Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Banking and Its Types
Banking and Its Types
Uploaded by
विनीत जैनOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Banking and Its Types
Banking and Its Types
Uploaded by
विनीत जैनCopyright:
Available Formats
Different types of Banking Bank - A financial institution licensed as a receiver of deposits.
There are two types of banks: commercial/retail banks and investment banks. In most countries, banks are regulated by the national government or central bank. Commercial banks are mainly concerned with managing withdrawals and deposits as well as supplying short-term loans to individuals and small businesses. Consumers primarily use these banks for basic checking and savings accounts, certificates of deposit and sometimes for home mortgages. Investment banks focus on providing services such as underwriting and corporate reorganization to institutional clients. While many banks have a brick-and-mortar and online presence, some banks have only an online presence. Online-only banks often offer consumers higher interest rates and lower fees. Convenience, interest rates and fees are the driving factors in consumers' decisions of which bank to do business with. As an alternative to banks, consumers can opt to use a credit union. Banking company is defined as a company which transacts the business of banking in India as per the banking Act 1949. Banking is defined as 'accepting, for the purpose of lending or investment, of deposits of money from the public, repayable on demand or otherwise, and withdraw able, by cheque, draft, and order or otherwise. 'Banks are defined as the financial institution or intermediary which helps in performing the banking activities. The different types if banking that takes place all over the world are: 1. Retail banking Typical mass-market banking in which individual customers use local branches of larger commercial banks. Services offered include savings and checking accounts, mortgages, personal loans, debit/credit cards and certificates of deposit (CDs). services as possible on behalf of retail clients. Some retail banks have even made a push into investment services such as wealth management, brokerage accounts, private banking and retirement planning. While some of these ancillary services are outsourced to third parties (often for regulatory reasons), they often intertwine with core retail banking accounts like checking and savings to allow for easier transfers and maintenance. The products that are offered by the retail banks are: Current accounts Savings accounts Debit cards ATM cards Credit cards Cheque Mortgages Home equity loans
Personal loans Time deposits/Term deposits Recurring deposits
The different types of retail banks are as follows: Private Banks which deals with assets of high net worth individuals provides wealth management and portfolio management services to them. Offshore banks which are located in jurisdictions with low taxation and regulation Savings banks accept savings deposits. Postal savings banks are savings banks associated with national postal systems Community development banks are the banks that provide financial services and credit to under-served markets or populations. 2. Wholesale banking Banking services between merchant banks and other financial institutions. Wholesale banking deals with larger institutions, where as retail banking would focus more on the individual or smaller business. Some services might include currency conversion, working capital financing and large trade transactions. This type of banking will provide services to other banks or large corporations. Some retail banking covers business transactions but not in the same scale as wholesale banking. think of it like the discount superstore that deals in such large amounts that they can offer special prices or reduced fees, on a per dollar basis. The products that are offered in whole sale banking are: Trade Finance products Cash Management Products Treasury Products Bridge Loans Syndicated Loans Infrastructure Loans Cross Currency/Interest Rate Swaps Foreign Currency Loans and many more depending upon the needs of the Corporates.
3. Investment banking A specific division of banking related to the creation of capital for other companies. Investment banks underwrite new debt and equity securities for all types of corporations. Investment banks also provide guidance to issuers regarding the issue and placement of stock. Investment banks also aid in the sale of securities in some instances. They also help to facilitate mergers and acquisitions, reorganizations and broker trades for both institutions and private investors. They can also trade securities for their own accounts. 4. Merchant banking A bank that deals mostly in (but is not limited to) international finance, long-term loans for companies and underwriting. Merchant banks do not provide regular banking services to the general public. Their knowledge in international finances make merchant banks specialists in dealing with multinational corporations. The main difference between investment banking and merchant banking is that it does not deal with trading. 5. Universal banking A banking system in which banks provide a wide variety of financial services, including both commercial and investment services. Universal banking is common in some European countries, including Switzerland. In the United States, however, banks are required to separate their commercial and investment banking services. Proponents of universal banking argue that it helps banks better diversify risk. Detractors think dividing up banks' operations is a less risky strategy. Universal banks may offer credit, loans, deposits, asset management, investment advisory, payment processing, securities transactions, underwriting and financial analysis. While a universal banking system allows banks to offer a multitude of services, it does not require them to do so. Banks in a universal system may still choose to specialize in a subset of banking services. 6. Central banking The entity responsible for overseeing the monetary system for a nation (or group of nations). Central banks have a wide range of responsibilities, from overseeing monetary policy to implementing specific goals such as currency stability, low inflation and full employment. Central banks also generally issue currency, function as the bank of the government, regulate the credit system, oversee commercial banks, manage exchange reserves and act as a lender of last resort. The central banking system in the U.S. is known as the Federal Reserve System (commonly known as "the Fed"), which is composed of 12 regional Federal Reserve Banks located in major cities throughout the country. The main tasks of the Federal Reserve are to supervise and regulate banks, implement monetary policy by buying and selling U.S. Treasury bonds and steer interest rates. Ben Bernanke currently serves as the chairman of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve. 7. Cooperative societies
Member-owned financial co-operative. These institutions are created and operated by its members and profits are shared amongst the owners. As soon as you deposit funds into a credit union account, you become a partial owner and participate in the union's profitability. Credit unions are formed by large corporations and organizations for their employees and members. 8. Islamic banking A banking system that is based on the principles of Islamic law (also known Shariah) and guided by Islamic economics. Two basic principles behind Islamic banking are the sharing of profit and loss and, significantly, the prohibition of the collection and payment of interest. Collecting interest is not permitted under Islamic law. Since this system of banking is grounded in Islamic principles, all the undertakings of the banks follow Islamic morals. Therefore, it could be said that financial transactions within Islamic banking are a culturally distinct form of ethical investing (for example, investments involving alcohol, gambling, pork, etc. are prohibited). The Dubai Islamic Bank has the distinction of being the world's first full-fledged Islamic bank, formed in 1975. 9. Internet banking The performance of banking activities via the Internet. Online banking is also known as "Internet banking" or "Web banking." A good online bank will offer customers just about every service traditionally available through a local branch, including accepting deposits (which is done online or through the mail), paying interest on savings and providing an online bill payment system. Online banks cannot provide direct ATM access, but they make provisions for consumers to use ATMs at other banks and retail stores, and they may reimburse consumers for any associated fees. Because of the reduced overhead costs associated with not having physical branches, online banks tend to offer consumers significant savings and pay higher interest rates. Online banks handle customer service tasks by phone, email or online chat. 10. Mobile banking The use of wireless handheld devices such as cellular phones and laptops to conduct commercial transactions online. Mobile commerce transactions continues to grow, and the term includes the purchase and sale of a wide range of goods and services, online banking, bill payment, information delivery and so on. Also known as m-commerce. The services that are extended through mobile banking are: Checking the statements Status on cheque Pin provision of ATM cards and credit cards Technical assistance through call centers Blockage of accounts
11. International banking A facility that allows depository institutions in the United States to offer deposit and loan services to foreign residents and institutions, while being exempted from reserve requirements imposed by the Federal Reserve and some state and local income taxes. Because of these exemptions, IBFs enable U.S. banks and U.S.-based financial institutions to compete more effectively for overseas deposits and loans business in the Eurocurrency markets. 12. Specialized banking Specialized banks are foreign exchange banks, industrial banks, development banks, exportimport banks catering to specific needs of these unique activities. These banks provide financial aid to industries, heavy projects and foreign trade activities.
INDIAN BANKING INDUSTRY 1. Scheduled banks 1.1 scheduled commerce banks 1.1.1 SBI & Associates Public sector banks 1.1.2 Nationalised banks (including IDBI) Public sector banks 1.1.3 Foreign banks 1.1.4 Regional rural banks 1.1.5 Other scheduled commerce banks 1.2 scheduled cooperative banks 1.2.1 Rural cooperative banks 1.2.1.1 short term (state, district and primary level cooperative banks) 1.2.1.2 long term (SCARDBs & PCARDBs) 1.2.2 Urban cooperative banks 1.2.2.1 Signal 1.2.2.2 Multi-state 2. Unscheduled banks
You might also like
- Basic Finance-An Introduction To Financial Institutions Investments and Management 10th Edition Mayo Test BankDocument10 pagesBasic Finance-An Introduction To Financial Institutions Investments and Management 10th Edition Mayo Test BankRobinson MojicaNo ratings yet
- SPA Bank TransactionDocument1 pageSPA Bank TransactionDavid Jhan Calderon100% (3)
- Verification of Funds Letter From BankDocument8 pagesVerification of Funds Letter From BankJames100% (1)
- Inside Job TermsDocument8 pagesInside Job TermsKavita SinghNo ratings yet
- A Principal's Mistake, Ngara GirlsDocument48 pagesA Principal's Mistake, Ngara GirlsOmbudsman KenyaNo ratings yet
- SubjectCodesandSyllabus July2010Document69 pagesSubjectCodesandSyllabus July2010Abhranil GuptaNo ratings yet
- Kikkoman Case AnalysisDocument5 pagesKikkoman Case Analysisविनीत जैनNo ratings yet
- Brigham-Financial Management Chapter2Document32 pagesBrigham-Financial Management Chapter2Dian Adi NugrahaNo ratings yet
- Fin Ins Chapter 1Document34 pagesFin Ins Chapter 1Mehedi HasanNo ratings yet
- Topic ReviewDocument11 pagesTopic ReviewNguyen Thi Bich NgocNo ratings yet
- Business Liechtenstein Company Formation: Legal FormsDocument61 pagesBusiness Liechtenstein Company Formation: Legal FormsakisNo ratings yet
- ICIDocument228 pagesICIZerohedgeNo ratings yet
- Money Market Securities - : Certificates of Deposit (CDS)Document4 pagesMoney Market Securities - : Certificates of Deposit (CDS)Crisha-mae JavillonarNo ratings yet
- Elements of Banking & InsuranceDocument77 pagesElements of Banking & InsuranceMADHULIKAANo ratings yet
- Crisis GlossaryDocument12 pagesCrisis Glossarysantu15038847420No ratings yet
- Banking Code V20152Document25 pagesBanking Code V20152dacoda204No ratings yet
- AttachmentDocument31 pagesAttachmentHambaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two Nature and Kinds of ContractsDocument8 pagesChapter Two Nature and Kinds of ContractsHarshad SavantNo ratings yet
- 1 Chapter LawDocument18 pages1 Chapter LawJose VirtualNo ratings yet
- Summery of Business Law-1Document25 pagesSummery of Business Law-1Khader MohamedNo ratings yet
- Law 202Document41 pagesLaw 202neffhbaculodmzNo ratings yet
- Role of MoneyDocument100 pagesRole of MoneyHamis Rabiam MagundaNo ratings yet
- How To Buy A Car Role-Play Assignment 2Document5 pagesHow To Buy A Car Role-Play Assignment 2api-542907826100% (1)
- BAnking Terms and InterviewsDocument25 pagesBAnking Terms and InterviewsassadbilalNo ratings yet
- Banking&Security UpdateDocument19 pagesBanking&Security Updateseunnuga93No ratings yet
- Amended Effective Jan. 1, 1992Document8 pagesAmended Effective Jan. 1, 1992mikhai_archezNo ratings yet
- The Bill of Exchange As A Means of Payment and SecurityDocument11 pagesThe Bill of Exchange As A Means of Payment and SecurityMarcus LentonNo ratings yet
- Legal Aspects of Business AssignementDocument6 pagesLegal Aspects of Business AssignementShameel AndhoorathodiNo ratings yet
- History of Bangladesh Bank & Central Banks Arount The WorldDocument7 pagesHistory of Bangladesh Bank & Central Banks Arount The WorldZahin SarwarNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash Equivalents: Print EmailDocument11 pagesCash and Cash Equivalents: Print EmailRobert PangitNo ratings yet
- Debt InstrumentsDocument46 pagesDebt InstrumentsPranav ViraNo ratings yet
- Glossary Accounting1Document125 pagesGlossary Accounting1salshaNo ratings yet
- Bank - A Financial Institution Licensed To Receive Deposits and Make Loans. Banks May AlsoDocument3 pagesBank - A Financial Institution Licensed To Receive Deposits and Make Loans. Banks May AlsoKyle PanlaquiNo ratings yet
- BUSN115 Final Exam Study Guide: TCO 1 Chapters 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 13 and 15 Weeks 1, 2, 4 and 5Document26 pagesBUSN115 Final Exam Study Guide: TCO 1 Chapters 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 13 and 15 Weeks 1, 2, 4 and 5acadia15No ratings yet
- Classification of ContractsDocument15 pagesClassification of ContractsmadhavNo ratings yet
- Financial Ratios Analysis: Nestle VS Engro FoodsDocument36 pagesFinancial Ratios Analysis: Nestle VS Engro FoodsMuaaz WaseemNo ratings yet
- HDFC Product DetailsDocument19 pagesHDFC Product DetailsPrincess BinsonNo ratings yet
- Concept of Securities in A CompanyDocument38 pagesConcept of Securities in A CompanyNandini Tarway100% (1)
- Free Version of Growthinks Retail Business Plan TemplateDocument14 pagesFree Version of Growthinks Retail Business Plan TemplateAvinash GhadaiNo ratings yet
- Credit Transactions - Car LoanDocument4 pagesCredit Transactions - Car LoanDonna CasequinNo ratings yet
- BA 5011 - MbfsDocument224 pagesBA 5011 - MbfsDrGArumugasamyNo ratings yet
- Concept of Asessment Year, Previous Year, Income, Capital and Revenue Receipts, Capital and Revenue ExpenditureDocument15 pagesConcept of Asessment Year, Previous Year, Income, Capital and Revenue Receipts, Capital and Revenue ExpenditureAnany UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Eguide The Minimum Criteria Needed To Qualify For 8 Different Loan Products PDFDocument12 pagesEguide The Minimum Criteria Needed To Qualify For 8 Different Loan Products PDFbabu1438No ratings yet
- Consumer Guide To Good CreditDocument122 pagesConsumer Guide To Good CreditQuinn HammondNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets and Services NotesDocument118 pagesFinancial Markets and Services NotesVikram KumarNo ratings yet
- Company Law FoundationDocument17 pagesCompany Law FoundationVanshika chalwaNo ratings yet
- Notes FS Unit-1Document23 pagesNotes FS Unit-1Vishal GoyalNo ratings yet
- Salem 2012-13 Budget Final in Depth Proposed 12-13Document14 pagesSalem 2012-13 Budget Final in Depth Proposed 12-13Statesman JournalNo ratings yet
- Consumer TheoryDocument15 pagesConsumer TheoryEdwince OchiengNo ratings yet
- PFSADocument84 pagesPFSAAkinlabi HendricksNo ratings yet
- Businessregulatoryframeworkmcqsslideshare 230524162337 E3eb4ba7Document33 pagesBusinessregulatoryframeworkmcqsslideshare 230524162337 E3eb4ba7jack jackNo ratings yet
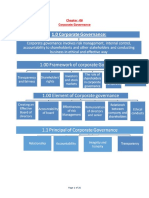
- Chapter - 06 Corporate Governance: Page 1 of 26Document26 pagesChapter - 06 Corporate Governance: Page 1 of 26masuda sultanaNo ratings yet
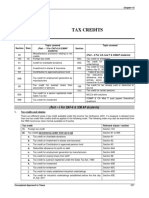
- Chapter-15 Tax CreditsDocument18 pagesChapter-15 Tax CreditsakhtarNo ratings yet
- A2 - Contmgmt2&3Document10 pagesA2 - Contmgmt2&3ideyNo ratings yet
- EBCL MARATHON Notes For Dec 20 Adv Chirag Chotrani, YES AcademyDocument529 pagesEBCL MARATHON Notes For Dec 20 Adv Chirag Chotrani, YES AcademySpiritual MorningsNo ratings yet
- Fcra Summary of RightsDocument8 pagesFcra Summary of Rightsmcg2wfNo ratings yet
- Of Shares Of: ST ND RDDocument6 pagesOf Shares Of: ST ND RDKingChryshAnneNo ratings yet
- (Gurgaon) (Mumbai) : US Mortgage Process OriginationDocument9 pages(Gurgaon) (Mumbai) : US Mortgage Process OriginationAshish RupaniNo ratings yet
- Group 2 Cash Transfer 701pDocument32 pagesGroup 2 Cash Transfer 701pJesa ClemeniaNo ratings yet
- Taxation NotesDocument36 pagesTaxation NotesJM CamalonNo ratings yet
- Datamining and Data Warehouse: By, M.E.Paar RivananDocument13 pagesDatamining and Data Warehouse: By, M.E.Paar Rivanannarayana143No ratings yet
- "Saving Your Home: A Step-by-Step Guide to Foreclosure Prevention”From Everand"Saving Your Home: A Step-by-Step Guide to Foreclosure Prevention”No ratings yet
- Option Strategies. Option Strategies.: Trading Strategies of Trading Strategies of Options. OptionsDocument1 pageOption Strategies. Option Strategies.: Trading Strategies of Trading Strategies of Options. Optionsविनीत जैनNo ratings yet
- IBS Hyderabad: End Semester (Revised) Examination Schedule Semester - IV (Class of 2013)Document1 pageIBS Hyderabad: End Semester (Revised) Examination Schedule Semester - IV (Class of 2013)विनीत जैनNo ratings yet
- Fortune at Bottom of PyramidDocument44 pagesFortune at Bottom of Pyramidविनीत जैनNo ratings yet
- Various Mobile Phone Brands: Brand VitalityDocument3 pagesVarious Mobile Phone Brands: Brand Vitalityविनीत जैनNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument33 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentsMerry Julianne DaymielNo ratings yet
- Wright Company Deposits All Cash Receipts On The Day WhenDocument1 pageWright Company Deposits All Cash Receipts On The Day WhenCharlotteNo ratings yet
- Liban AnalyseDocument12 pagesLiban AnalyseSatish ReddyNo ratings yet
- Negotiable Instruments - Dishonour and Discharge - Group VDocument56 pagesNegotiable Instruments - Dishonour and Discharge - Group VSaurabh PatelNo ratings yet
- Branch Banking Operations Batch 10 (Compatibility Mode)Document9 pagesBranch Banking Operations Batch 10 (Compatibility Mode)Khushbakht BalochNo ratings yet
- eBILL Oct2016 1.48527906Document8 pageseBILL Oct2016 1.48527906norezanharudinNo ratings yet
- Cecchetti5e-Chapter 01-Test Bank-RevisedDocument10 pagesCecchetti5e-Chapter 01-Test Bank-RevisedNoor Al JburiNo ratings yet
- Balance Sheet MaricoDocument2 pagesBalance Sheet Maricoajisha10No ratings yet
- MT 103 Gpi 23.8M CodesDocument2 pagesMT 103 Gpi 23.8M CodesEllerNo ratings yet
- Online Banking Questionnaire SampleDocument4 pagesOnline Banking Questionnaire SampleMukesh Arya100% (4)
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument18 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentsNoella Marie BaronNo ratings yet
- 2024 02 2 15 14 37 Statement - 1706867077138Document29 pages2024 02 2 15 14 37 Statement - 1706867077138Anil NayakNo ratings yet
- 5 Porter's Forces Analysis - VuHueDocument2 pages5 Porter's Forces Analysis - VuHueHana VũNo ratings yet
- FNCE90047 - 2019 - S1 - W10 - Workshop - Question With Solution PDFDocument3 pagesFNCE90047 - 2019 - S1 - W10 - Workshop - Question With Solution PDFMia RenNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets and Institutions, 9e: Chapter 15 The Foreign Exchange MarketDocument26 pagesFinancial Markets and Institutions, 9e: Chapter 15 The Foreign Exchange MarketDương Thanh HuyềnNo ratings yet
- Mapirani Polinja Za DMEE StrukturaDocument3 pagesMapirani Polinja Za DMEE StrukturaKrali MarkoNo ratings yet
- Summary - Banking Business PDFDocument37 pagesSummary - Banking Business PDFsatyakidutta007No ratings yet
- OrderForm Pipeline-Forecaster VNDocument1 pageOrderForm Pipeline-Forecaster VNshengchanNo ratings yet
- Sample Invoice For Service ProvidersDocument2 pagesSample Invoice For Service Providers? New Emoji CharacterNo ratings yet
- LBP Enrollment Form BlankDocument1 pageLBP Enrollment Form BlankmatsanantoniozambalesNo ratings yet
- Investment BankingDocument23 pagesInvestment BankingAnkit BhatnagarNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - 3 Corporate BankingDocument75 pagesUnit 1 - 3 Corporate BankingNarinder BhasinNo ratings yet
- FeesDocument2 pagesFeesAryaman SinghNo ratings yet
- Current Issues Regarding Islamic Finance and Banking in MalaysiaDocument12 pagesCurrent Issues Regarding Islamic Finance and Banking in MalaysiaDylaLaven100% (1)
- PF Withdrawl Forms 19 SampleDocument2 pagesPF Withdrawl Forms 19 SamplePrasanta SahooNo ratings yet
- BankFin Midterm Mod 4Document6 pagesBankFin Midterm Mod 4Devon DebarrasNo ratings yet
- 4.0 Adjustable Rate & Variable Payment MortgagesDocument10 pages4.0 Adjustable Rate & Variable Payment MortgageserickekutuNo ratings yet
- Principles of LendingDocument11 pagesPrinciples of LendingSagar ChoudharyNo ratings yet