NASA – National Aeronautics and Space Administration

Table of contents
A world-wide space leader
On October 4, 1957, the Soviet Union launched the world’s first satellite into orbit. While it was a dummy payload, with very few scientific or military instruments on board, it stroke fear to non-communist countries around the world.
On the other side of the world, what was believed to be the Western Super power, the United States, was struggling to keep up with the Soviet Union. So in 1958, Congress drafted and approved the National Aeronautics and Space Act. It was then signed into law by President Dwight Eisenhower on July 29, 1958. With that, the National Aeronautics and Space Administration was created.

NASA’s goal since then has been to develop new technologies for both use in our atmosphere and in space. It was also designed to lead the nations new civil space program in openness, a contrast to the Soviet Union.
Since then the agencies has grown and now leads the world in both funding and number of projects it can run. NASA has become the organizer of other space agencies to collaborate to do bigger things than what we could do on our own, as well as be the champion of commercial space applications. (Sometimes.)
NASA is headquartered in Washington DC, and the current administrator is former US Senator Bill Nelson.
Space Exploration
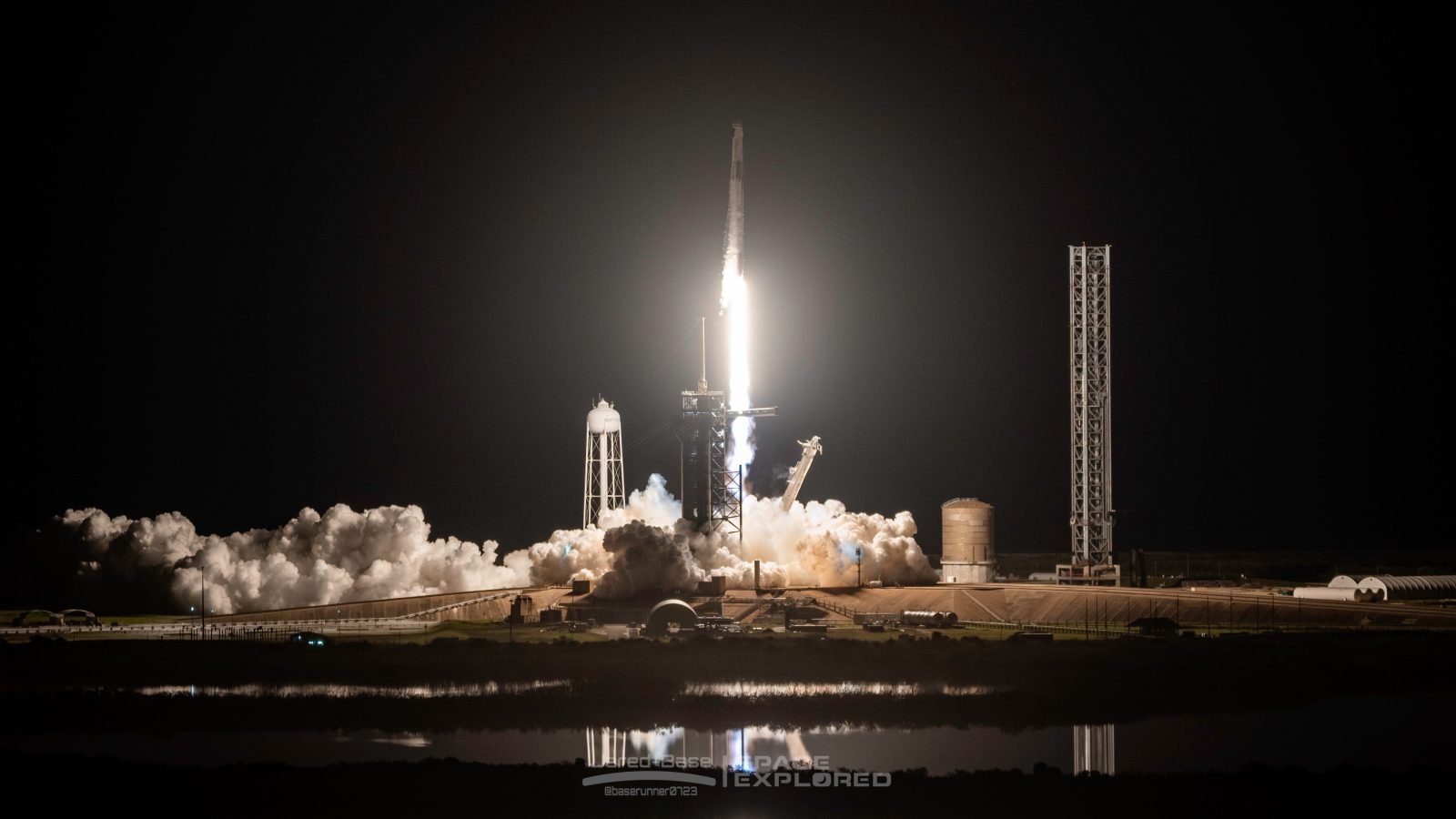
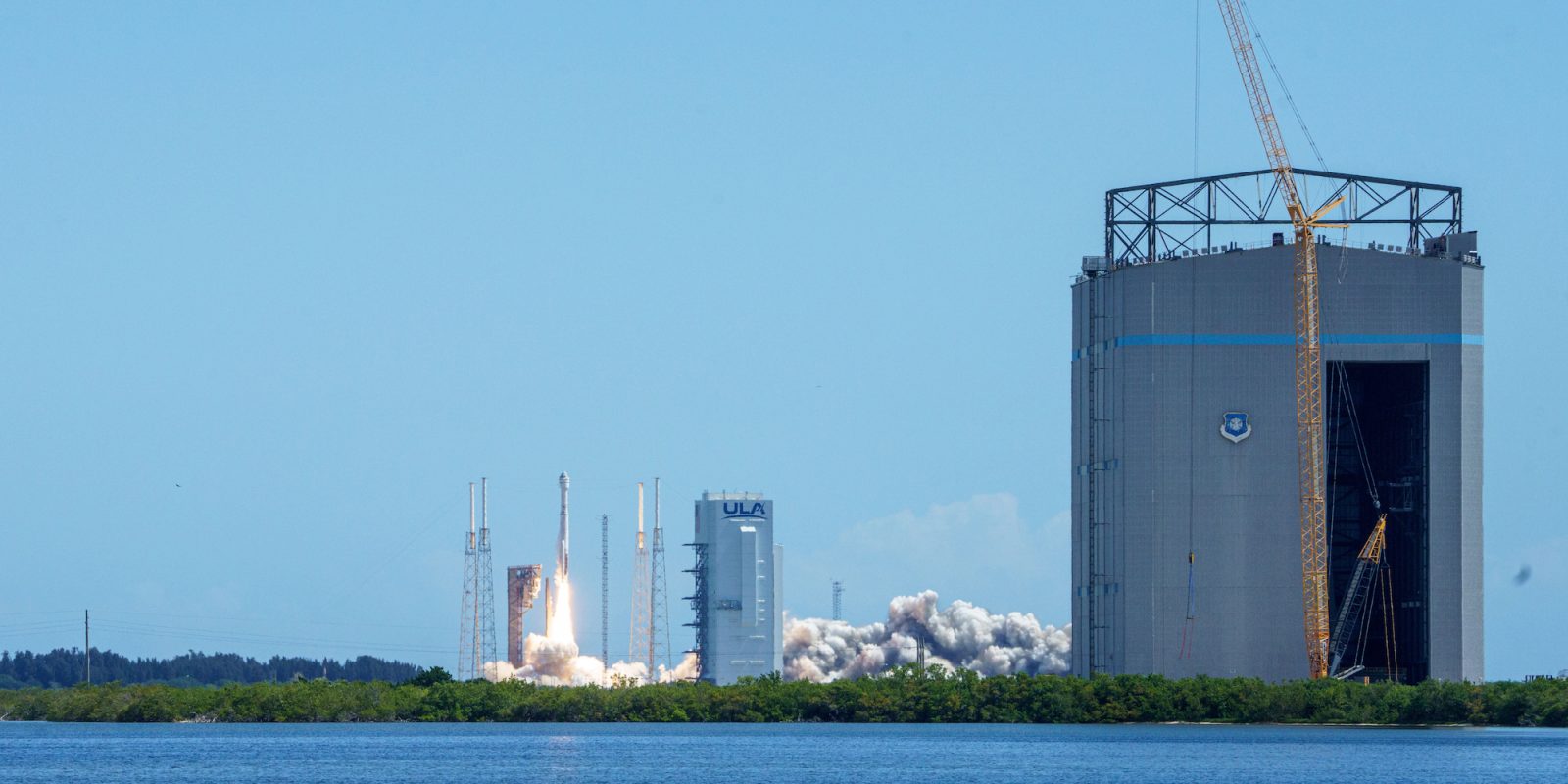
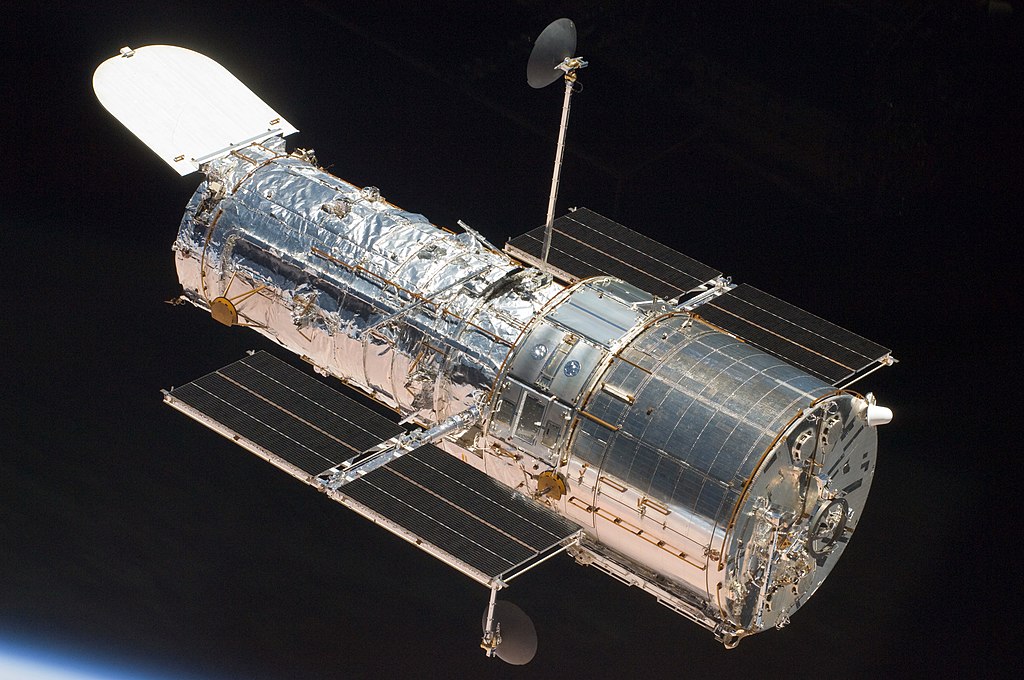
Since the agencies beginning, space exploration has been NASA’s primary mission. Beginning with Project Mercury, to Gemini, Apollo, the Space Shuttle, and now Artemis, NASA leads the world in expanding exploration of space.
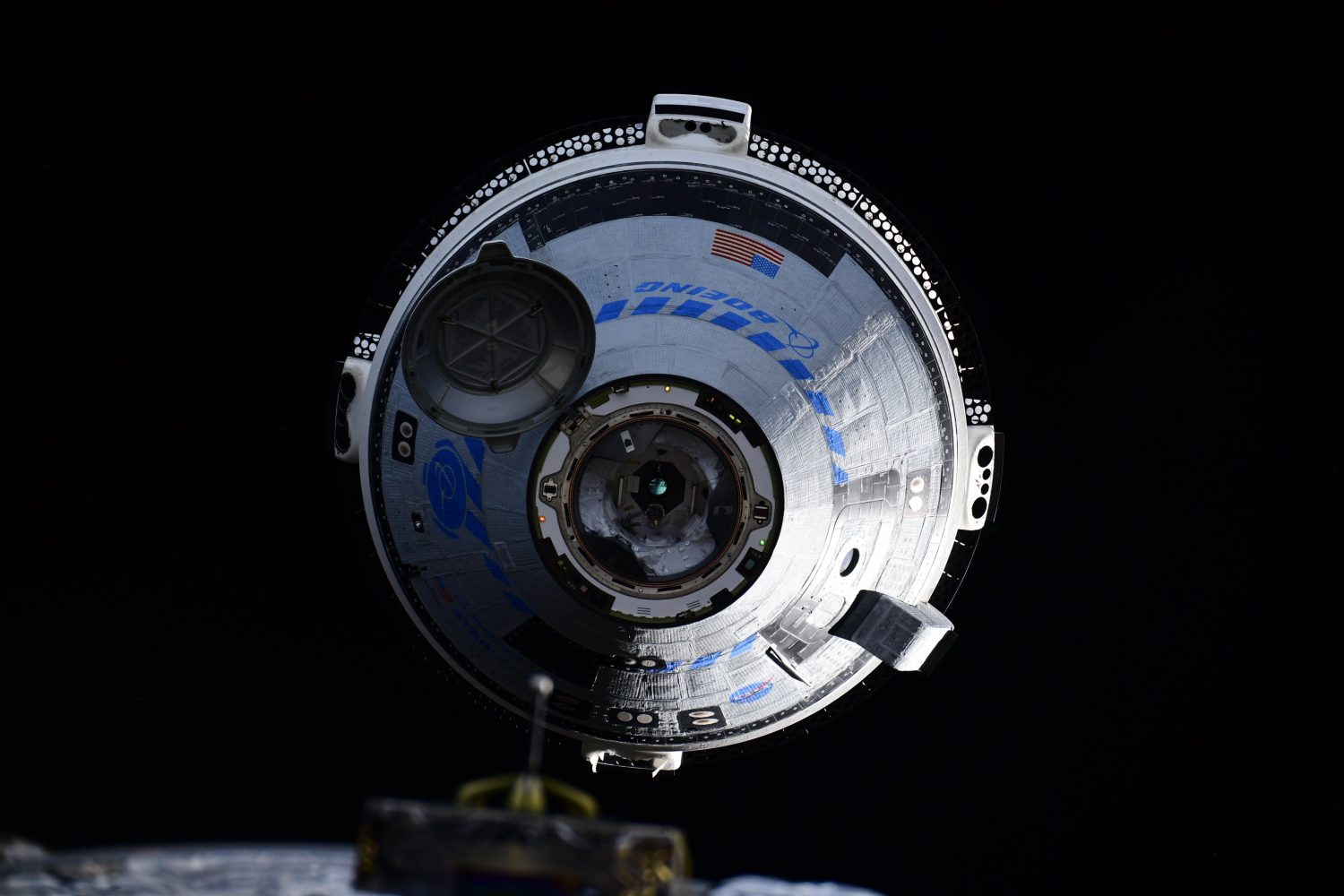
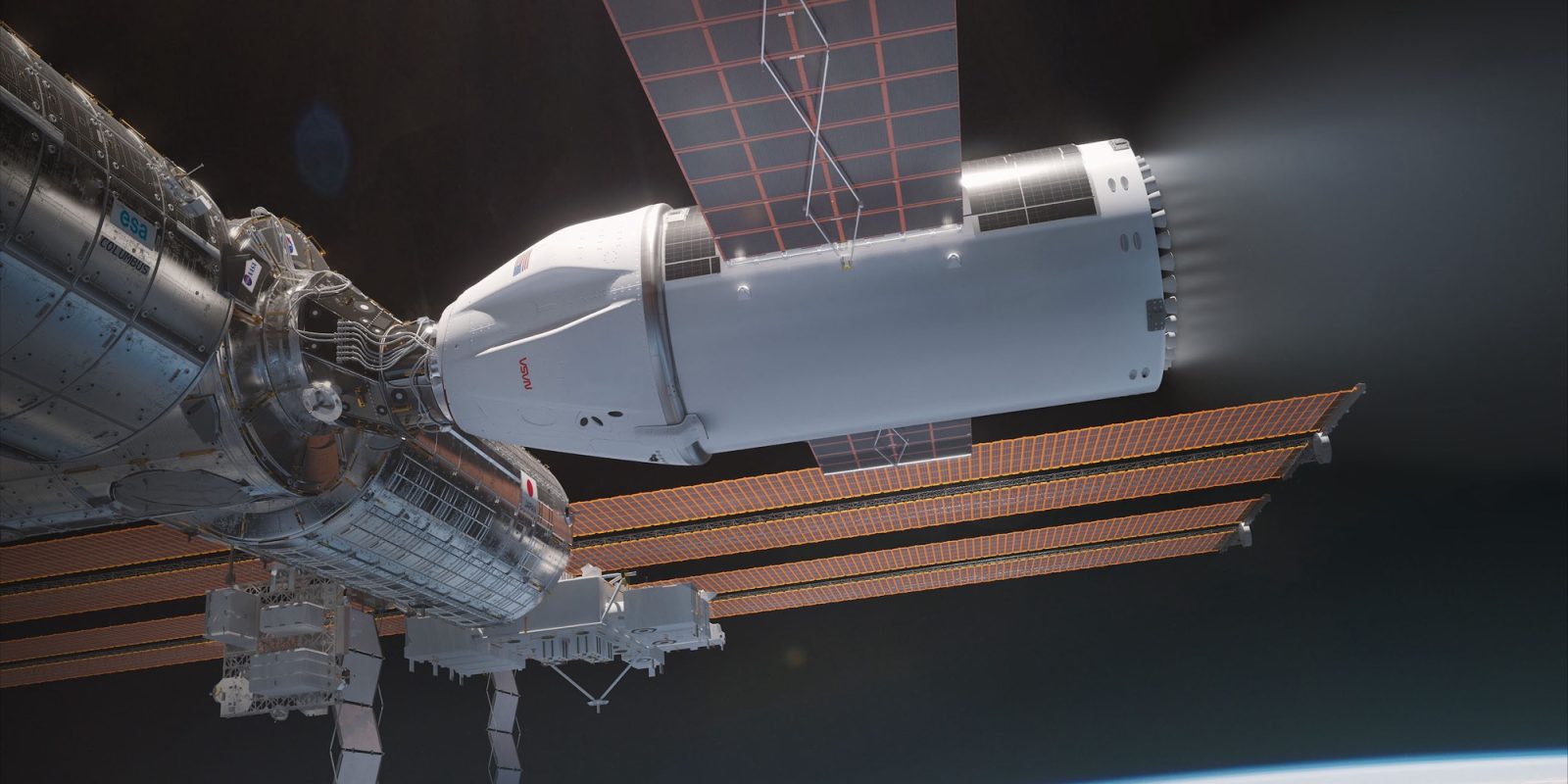
International Space Station
Arguably the largest ongoing space mission that NASA is involved in is the International Space Station (ISS). The ISS is a habitable modular space station involving five space agencies: NASA, Roscosmos, JAXA, ESA, and CSA. Construction of the orbital laboratory began on November 20, 1998.
NASA’s four enduring strategic goals are as follows:
- Expand human knowledge via new scientific discoveries
- Extend human presence deeper into space for sustainable, long-term utilization
- Address national issues and catalyze economic growth
- Optimize capabilities and operations
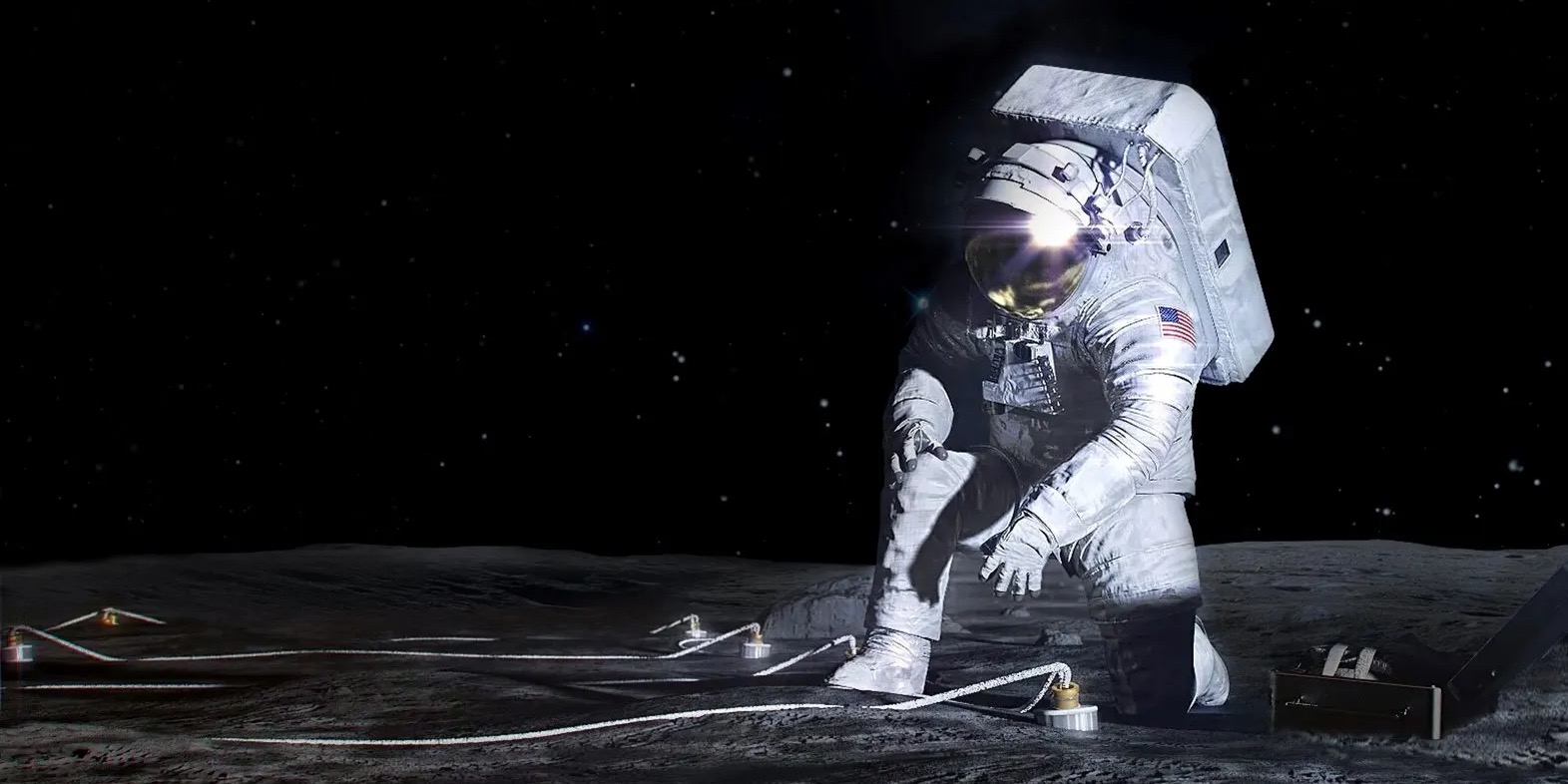
The Artemis Program
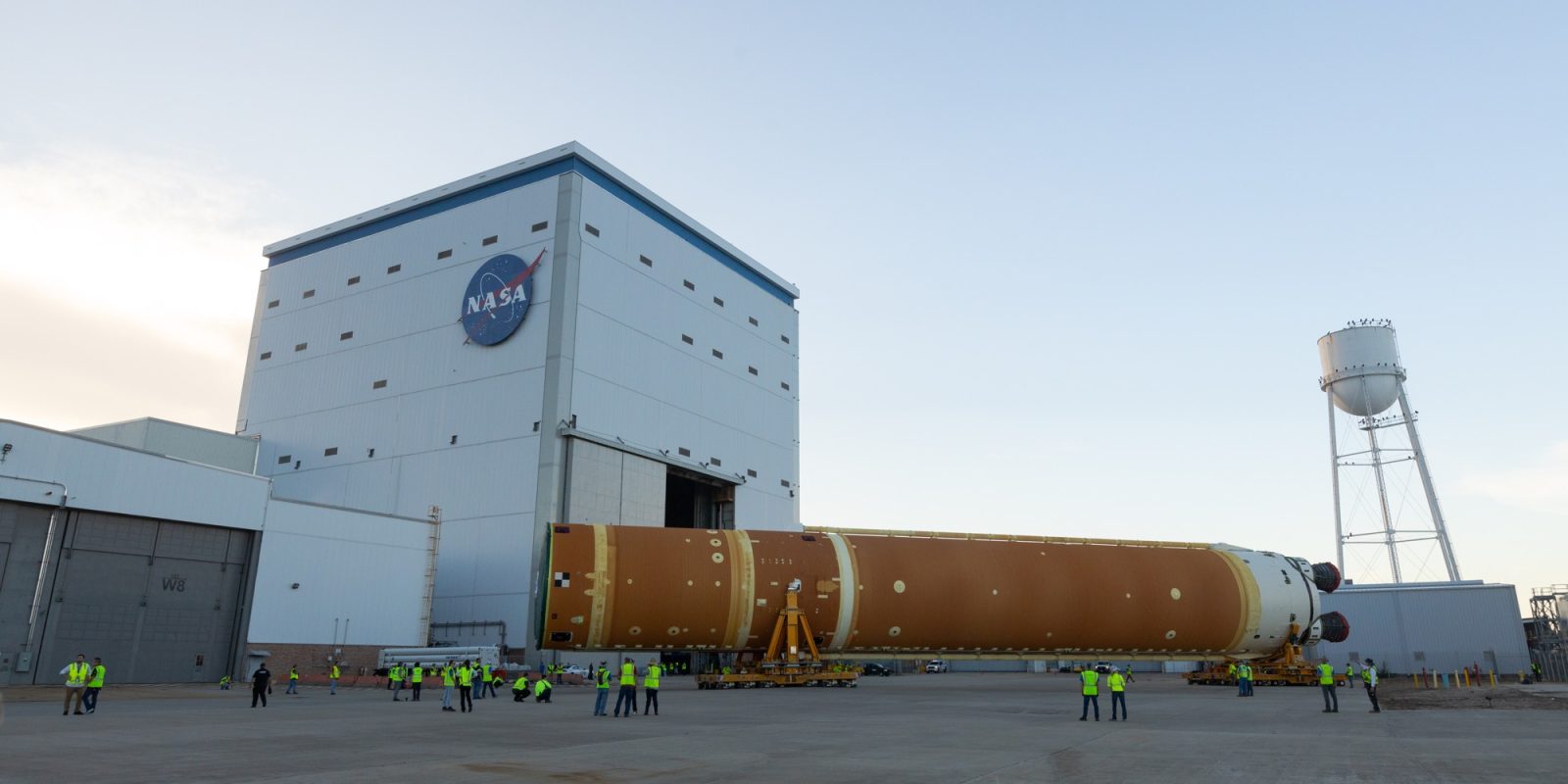
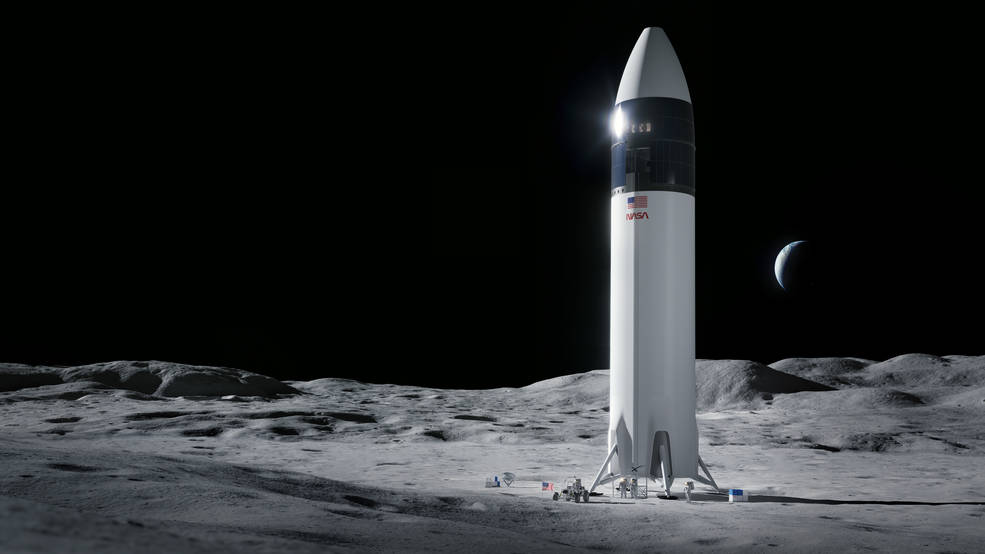
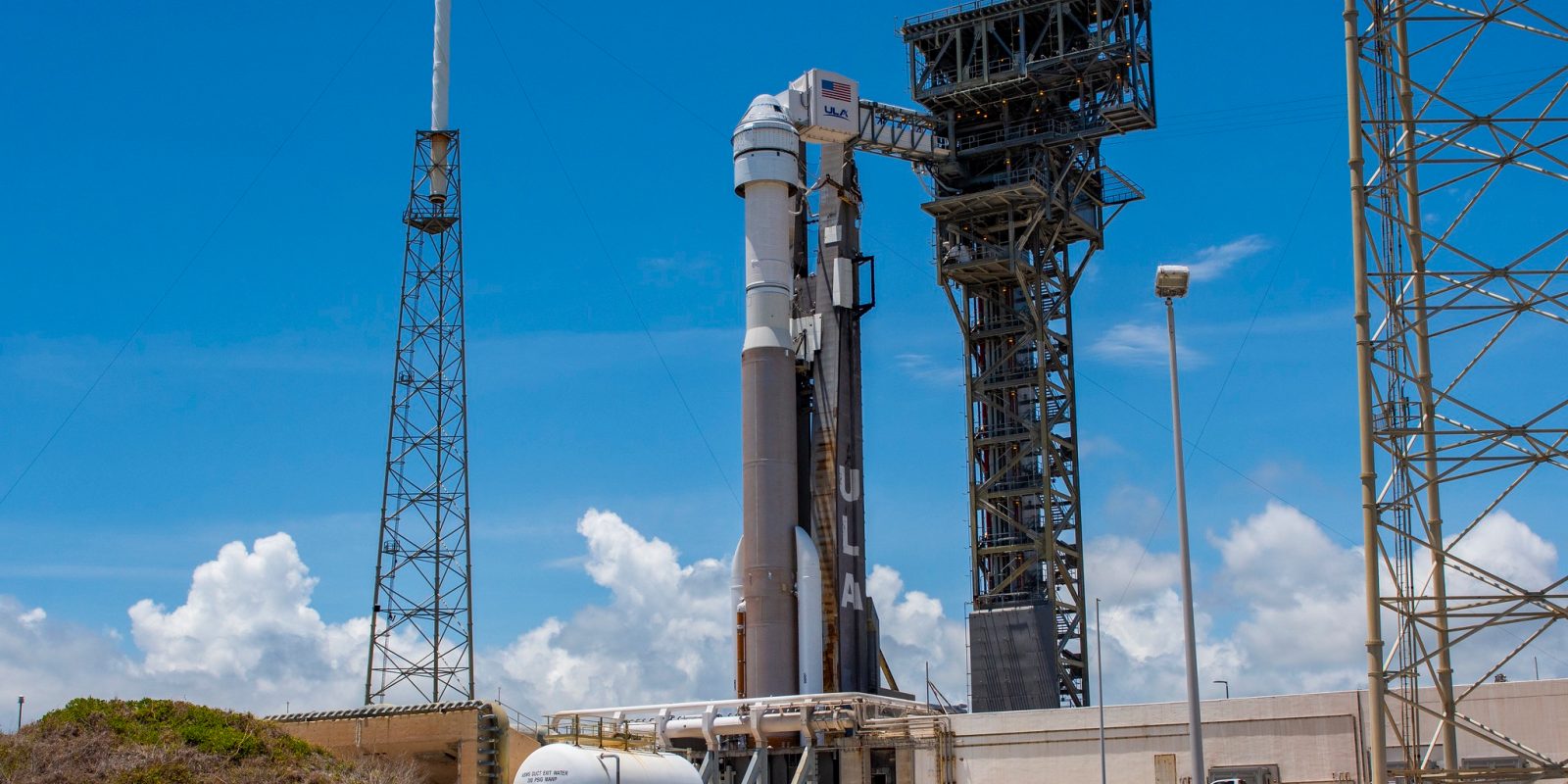
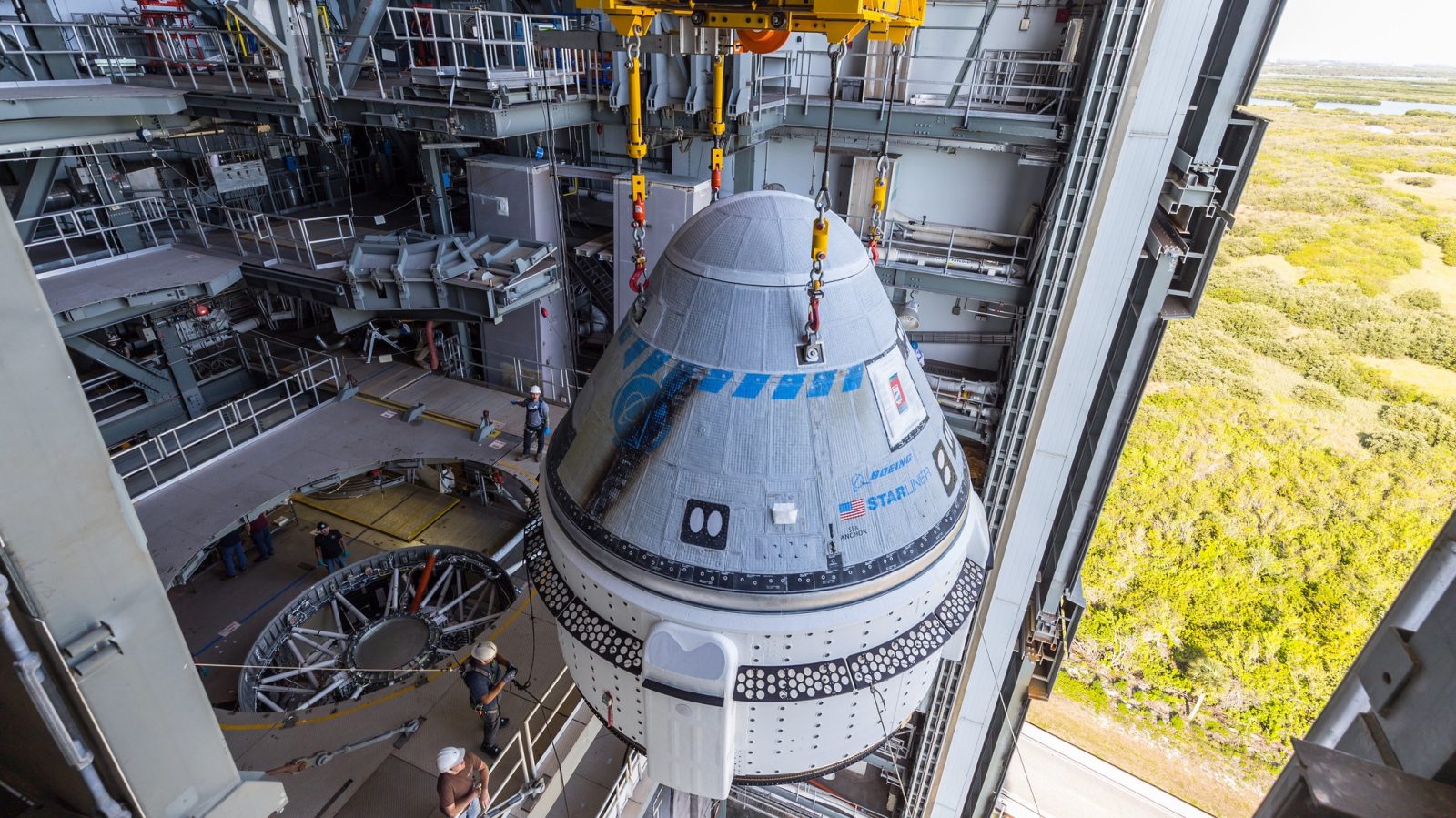
Currently, NASA’s major space exploration program is a daring adventure to return humanity to the Moon. The plan consists of the agency’s SLS rocket and Orion space capsule. The program originally started as a fully public program but has since switched over to using the growing commercial space sector to help develop parts of the program.
Artemis consists of multiple programs and contracts to meet its goal of returning humanity back to Moon sustainably and to stay this time. To do that, NASA has taken a big bet that in the future there will be a commercial market for access to the Moon.
NASA developed the primary launcher for crew, SLS and Orion, while it has partnered with the commercial industry for everything else. Contracts have been signed for NASA to purchase lunar landers, spacesuits, rovers, and resupply services commercially rather than owning the systems itself.
Eventually, NASA could be just one of many customers served by these services it helped create.