿਅਵਰਤ ਨੇ ਧਰਤੀ ਨੂੰ ਸੱਤ ਹਿੱਸਿਆਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਵੰਡ ਕੇ ਇੱਕ-ਇੱਕ ਹਿੱਸਾ ਹਰ ਇੱਕ ਪੁੱਤ ਨੂੰ ਸੌਂਪ ਦਿੱਤਾ। ਇਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਵਿੱਚੋਂ ਇੱਕ ਸੀ ਅਗਨੀਧਰ ਜਿਸ ਨੂੰ ਜੰਬੂਦੀਪ ਦਾ ਸ਼ਾਸਨ ਸਪੁਰਦ ਕੀਤਾ ਗਿਆ। ਬੁਢੇਪੇ ਵਿੱਚ ਅਗਨੀਧਰ ਨੇ ਆਪਣੇ ਨੌਂ ਪੁੱਤਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਜੰਬੂਦੀਪ ਦੇ ਨੌਂ ਵੱਖਰੇ ਸਥਾਨਾਂ ਦਾ ਸ਼ਾਸਨ ਸੰਭਲਿਆ। ਇਹਨਾਂ ਨੌਂ ਪੁੱਤਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਵੱਡਾ ਸੀ ਧੁੰਨੀ ਜਿਸ ਨੂੰ ਹਿਮਵਰਸ਼ ਦਾ ਧਰਤੀ-ਭਾਗ ਮਿਲਿਆ। ਇਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੇ ਹਿਮਵਰਸ਼ ਨੂੰ ਆਪ ਦੇ ਨਾਮ ਅਜਨਾਭ ਨਾਲ ਜੋੜ ਕੇ ਅਜਨਾਭਵਰਸ਼ ਦਾ ਫੈਲਾਅ ਕੀਤਾ। ਇਹ ਹਿਮਵਰਸ਼ ਜਾਂ ਅਜਨਾਭਵਰਸ਼ ਹੀ ਪ੍ਰਾਚੀਨ ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇਸ਼ ਸੀ। ਰਾਜਾ ਧੁੰਨੀ ਦੇ ਪੁੱਤ ਸਨ ਰਿਸ਼ਭ। ਰਿਸ਼ਭਦੇਵ ਦੇ ਸੌ ਪੁੱਤਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਭਰਤ ਜੇਠੇ ਅਤੇ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਗੁਣਵਾਨ ਸਨ। ਰਿਸ਼ਭਦੇਵ ਨੇ ਬਾਣਪ੍ਰਸਥ ਲੈਣ ਤੇ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਰਾਜਪਾਟ ਸੌਂਪ ਦਿੱਤਾ। ਪਹਿਲਾਂ ਹਿੰਦੁਸਤਾਨ ਦਾ ਨਾਮ ਰਿਸ਼ਭਦੇਵ ਦੇ ਪਿਤਾ ਨਾਭਰਾਜ ਦੇ ਨਾਮ ਤੇ ਅਜਨਾਭਵਰਸ਼ ਪ੍ਰਸਿੱਧ ਸੀ। ਭਰਤ ਦੇ ਨਾਮ ਤੋਂ ਹੀ ਲੋਕ ਅਜਨਾਭਖੰਡ ਨੂੰ ਹਿੰਦੁਸਤਾਨ ਕਹਿਣ ਲੱਗੇ।
ਫੌਜੀ ਤਾਕਤ
[ਸੋਧੋ]੧੯੪੭ ਵਿੱਚ ਆਪਣੀ ਆਜ਼ਾਦੀ ਦੇ ਬਾਅਦ ਵਲੋਂ, ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਜਿਆਦਾਤਰ ਦੇਸ਼ਾਂ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ਸੌਹਾਰਦਪੂਰਣ ਸੰਬੰਧ ਬਣਾਇ ਰੱਖਿਆ ਹੈ। ੧੯੫੦ ਦੇ ਦਹਾਕੇ ਵਿੱਚ, ਇਹ ਮਜ਼ਬੂਤੀ ਵਲੋਂ ਅਫਰੀਕਾ ਅਤੇ ਏਸ਼ਿਆ ਵਿੱਚ ਯੂਰਪੀ ਕਲੋਨੀਆਂ ਦੀ ਆਜ਼ਾਦੀ ਦਾ ਸਮਰਥਨ ਕੀਤਾ ਅਤੇ ਗੁਟ-ਨਿਰਲੇਪ ਅੰਦੋਲਨ ਵਿੱਚ ਇੱਕ ਆਗੂ ਭੂਮਿਕਾ ਨਿਭਾਈ। ੧੯੮੦ ਦੇ ਦਹਾਕੇ ਵਿੱਚ ਭਾਰਤ ਗੁਆਂਢੀ ਦੇ ਸੱਦੇ ਉੱਤੇ ਦੋ ਦੇਸ਼ਾਂ ਸੰਖਿਪਤ ਫੌਜੀ ਹਸਤੱਕਖੇਪ ਕੀਤਾ, ਮਾਲਦੀਵ, ਸ਼੍ਰੀਲੰਕਾ ਅਤੇ ਹੋਰ ਦੇਸ਼ਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਆਪਰੇਸ਼ਨ ਥੋਹਰ ਵਿੱਚ ਭਾਰਤੀ ਸ਼ਾਂਤੀ ਫੌਜ ਭੇਜਿਆ। ਹਾਲਾਂਕਿ, ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਗੁਆਂਢੀ ਦੇਸ਼ ਪਾਕਿਸਤਾਨ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ਇੱਕ ਤਨਾਵ ਸੰਬੰਧ ਪਿਆ ਰਿਹਾ, ਅਤੇ ਦੋਨਾਂ ਦੇਸ਼ ਚਾਰ ਵਾਰ ਯੁਧਦਰ (੧੯੪੭, ੧੯੬੫, ੧੯੭੧ ਅਤੇ ੧੯੯੯ ਵਿੱਚ) ਲਈ ਚਲਾ ਹੈ। ਕਸ਼ਮੀਰ ਵਿਵਾਦ ਇਸ ਯੁੱਧਾਂ ਦੇ ਪ੍ਰਮੁੱਖ ਕਾਰਨ ਸੀ, ੧੯੭੧ ਨੂੰ ਛੱਡਕੇ ਜੋ ਤਤਕਾਲੀਨ ਪੂਰਵੀ ਪਾਕਿਸਤਾਨ ਵਿੱਚ ਨਾਗਰਿਕ ਅਸ਼ਾਂਤਿ ਲਈ ਕੀਤਾ ਗਿਆ ਸੀ। ੧੯੬੨ ਦੇ ਭਾਰਤ - ਚੀਨ ਲੜਾਈ ਅਤੇ ਪਾਕਿਸਤਾਨ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ੧੯੬੫ ਦੇ ਲੜਾਈ ਦੇ ਬਾਅਦ ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਕਰੀਬ ਫੌਜੀ ਅਤੇ ਆਰਥਕ ਵਿਕਾਸ ਦਿੱਤੀ। ਸੋਵਿਅਤ ਸੰਘ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ਸਬੰਧਾਂ, ਸੰਨ ੧੯੬੦ ਦੇ ਦਸ਼ਕ ਵਲੋਂ, ਸੋਵਿਅਤ ਸੰਘ ਭਾਰਤ ਦਾ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਬਹੁਤ ਹਥਿਆਰ ਆਪੂਰਤੀਕਰਤਾ ਦੇ ਰੂਪ ਵਿੱਚ ਉਭਰੀ ਸੀ।
ਅੱਜ ਰੂਸ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ਸਾਮਰਿਕ ਸਬੰਧਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਜਾਰੀ ਰੱਖਣ ਦੇ ਇਲਾਵਾ, ਭਾਰਤ ਫੈਲਿਆ ਇਜਰਾਇਲ ਅਤੇ ਫ਼ਰਾਂਸ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ਰੱਖਿਆ ਸੰਬੰਧ ਰੱਖਿਆ ਹੈ। ਹਾਲ ਦੇ ਸਾਲਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ, ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਖੇਤਰੀ ਸਹਿਯੋਗ ਅਤੇ ਸੰਸਾਰ ਵਪਾਰ ਸੰਗਠਨ ਲਈ ਇੱਕ ਦੱਖਣ ਏਸ਼ੀਆਈ ਏਸੋਸਿਏਸ਼ਨ ਵਿੱਚ ਪ੍ਰਭਾਵਸ਼ਾਲੀ ਭੂਮਿਕਾ ਨਿਭਾਈ ਹੈ। ੧੦, ੦੦੦ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰ ਫੌਜੀ ਅਤੇ ਪੁਲਿਸ ਕਰਮੀਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਚਾਰ ਮਹਾਂਦੀਪਾਂ ਭਰ ਵਿੱਚ ਪੈਂਤੀ ਸੰਯੁਕਤ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰ ਸ਼ਾਂਤੀ ਅਭਿਆਨਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਸੇਵਾ ਪ੍ਰਦਾਨ ਕੀਤੀ ਹੈ। ਭਾਰਤ ਵੀ ਵੱਖਰਾ ਬਹੁਪਕਸ਼ੀਏ ਮੰਚਾਂ, ਖਾਸਕਰ ਪੂਰਵੀ ਏਸ਼ਿਆ ਸਿਖਰ ਬੈਠਕ ਅਤੇ G – ੮੫ ਬੈਠਕ ਵਿੱਚ ਇੱਕ ਸਰਗਰਮ ਭਾਗੀਦਾਰ ਰਿਹਾ ਹੈ। ਆਰਥਕ ਖੇਤਰ ਵਿੱਚ ਭਾਰਤ ਦੱਖਣ ਅਮਰੀਕਾ, ਅਫਰੀਕਾ ਅਤੇ ਏਸ਼ਿਆ ਦੇ ਵਿਕਾਸਸ਼ੀਲ ਦੇਸ਼ਾਂ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ਘਨਿਸ਼ਠ ਸੰਬੰਧ ਰੱਖਦੇ ਹੈ। ਹੁਣ ਭਾਰਤ ਇੱਕ ਪੂਰਵ ਦੇ ਵੱਲ ਵੇਖੋ ਨੀਤੀ ਵਿੱਚ ਵੀ ਸੰਜੋਗ ਕੀਤਾ ਹੈ। ਇਹ ਆਸਿਆਨ ਦੇਸ਼ਾਂ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ਆਪਣੀ ਭਾਗੀਦਾਰੀ ਨੂੰ ਮਜ਼ਬੂਤ ਬਣਾਉਣ ਦੇ ਮੁੱਦੀਆਂ ਦੀ ਇੱਕ ਫੈਲਿਆ ਲੜੀ ਹੈ ਜਿਸ ਵਿੱਚ ਜਾਪਾਨ ਅਤੇ ਦੱਖਣ ਕੋਰੀਆ ਨੇ ਵੀ ਮਦਦ ਕੀਤਾ ਹੈ। ਇਹ ਵਿਸ਼ੇਸ਼ ਰੂਪ ਵਲੋਂ ਆਰਥਕ ਨਿਵੇਸ਼ ਅਤੇ ਖੇਤਰੀ ਸੁਰੱਖਿਆ ਦੀ ਕੋਸ਼ਿਸ਼ ਹੈ।
੧੯੭੪ ਵਿੱਚ ਭਾਰਤ ਆਪਣੀ ਪਹਿਲੀ ਪਰਮਾਣੁ ਹਥਿਆਰਾਂ ਦਾ ਪ੍ਰੀਖਿਆ ਕੀਤਾ ਅਤੇ ਅੱਗੇ ੧੯੯੮ ਵਿੱਚ ਭੂਮੀਗਤ ਪ੍ਰੀਖਿਆ ਕੀਤਾ। ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਕੋਲ ਹੁਣ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ – ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੇ ਪਰਮਾਣੁ ਹਥਿਆਰਾਂ ਹੈ। ਭਾਰਤ ਹੁਣੇ ਰੂਸ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ਮਿਲ ਕੇ ਪੰਜਵੀਂ ਪੀੜ ਦੇ ਜਹਾਜ਼ ਬਣਾ ਰਹੇ ਹੈ।
ਹਾਲ ਹੀ ਵਿੱਚ, ਭਾਰਤ ਦਾ ਸੰਯੁਕਤ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੇ ਅਮਰੀਕਾ ਅਤੇ ਯੂਰੋਪੀ ਸੰਘ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ਆਰਥਕ, ਸਾਮਰਿਕ ਅਤੇ ਫੌਜੀ ਸਹਿਯੋਗ ਵੱਧ ਗਿਆ ਹੈ। ੨੦੦੮ ਵਿੱਚ, ਭਾਰਤ ਅਤੇ ਸੰਯੁਕਤ ਰਾਜ ਅਮਰੀਕਾ ਦੇ ਵਿੱਚ ਗ਼ੈਰ ਫ਼ੌਜੀ ਪਰਮਾਣੁ ਸਮੱਝੌਤੇ ਹਸਤਾਖਰ ਕੀਤੇ ਗਏ ਸਨ। ਹਾਲਾਂਕਿ ਉਸ ਸਮੇਂ ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਕੋਲ ਪਰਮਾਣੁ ਹਥਿਆਰ ਸੀ ਅਤੇ ਪਰਮਾਣੁ ਅਪ੍ਰਸਾਰ ਸੁਲਾਹ (ਏਨਪੀਟੀ) ਦੇ ਪੱਖ ਵਿੱਚ ਨਹੀਂ ਸੀ ਇਹ ਅੰਤਰਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਪਰਮਾਣੁ ਊਰਜਾ ਏਜੰਸੀ ਅਤੇ ਨਿਊਕਲਿਅਰ ਸਪਲਾਇਰਸ ਗਰੁਪ (ਏਨਏਸਜੀ) ਵਲੋਂ ਛੁੱਟ ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤ ਹੈ, ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀ ਪਰਮਾਣੁ ਤਕਨੀਕੀ ਅਤੇ ਵਣਜ ਉੱਤੇ ਪਹਿਲਾਂ ਰੋਕ ਖ਼ਤਮ . ਭਾਰਤ ਸੰਸਾਰ ਦਾ ਛੇਵਾਂ ਅਸਲੀ ਪਰਮਾਣੁ ਹਥਿਆਰ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰਤ ਬੰਨ ਗਿਆ ਹੈ। ਏਨਏਸਜੀ ਛੁੱਟ ਦੇ ਬਾਅਦ ਭਾਰਤ ਵੀ ਰੂਸ, ਫ਼ਰਾਂਸ, ਯੂਨਾਇਟੇਡ ਕਿੰਗਡਮ, ਅਤੇ ਕਨਾਡਾ ਸਹਿਤ ਦੇਸ਼ਾਂ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ਗ਼ੈਰ ਫ਼ੌਜੀ ਪਰਮਾਣੁ ਊਰਜਾ ਸਹਿਯੋਗ ਸਮੱਝੌਤੇ ਉੱਤੇ ਹਸਤਾਖਰ ਕਰਣ ਵਿੱਚ ਸਮਰੱਥਾਵਾਨ ਹੈ।
ਲਗਭਗ ੧ . ੩ ਮਿਲਿਅਨ ਸਰਗਰਮ ਸੈਨਿਕਾਂ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ, ਭਾਰਤੀ ਫੌਜ ਦੁਨੀਆ ਵਿੱਚ ਤੀਜਾ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਬਹੁਤ ਹੈ। ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀ ਸ਼ਸਤਰਬੰਦ ਫੌਜ ਵਿੱਚ ਇੱਕ ਭਾਰਤੀ ਫੌਜ, ਨੌਸੇਨਾ, ਹਵਾ ਫੌਜ, ਅਤੇ ਅਰੱਧਸੈਨਿਕ ਜੋਰ, ਤਟਰਕਸ਼ਕ, ਅਤੇ ਸਾਮਰਿਕ ਜਿਵੇਂ ਸਹਾਇਕ ਜੋਰ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ। ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰਪਤੀ ਭਾਰਤੀ ਸ਼ਸਤਰਬੰਦ ਬਲਾਂ ਦੇ ਸਰਵੋੱਚ ਕਮਾਂਡਰ ਹੈ। ਸਾਲ ੨੦੧੧ ਵਿੱਚ ਭਾਰਤੀ ਰੱਖਿਆ ਬਜਟ ੩੬ . ੦੩ ਅਰਬ ਅਮਰਿਕੀ ਡਾਲਰ ਰਿਹਾ (ਜਾਂ ਸਕਲ ਘਰੇਲੂ ਉਤਪਾਦ ਦਾ ੧ . ੮੩ %)। ੨੦੦੮ ਦੇ ਇੱਕ SIPRI ਰਿਪੋਰਟ ਦੇ ਅਨੁਸਾਰ, ਭਾਰਤ ਖਰੀਦ ਸ਼ਕਤੀ ਦੇ ਮਾਮਲੇ ਵਿੱਚ ਭਰਤੀਏ ਫੌਜ ਦੇ ਫੌਜੀ ਖਰਚ ੭੨ . ੭ ਅਰਬ ਅਮਰੀਕੀ ਡਾਲਰ ਰਿਹਾ। ਸਾਲ 2011 ਵਿੱਚ ਭਾਰਤੀ ਰੱਖਿਆ ਮੰਤਰਾਲਾ ਦੇ ਵਾਰਸ਼ਿਕ ਰੱਖਿਆ ਬਜਟ ਵਿੱਚ ੧੧ . ੬ ਫ਼ੀਸਦੀ ਦਾ ਵਾਧਾ ਹੋਇਆ, ਹਾਲਾਂਕਿ ਇਹ ਪੈਸਾ ਸਰਕਾਰ ਦੀ ਹੋਰਸ਼ਾਖਾਵਾਂਦੇ ਮਾਧਿਅਮ ਵਲੋਂ ਫੌਜੀ ਦੇ ਵੱਲ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਹੋਏ ਪੈਸੀਆਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਸ਼ਮਿਲ ਨਹੀਂ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ। ਭਾਰਤ ਦੁਨੀਆ ਦੇ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਵੱਡੇ ਹਥਿਆਰ ਆਯਾਤਕ ਬੰਨ ਗਿਆ ਹੈ।
ਸਮੱਸਿਆਵਾਂ
[ਸੋਧੋ]ਅੰਦਰੂਨੀ ਸਮੱਸਿਆਵਾਂ
[ਸੋਧੋ]- ਅੱਤਵਾਦ – ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਡਰ ਤੇ ਦਹਿਸ਼ਤ ਦਾ ਮਹੌਲ ਕਾਇਮ ਕਰਨ ਲਈ ਕਈ ਅੱਤਵਾਦੀ ਸਮੂਹ ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿਰੋਧੀ ਕਾਰਵਾਈਆਂ ਕਰਦੇ ਰਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ ਜਿਸ ਕਾਰਨ ਦੇਸ਼ ਦਾ ਕਾਫੀ ਜਾਨੀ ਅਤੇ ਮਾਲੀ ਨੁਕਸਾਨ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ। ਅੱਤਵਾਦੀਆਂ ਨੇ ਭਾਰਤ ਦੀ ਸੰਸਦ, ਤਾਜ ਹੋਟਲ, ਕਸ਼ਮੀਰ, ਪਠਾਨਕੋਟ ਏਅਰਬੇਸ ਸਮੇਤ ਹੋਰ ਵੀ ਕਈ ਅਜਿਮ ਜਗ੍ਹਾਹਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਨਿਸ਼ਾਨਾ ਬਣਾ ਦਹਿਸ਼ਤ ਫੈਲਾਉਣ ਦੀ ਕੋਸ਼ਿਸ਼ ਕੀਤੀ ਹੈ।
- ਨਕਸਲਵਾਦ
- ਨਸ਼ੇ – ਦੇਸ਼ਾਂ-ਵਿਦੇਸ਼ਾਂ 'ਚੋਂ ਹੋ ਰਹੀ ਨਸ਼ਾ ਤਸਕਰੀ ਕਾਰਨ ਕਾਫੀ ਤੇਜ਼ੀ ਨਾਲ ਨਸ਼ਾ ਕਰਨ ਵਾਲਿਆਂ ਦੀ ਗਿਣਤੀ ਵਧੀ ਹੈ। ਸਰਹੱਦੀ ਇਲਾਕਿਆਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਇਹ ਸਮੱਸਿਆ ਕਾਫੀ ਗੰਭੀਰ ਹੈ।
ਬਾਹਰੀ ਸਮੱਸਿਆਵਾਂ
[ਸੋਧੋ]- ਕਸ਼ਮੀਰ ਮੁੱਦਾ – ਕਸ਼ਮੀਰ ਦੇ ਝਗੜੇ ਕਾਰਨ ਭਾਰਤ ਪਾਕਿਸਤਾਨ ਦੇ ਸਬੰਧ ਹਮੇਸ਼ਾ ਤੋ ਹੀ ਉਲਝੇ ਅਤੇ ਤਣਾਅਪੂਰਣ ਰਹੇ ਹਨ। ਕਦੇ ਪਾਣੀ ਦੀ ਵੰਡ, ਕਦੇ ਕਰਜੇ ਦੀ ਵੰਡ ਤੇ ਕਦੇ ਕਸ਼ਮੀਰੀ ਲੋਕਾਂ ਦੀਆਂ ਜਾਇਦਾਦਾਂ ਦੀ ਵੰਡ ਕਾਰਨ ਮਤਭੇਦ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੀ ਰਹਿੰਦਾ ਹੈ। ਸੰਨ 1947-48 ਦੌਰਾਨ ਪਾਕਿਸਤਾਨ ਨੇ ਹਜ਼ਾਰਾਂ ਚੀਨੀਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਪਾਕਿਸਤਾਨੀ ਬਣਾ ਕੇ ਘੁਸਪੈਠ ਕਰਵਾਈ ਗਈ। 1999 ਵਿੱਚ ਪਾਕਿਸਤਾਨ ਨੇ ਅਫ਼ਗਾਨ ਗੁਜਬਦੀਨ ਪਾਕ ਸੈਨਿਕਾਂ ਅਤੇ ਸਿੱਖਿਅਤ ਕਸ਼ਮੀਰੀ ਅੱਤਵਾਦੀਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਭੇਜ ਕੇ ਕਾਰਗਿਲ 'ਤੇ ਕਬਜ਼ਾ ਕਰ ਲਿਆ ਜੋ ਕਿ ਬਾਅਦ ਵਿੱਚ ਭਾਰਤੀ ਸੈਨਾ ਨੇ ਫ਼ਿਰ ਆਪਣੇ ਕਬਜੇ ਹੇਠ ਕਰ ਲਿਆ। ਪਾਕਿਸਤਾਨ ਸ਼ੁਰੂ ਤੋਂ ਹਈ ਕਸ਼ਮੀਰ 'ਤੇ ਆਪਣਾ ਹੱਕ ਜਤਾਉਂਦਾ ਹੈ। ਇਸੇ ਕਰਕੇ ਭਾਰਤ-ਪਾਕਿਸਤਾਨ ਵਿੱਚ ਆਪਸੀ ਮਤਭੇਦ ਹੈ। ਇਸ ਮੁੱਦੇ ਦੇ ਹੱਲ ਲਈ 1950 ਵਿੱਚ ਨਹਿਰੂ-ਲਿਆਕਤ ਅਲੀ ਸਮਝੌਤਾ ਵੀ ਹੋਇਆ ਸੀ। ਹੁਣ ਇਸ ਮਾਮਲੇ ਸਬੰਧੀ ਯੂ.ਐਨ.ਓ ਨੂੰ ਦਰਖ਼ਾਸਤ ਕੀਤੀ ਗਈ ਹੈ।
ਨੋਟ
[ਸੋਧੋ]- ↑ "[...] ਜਨ ਗਣ ਮਨ ਭਾਰਤ ਦਾ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਗੀਤ ਹੈ, ਜੋ ਕਿ ਮੌਕੇ ਦੇ ਆਉਣ 'ਤੇ ਸਰਕਾਰ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਅਧਿਕਾਰਤ ਸ਼ਬਦਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਅਜਿਹੇ ਬਦਲਾਅ ਦੇ ਅਧੀਨ ਹੈ; ਅਤੇ ਗੀਤ ਵੰਦੇ ਮਾਤਰਮ, ਜਿਸ ਨੇ ਭਾਰਤੀ ਆਜ਼ਾਦੀ ਦੇ ਸੰਘਰਸ਼ ਵਿਚ ਇਤਿਹਾਸਕ ਭੂਮਿਕਾ ਨਿਭਾਈ ਹੈ, ਨੂੰ ਜਨ ਗਣ ਮਨ ਨਾਲ ਬਰਾਬਰ ਸਨਮਾਨ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਜਾਵੇਗਾ ਅਤੇ ਇਸ ਦੇ ਬਰਾਬਰ ਦਰਜਾ ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤ ਹੋਵੇਗਾ।[5]
- ↑ ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਸੰਵਿਧਾਨ ਦੇ ਭਾਗ XVII ਦੇ ਅਨੁਸਾਰ, ਦੇਵਨਾਗਰੀ ਲਿਪੀ ਵਿੱਚ ਹਿੰਦੀ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਇੱਕ ਵਾਧੂ ਭਾਸ਼ਾ ਵਜੋਂ ਸੰਘ ਦੀ ਸਰਕਾਰੀ ਭਾਸ਼ਾ ਹੈ। ।[1][6][7] ਰਾਜ ਅਤੇ ਕੇਂਦਰ ਸ਼ਾਸਿਤ ਪ੍ਰਦੇਸ਼ ਦੀ ਹਿੰਦੀ ਜਾਂ ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ ਤੋਂ ਇਲਾਵਾ ਆਪਣੀ ਵੱਖਰੀ ਸਰਕਾਰੀ ਭਾਸ਼ਾ ਹੋ ਸਕਦੀ ਹੈ।
- ↑ Different sources give widely differing figures, primarily based on how the terms "language" and "dialect" are defined and grouped. Ethnologue lists 461 tongues for India (out of 6,912 worldwide), 447 of which are living, while 14 are extinct.[13][14]
- ↑ "ਦੇਸ਼ ਦਾ ਸਹੀ ਆਕਾਰ ਬਹਿਸ ਦਾ ਵਿਸ਼ਾ ਹੈ ਕਿਉਂਕਿ ਕੁਝ ਸਰਹੱਦਾਂ ਵਿਵਾਦਿਤ ਹਨ। ਭਾਰਤ ਸਰਕਾਰ ਕੁੱਲ ਖੇਤਰ ਨੂੰ ਇਸ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਸੂਚੀਬੱਧ ਕਰਦੀ ਹੈ 3,287,260 km2 (1,269,220 sq mi) ਅਤੇ ਕੁੱਲ ਜ਼ਮੀਨੀ ਖੇਤਰ 3,060,500 km2 (1,181,700 sq mi); ਸੰਯੁਕਤ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰ ਕੁੱਲ ਖੇਤਰ ਨੂੰ ਇਸ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਸੂਚੀਬੱਧ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ 3,287,263 km2 (1,269,219 sq mi) ਅਤੇ ਕੁੱਲ ਜ਼ਮੀਨੀ ਖੇਤਰ 2,973,190 km2 (1,147,960 sq mi)."[16]
- ↑ ਦੇਖੋ ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਮਿਤੀ ਅਤੇ ਸਮਾਂ ਸੰਕੇਤ
- ↑ The Government of India also regards Afghanistan as a bordering country, as it considers all of Kashmir to be part of India. However, this is disputed, and the region bordering Afghanistan is administered by Pakistan. Source: "Ministry of Home Affairs (Department of Border Management)" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 March 2015. Retrieved 1 September 2008.
- ↑ "A Chinese pilgrim also recorded evidence of the caste system as he could observe it. According to this evidence the treatment meted out to untouchables such as the Chandalas was very similar to that which they experienced in later periods. This would contradict assertions that this rigid form of the caste system emerged in India only as a reaction to the Islamic conquest."[45]
- ↑ "Shah Jahan eventually sent her body 800 km (500 mi) to Agra for burial in the Rauza-i Munauwara ("Illuminated Tomb") – a personal tribute and a stone manifestation of his imperial power. This tomb has been celebrated globally as the Taj Mahal."[53]
<ref> tag with name "remaining religions" defined in <references> is not used in prior text.ਬਾਹਰੀ ਕੜੀਆਂ
[ਸੋਧੋ]- There's No National Language in India: Gujarat High Court, Times Of India, 6 January 2007, archived from the original on 29 ਜਨਵਰੀ 2014, retrieved 17 July 2011
ਹਵਾਲੇ
[ਸੋਧੋ]- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 National Informatics Centre 2005.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 "National Symbols | National Portal of India". India.gov.in. Archived from the original on 4 February 2017. Retrieved 1 March 2017.
ਭਾਰਤ ਦਾ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਗੀਤ ਜਨ ਗਣ ਮਨ, ਮੂਲ ਰੂਪ ਵਿੱਚ ਰਾਬਿੰਦਰਨਾਥ ਟੈਗੋਰ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਬੰਗਾਲੀ ਵਿੱਚ ਰਚਿਆ ਗਿਆ ਸੀ, ਨੂੰ ਸੰਵਿਧਾਨ ਸਭਾ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਇਸਦੇ ਹਿੰਦੀ ਸੰਸਕਰਣ ਵਿੱਚ 24 ਜਨਵਰੀ 1950 ਨੂੰ ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਗੀਤ ਵਜੋਂ ਅਪਣਾਇਆ ਗਿਆ ਸੀ।
- ↑ "National anthem of India: a brief on 'Jana Gana Mana'". News18. 14 August 2012. Archived from the original on 17 April 2019. Retrieved 7 June 2019.
- ↑ Wolpert 2003, p. 1.
- ↑ Constituent Assembly of India 1950.
- ↑ Ministry of Home Affairs 1960.
- ↑ "Profile | National Portal of India". India.gov.in. Archived from the original on 30 August 2013. Retrieved 23 August 2013.
- ↑ "Constitutional Provisions – Official Language Related Part-17 of the Constitution of India". Department of Official Language via Government of India. Archived from the original on 18 April 2021. Retrieved 18 April 2021.
- ↑ ਹਵਾਲੇ ਵਿੱਚ ਗ਼ਲਤੀ:Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedTimes News Network - ↑ ਹਵਾਲੇ ਵਿੱਚ ਗ਼ਲਤੀ:Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedNoneNtl - ↑ ਹਵਾਲੇ ਵਿੱਚ ਗ਼ਲਤੀ:Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedPress Trust of India - ↑ "50th Report of the Commissioner for Linguistic Minorities in India (July 2012 to June 2013)" (PDF). Commissioner for Linguistic Minorities, Ministry of Minority Affairs, Government of India. Archived from the original (PDF) on 8 July 2016. Retrieved 26 December 2014.
- ↑ Lua error in ਮੌਡਿਊਲ:Citation/CS1 at line 3162: attempt to call field 'year_check' (a nil value).
- ↑ "Ethnologue : Languages of the World (Seventeenth edition) : Statistical Summaries". Ethnologue by SIL International. Archived from the original on 17 December 2014. Retrieved 17 December 2014.
- ↑ ਹਵਾਲੇ ਵਿੱਚ ਗ਼ਲਤੀ:Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedCensus2011religion - ↑ Library of Congress 2004.
- ↑ Population Projections for India and States, 2011-2036 (in ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ). 2020-07-01.
- ↑ "Population Enumeration Data (Final Population)". 2011 Census Data. Office of the Registrar General & Census Commissioner, India. Archived from the original on 22 May 2016. Retrieved 17 June 2016.
- ↑ "A – 2 Decadal Variation in Population Since 1901" (PDF). 2011 Census Data. Office of the Registrar General & Census Commissioner, India. Archived from the original (PDF) on 30 April 2016. Retrieved 17 June 2016.
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 20.2 20.3 "World Economic Outlook Database: October 2022". Imf. International Monetary Fund. October 2022. Retrieved 11 October 2022.
- ↑ "Gini Index coefficient". The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency. Archived from the original on 7 July 2021. Retrieved 10 July 2021.
- ↑ "Gini index (World Bank estimate) – India". World bank.
- ↑ "Human Development Report 2021/2022" (PDF) (in ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ੀ). United Nations Development Programme. 8 September 2022. Retrieved 8 September 2022.
- ↑ "List of all left- & right-driving countries around the world". worldstandards.eu. 13 May 2020. Retrieved 10 June 2020.
- ↑ –Lua error in ਮੌਡਿਊਲ:Citation/CS1 at line 3162: attempt to call field 'year_check' (a nil value). "Official name: Republic of India.";
–Lua error in ਮੌਡਿਊਲ:Citation/CS1 at line 3162: attempt to call field 'year_check' (a nil value). "Official name: Republic of India; Bharat Ganarajya (Hindi)";
–Lua error in ਮੌਡਿਊਲ:Citation/CS1 at line 3162: attempt to call field 'year_check' (a nil value). "Official name: Republic of India; Bharat.";
–Lua error in ਮੌਡਿਊਲ:Citation/CS1 at line 3162: attempt to call field 'year_check' (a nil value). "Official name: English: Republic of India; Hindi:Bharat Ganarajya";
–Lua error in ਮੌਡਿਊਲ:Citation/CS1 at line 3162: attempt to call field 'year_check' (a nil value). "Official name: Republic of India";
–Lua error in ਮੌਡਿਊਲ:Citation/CS1 at line 3162: attempt to call field 'year_check' (a nil value). "Officially, Republic of India";
–Lua error in ਮੌਡਿਊਲ:Citation/CS1 at line 3162: attempt to call field 'year_check' (a nil value). "Official name: Republic of India";
–Lua error in ਮੌਡਿਊਲ:Citation/CS1 at line 3162: attempt to call field 'year_check' (a nil value). "India (Republic of India; Bharat Ganarajya)" - ↑ Biswas, Soutik (2023-05-01). "Most populous nation: Should India rejoice or panic?". BBC News. British Broadcasting Corporation. Retrieved 2023-05-03.
- ↑ Lua error in ਮੌਡਿਊਲ:Citation/CS1 at line 3162: attempt to call field 'year_check' (a nil value).
- ↑ Metcalf & Metcalf 2012, p. 327: "Even though much remains to be done, especially in regard to eradicating poverty and securing effective structures of governance, India's achievements since independence in sustaining freedom and democracy have been singular among the world's new nations."
- ↑ Lua error in ਮੌਡਿਊਲ:Citation/CS1 at line 3162: attempt to call field 'year_check' (a nil value).
- ↑ Fisher 2018, pp. 184–185: "Since 1947, India's internal disputes over its national identity, while periodically bitter and occasionally punctuated by violence, have been largely managed with remarkable and sustained commitment to national unity and democracy."
- ↑ Petraglia & Allchin 2007, p. 10, "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by modern humans originating in Africa. ... Coalescence dates for most non-European populations average to between 73–55 ka."
- ↑ Dyson 2018, p. 1, "Modern human beings—Homo sapiens—originated in Africa. Then, intermittently, sometime between 60,000 and 80,000 years ago, tiny groups of them began to enter the north-west of the Indian subcontinent. It seems likely that initially they came by way of the coast. ... it is virtually certain that there were Homo sapiens in the subcontinent 55,000 years ago, even though the earliest fossils that have been found of them date to only about 30,000 years before the present."
- ↑ Fisher 2018, p. 23, "Scholars estimate that the first successful expansion of the Homo sapiens range beyond Africa and across the Arabian Peninsula occurred from as early as 80,000 years ago to as late as 40,000 years ago, although there may have been prior unsuccessful emigrations. Some of their descendants extended the human range ever further in each generation, spreading into each habitable land they encountered. One human channel was along the warm and productive coastal lands of the Persian Gulf and northern Indian Ocean. Eventually, various bands entered India between 75,000 years ago and 35,000 years ago."
- ↑ Dyson 2018, p. 28
- ↑ (a) Dyson 2018, pp. 4–5;
(b) Fisher 2018, p. 33 - ↑ Lua error in ਮੌਡਿਊਲ:Citation/CS1 at line 3162: attempt to call field 'year_check' (a nil value).
- ↑ (a) Lua error in ਮੌਡਿਊਲ:Citation/CS1 at line 3162: attempt to call field 'year_check' (a nil value).
(b) Lua error in ਮੌਡਿਊਲ:Citation/CS1 at line 3162: attempt to call field 'year_check' (a nil value).
(c) Ludden 2014, p. 19, "In Punjab, a dry region with grasslands watered by five rivers (hence 'panch' and 'ab') draining the western Himalayas, one prehistoric culture left no material remains, but some of its ritual texts were preserved orally over the millennia. The culture is called Aryan, and evidence in its texts indicates that it spread slowly south-east, following the course of the Yamuna and Ganga Rivers. Its elite called itself Arya (pure) and distinguished themselves sharply from others. Aryans led kin groups organized as nomadic horse-herding tribes. Their ritual texts are called Vedas, composed in Sanskrit. Vedic Sanskrit is recorded only in hymns that were part of Vedic rituals to Aryan gods. To be Aryan apparently meant to belong to the elite among pastoral tribes. Texts that record Aryan culture are not precisely datable, but they seem to begin around 1200 BCE with four collections of Vedic hymns (Rg, Sama, Yajur, and Artharva)."
(d) Dyson 2018, pp. 14–15, "Although the collapse of the Indus valley civilization is no longer believed to have been due to an 'Aryan invasion' it is widely thought that, at roughly the same time, or perhaps a few centuries later, new Indo-Aryan-speaking people and influences began to enter the subcontinent from the north-west. Detailed evidence is lacking. Nevertheless, a predecessor of the language that would eventually be called Sanskrit was probably introduced into the north-west sometime between 3,900 and 3,000 years ago. This language was related to one then spoken in eastern Iran; and both of these languages belonged to the Indo-European language family. ... It seems likely that various small-scale migrations were involved in the gradual introduction of the predecessor language and associated cultural characteristics. However, there may not have been a tight relationship between movements of people on the one hand, and changes in language and culture on the other. Moreover, the process whereby a dynamic new force gradually arose—a people with a distinct ideology who eventually seem to have referred to themselves as 'Arya'—was certainly two-way. That is, it involved a blending of new features which came from outside with other features—probably including some surviving Harappan influences—that were already present. Anyhow, it would be quite a few centuries before Sanskrit was written down. And the hymns and stories of the Arya people—especially the Vedas and the later Mahabharata and Ramayana epics—are poor guides as to historical events. Of course, the emerging Arya were to have a huge impact on the history of the subcontinent. Nevertheless, little is known about their early presence.";
(e) Robb 2011, pp. 46–, "The expansion of Aryan culture is supposed to have begun around 1500 BCE. It should not be thought that this Aryan emergence (though it implies some migration) necessarily meant either a sudden invasion of new peoples, or a complete break with earlier traditions. It comprises a set of cultural ideas and practices, upheld by a Sanskrit-speaking elite, or Aryans. The features of this society are recorded in the Vedas." - ↑ (a) Lua error in ਮੌਡਿਊਲ:Citation/CS1 at line 3162: attempt to call field 'year_check' (a nil value).;
(b) Lua error in ਮੌਡਿਊਲ:Citation/CS1 at line 3162: attempt to call field 'year_check' (a nil value).;
(c) Lua error in ਮੌਡਿਊਲ:Citation/CS1 at line 3162: attempt to call field 'year_check' (a nil value).
(d) Lua error in ਮੌਡਿਊਲ:Citation/CS1 at line 3162: attempt to call field 'year_check' (a nil value). - ↑ Dyson 2018, pp. 16, 25
- ↑ Dyson 2018, p. 16
- ↑ Fisher 2018, p. 59
- ↑ (a) Dyson 2018, pp. 16–17;
(b) Fisher 2018, p. 67;
(c) Robb 2011, pp. 56–57;
(d) Ludden 2014, pp. 29–30. - ↑ (a) Ludden 2014, pp. 28–29;
(b) Lua error in ਮੌਡਿਊਲ:Citation/CS1 at line 3162: attempt to call field 'year_check' (a nil value). - ↑ (a) Dyson 2018, p. 20;
(b) Stein 2010, p. 90;
(c) Lua error in ਮੌਡਿਊਲ:Citation/CS1 at line 3162: attempt to call field 'year_check' (a nil value). - ↑ 45.0 45.1 Kulke & Rothermund 2004, p. 93.
- ↑ Asher & Talbot 2006, p. 17
- ↑ (a) Ludden 2014, p. 54;
(b) Asher & Talbot 2006, pp. 78–79;
(c) Fisher 2018, p. 76 - ↑ (a) Ludden 2014, pp. 68–70;
(b) Asher & Talbot 2006, pp. 19, 24 - ↑ (a) Dyson 2018, p. 48;
(b) Asher & Talbot 2006, p. 52 - ↑ Asher & Talbot 2006, p. 74
- ↑ Asher & Talbot 2006, p. 267
- ↑ Asher & Talbot 2006, p. 152
- ↑ 53.0 53.1 Fisher 2018, p. 106
- ↑ (a) Asher & Talbot 2006, p. 289
(b) Fisher 2018, p. 120 - ↑ Lua error in ਮੌਡਿਊਲ:Citation/CS1 at line 3162: attempt to call field 'year_check' (a nil value).
- ↑ Peers 2013, p. 76.
- ↑ Lua error in ਮੌਡਿਊਲ:Citation/CS1 at line 3162: attempt to call field 'year_check' (a nil value).
- ↑ Lua error in ਮੌਡਿਊਲ:Citation/CS1 at line 3162: attempt to call field 'year_check' (a nil value).
- ↑ Lua error in ਮੌਡਿਊਲ:Citation/CS1 at line 3162: attempt to call field 'year_check' (a nil value).
- ↑ Fisher 2018, pp. 173–174: "The partition of South Asia that produced India and West and East Pakistan resulted from years of bitter negotiations and recriminations ... The departing British also decreed that the hundreds of princes, who ruled one-third of the subcontinent and a quarter of its population, became legally independent, their status to be settled later. Geographical location, personal and popular sentiment, and substantial pressure and incentives from the new governments led almost all princes eventually to merge their domains into either Pakistan or India. ... Each new government asserted its exclusive sovereignty within its borders, realigning all territories, animals, plants, minerals, and all other natural and human-made resources as either Pakistani or Indian property, to be used for its national development... Simultaneously, the central civil and military services and judiciary split roughly along religious 'communal' lines, even as they divided movable government assets according to a negotiated formula: 22.7 percent for Pakistan and 77.3 percent for India."
- ↑ Lua error in ਮੌਡਿਊਲ:Citation/CS1 at line 3162: attempt to call field 'year_check' (a nil value).
- ↑ Lua error in ਮੌਡਿਊਲ:Citation/CS1 at line 3162: attempt to call field 'year_check' (a nil value).
- ↑ Lua error in ਮੌਡਿਊਲ:Citation/CS1 at line 3162: attempt to call field 'year_check' (a nil value).
- ↑ (a) Copland 2001, pp. 71–78;
(b) Metcalf & Metcalf 2006, p. 222. - ↑ Dyson 2018, pp. 219, 262
- ↑ Fisher 2018, p. 8
- ↑ Metcalf & Metcalf 2012, pp. 265–266
- ↑ Metcalf & Metcalf 2012, p. 266
- ↑ Dyson 2018, p. 216
- ↑ (a) "Kashmir, region Indian subcontinent", Encyclopaedia Britannica, archived from the original on 13 August 2019, retrieved 15 August 2019,
Kashmir, region of the northwestern Indian subcontinent ... has been the subject of dispute between India and Pakistan since the partition of the Indian subcontinent in 1947.
;
(b) Pletcher, Kenneth, "Aksai Chin, Plateau Region, Asia", Encyclopaedia Britannica, archived from the original on 2 April 2019, retrieved 16 August 2019,Aksai Chin, Chinese (Pinyin) Aksayqin, portion of the Kashmir region, ... constitutes nearly all the territory of the Chinese-administered sector of Kashmir that is claimed by India
;
(c) Bosworth, C. E (2006). "Kashmir". Encyclopedia Americana: Jefferson to Latin. Scholastic Library Publishing. p. 328. ISBN 978-0-7172-0139-6. https://books.google.com/books?id=l_cWAQAAMAAJ&pg=PA328. "KASHMIR, kash'mer, the northernmost region of the Indian subcontinent, administered partly by India, partly by Pakistan, and partly by China. The region has been the subject of a bitter dispute between India and Pakistan since they became independent in 1947". - ↑ Lua error in ਮੌਡਿਊਲ:Citation/CS1 at line 3162: attempt to call field 'year_check' (a nil value).
- ↑ Lua error in ਮੌਡਿਊਲ:Citation/CS1 at line 3162: attempt to call field 'year_check' (a nil value).
- ↑ Lua error in ਮੌਡਿਊਲ:Citation/CS1 at line 3162: attempt to call field 'year_check' (a nil value).
- ↑ ਹਵਾਲੇ ਵਿੱਚ ਗ਼ਲਤੀ:Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedISFR - ↑ Karanth & Gopal 2005, p. 374.
- ↑ Lua error in ਮੌਡਿਊਲ:Citation/CS1 at line 3162: attempt to call field 'year_check' (a nil value).
- ↑ United Nations Population Division.
- ↑ Burnell & Calvert 1999.
- ↑ Election Commission of India.
- ↑ Lua error in ਮੌਡਿਊਲ:Citation/CS1 at line 3162: attempt to call field 'year_check' (a nil value).
- ↑ Malik & Singh 1992.
- ↑ Banerjee 2005.
- ↑ Halarnkar, Samar (13 June 2012). "Narendra Modi makes his move". BBC News.
The right-wing Hindu nationalist Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP), India's primary opposition party
- ↑ Sarkar 2007.
- ↑ Chander 2004.
- ↑ Bhambhri 1992.
- ↑ "Narasimha Rao Passes Away". The Hindu. 24 December 2004. Archived from the original on 13 February 2009. Retrieved 2 November 2008.
- ↑ Dunleavy, Diwakar & Dunleavy 2007.
- ↑ Kulke & Rothermund 2004.
- ↑ Business Standard 2009.
- ↑ "BJP first party since 1984 to win parliamentary majority on its own". DNA. Indo-Asian News Service. 16 May 2014. Archived from the original on 21 May 2014. Retrieved 20 May 2014.
- ↑ "Droupadi Murmu Swearing-in Live: My election is the greatness of India, mother of democracy, says President Murmu". The Indian Express. 25 July 2022. Retrieved 26 July 2022.
- ↑ Pylee 2003a.
- ↑ Dutt 1998.
- ↑ Wheare 1980.
- ↑ Echeverri-Gent 2002.
- ↑ Sinha 2004.



